All Zone 5 (or hardier) Plants
Sort by:
488 products
488 products
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Phellodendron amurense
History: Amur Cork is native to Eastern Asia where it has long served a variety of uses. It is one of the fifty essential herbs in traditional Chinese medicine and is used to treat a variety of ailments. Dye extracted from the bright yellow inner bark has insecticidal properties and was used on important documents including the Diamond Sutra, one of the most important Buddhist sutras. It was introduced to the US in 1856 and by the 1900s was being planted widely as an ornamental tree. In some States it is considered an invasive species.
Why We Grow It: These hardy trees have quite the storied history and make appealing ornamental trees. The banana yellow inner back is a fascinating sight to behold.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Juliet dwarf sour cherries are one of several dwarf sour cherries developed and released by the University of Saskatchewan with the goal of creating sour cherries that were cold hardy, shorter in stature, and produced good quality fruit. This initiative began in the 1940s and Juliet was released as part of the Romance series in 2004.
Why We Grow It: With good yield and deep red medium-sized fruit, Juliet is a favourite for those that enjoy the sweet-tart flavour! This is an excellent variety for the fresh market or processing. For anyone short on garden space, these cherry bushes reach 6-8 feet at maturity.
Check our our blog post with some tasty sour cherry recipes!
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Rhus typhina
History: Staghorn sumac is native to southeastern Canada and the northeastern United States. The red fruit is eaten by birds in winter and beekeepers will even occasionally use it in their smokers as fuel. Parts of the plant have been used to make dyes.
Why We Grow It: Sumac is a useful plant for naturalizing areas as they tend to form thick groves, which, according to Steph, also make great play areas for children! The fruit can be made into a lemonade-like drink or jelly. Good forage source for honey bees as well.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Winesap's origins are unclear but it is believed to have originated from New Jersey pre-1800s where it was popular for making cider. It is first mentioned in a couple of books on apples in the early 1800s. Winesap was popular in the US until the 1950s due to its good keeping ability but the advent of better storage technology allowed better tasting apple varieties to eclipse it. It is still quit popular with backyard orchardists.
Why We Grow It: Winesap's all-purpose nature helps to explain why it hasn't faded into total obscurity like some other varieties. The medium-large red and yellow skinned fruit is good for cooking and making cider. It has sweet flesh with some tang or 'winey' flavour that is also decent for fresh eating. On top of that, the tree is productive, very resistant to fireblight, and the fruit stores well.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Spartan apples are a Canadian variety that was developed at the Pacific Agri-Food Research Centre in Summerland, BC in 1936 by Dr. R.C. Palmer. Of particular interest is the fact that Spartan apples are the first apple variety created by a formal scientific breeding program. They have been popular in North America ever since and are even commonly found in gardens in the UK.
Why We Grow It: This variety is known for its sweet/acid flavour and pleasant crunch, especially when eaten fresh off the tree. They tend to soften rather quickly after they are picked but luckily the fruit hangs on the tree 2-3 weeks after its ripe which helps to extend the optimal time to enjoy this variety. Spartan apples are also known for being relatively easy to grow, having decent disease resistance, heavy crops, and an ability to keep all winter.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Yellow Transparent (aka Harvest Apple and White Transparent) originated as a chance seedling in a nursery in Riga, Latvia around 1850. At the time Latvia was part of the Russian Empire so this variety is often considered Russian. Due to its early ripening and cold hardiness, this variety was widely grown in Europe, especially northern countries, where it is still grown today. It was imported to the US in the 1870s as part of an effort to import cold hardy Russian species that could potentially survive in states with harsher winters and became quite popular.
Why We Grow It: This classic early apple deserves a home in every home orchard. The fruit features pale yellow skin that almost looks transparent and white flesh with a sharp, sweet flavour. It can be eaten fresh but also makes a great applesauce. Like many early ripening apples, the fruit does not last long.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Thunderchild is a crabapple that was developed by Percy Wright, a prairie plant breeder in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. Although it is unknown when exactly Thunderchild was created, it likely came about in the 1900s and can still be seen as a common ornamental tree in the area.
Why We Grow It: Thunderchild makes for a lovely ornamental tree with a profusion of pink blossoms in the spring and deep red foliage. The tiny dark red fruits it produces can be used in cider blends and to make jellies with a gorgeous orange hue. The tree is quite cold hardy and generally disease resistant.
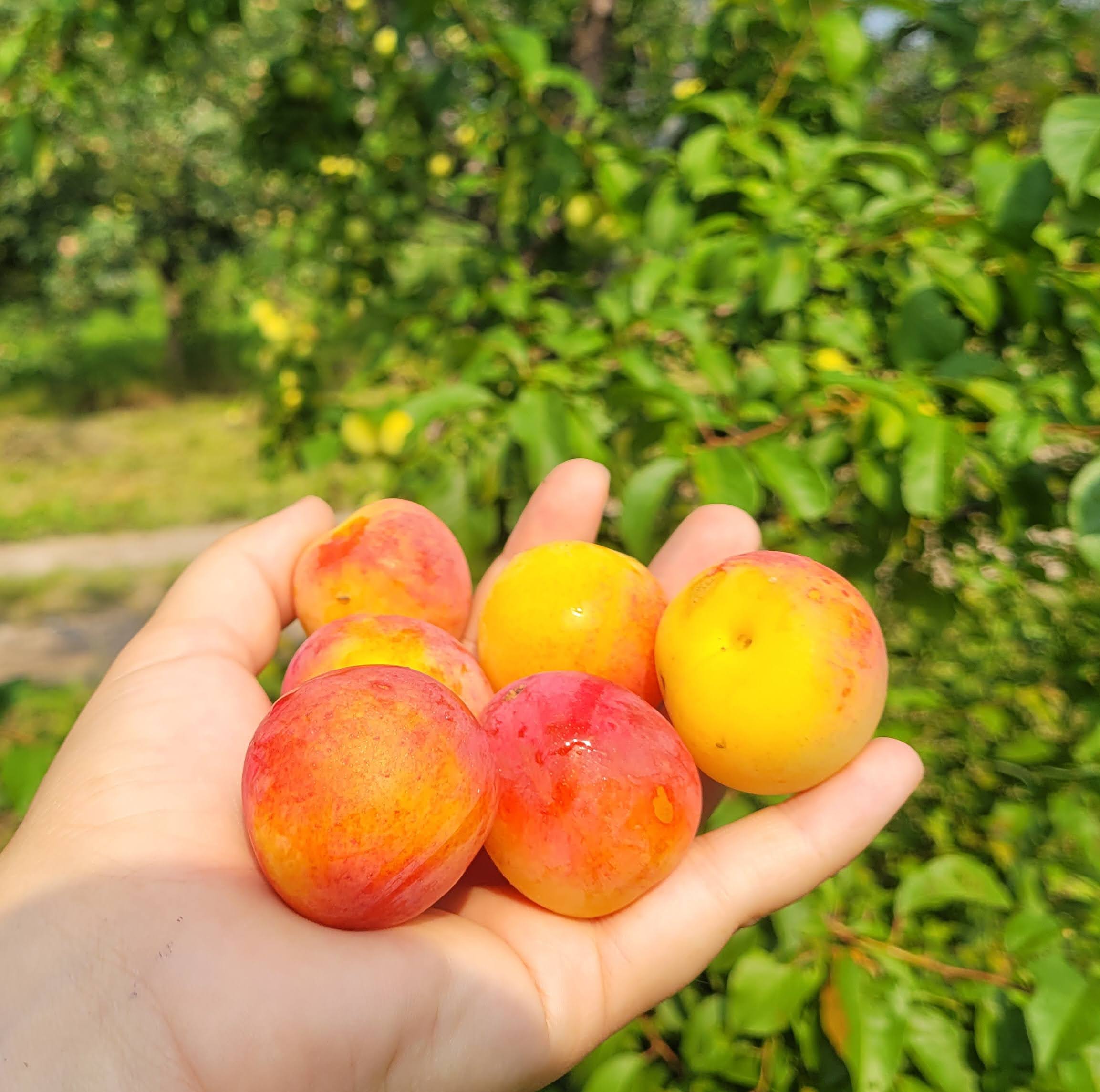
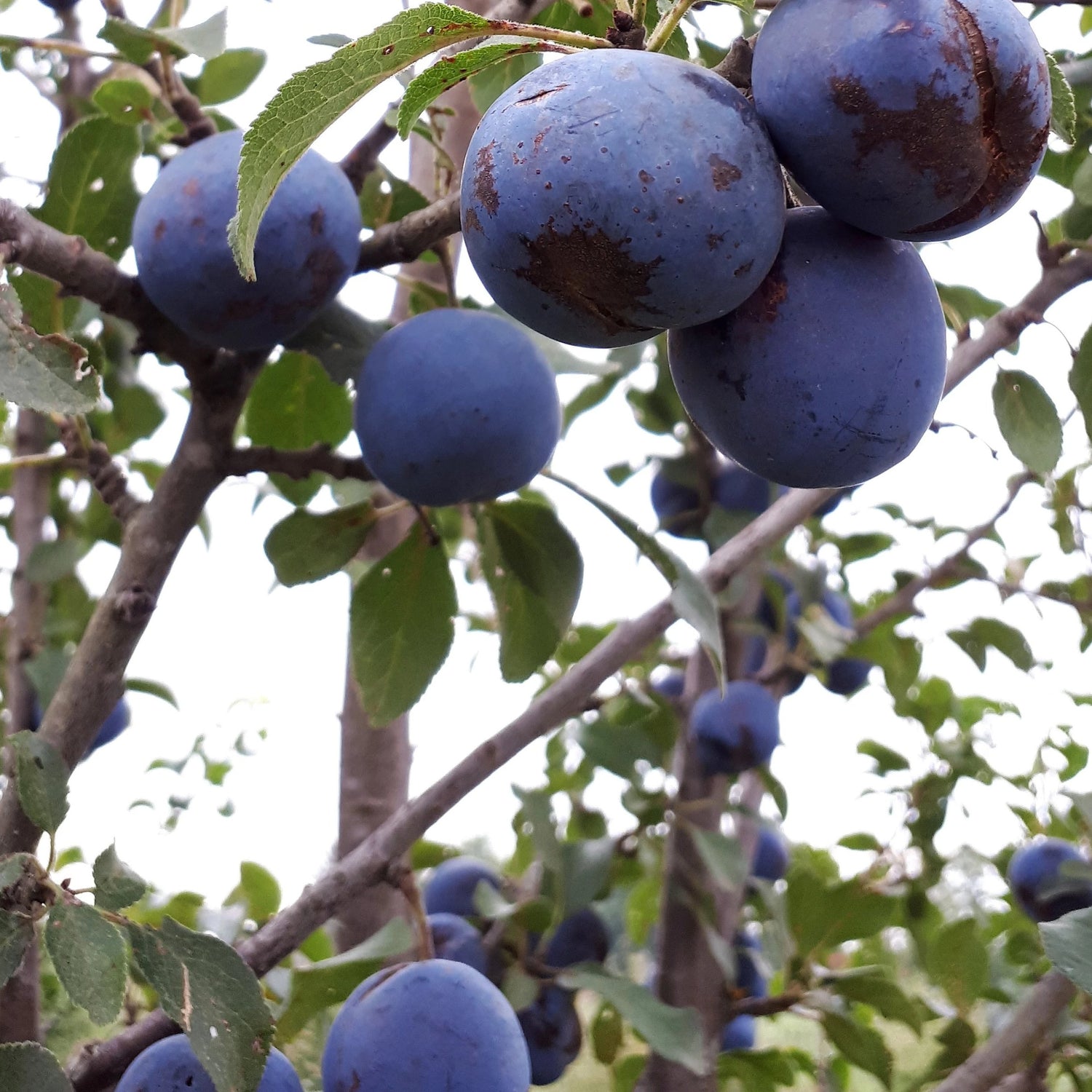
Species: Prunus sp
History: These seedlings are grown from Damson plum seeds collected from our orchard. Damson is a plum that may stem from antiquity!
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! The parent variety, Damson, produces small blue fruit that are sweet and a little spiced. They are suitable for fresh eating and great for jams, preserves, etc. For a more detailed description, see the Damson page on our website here.
Please Note: Since plums tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
History: Karneval (translated from Czech as 'Carnival') was developed at the Institute of Experimental Botany in Prague in the Czech Republic by Dr. Jaroslav Tupý. It is a cross between Vanda and Cripps Pink. It was released in 2011 and like many other modern apples, boasts a sweeter flavour and good disease resistance. However, the main reason this apple was likely selected and given its fun name was for the bright red striped that adorn it.
Why We Grow It: Karneval is medium sized apple that is sweet, juicy and just a little tart and aromatic. However, this apple is best known for its unique appearance: yellow skin with distinct red stripes that would make it feel at home at the circus. Great flavour, striking visual appeal, good storage capabilities, and good disease resistance make this apple an excellent choice for any grower.
History: Granny Smith was discovered by Maria Ann "Granny" Smith as a chance seedling on her and her husband's farm in Australia in 1868. Having grown from apple seeds she had tossed, she found it to be an exceptional apple. She propagated it and brought the apples to market, earning the variety local popularity. She passed away two years later but local growers kept the variety going until it was noticed by the New South Wales Department of Agriculture in 1895. Thanks to its excellent shelf life, it became an important agricultural export and remains one of the most popular apple varieties in the world today. There has been an annual Granny Smith Festival in Eastwood since 1985 to commemorate Maria Ann Smith and her apple that attracts over 80k attendees each year.
Why We Grow It: This classic green apple barely needs an introduction! It is well known for its sweet and sharp flavour that is a delight for fresh eating and for its usage in cooking and baking. As an added bonus, Granny Smith also keeps well in storage and tends to start producing fruit at a young age.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: White Lady was created by Zaiger Genetics in California as part of their fruit breeding enterprise. It was selected for its unique white flesh, reddish skin, and overall excellent fruit quality. The variety was introduced in 1986.
Why We Grow It: White Lady is a unique variety featuring red blush over white skin and firm, white flesh. This freestone peach has quite low acidity giving it a very sweet flavour and it is great for fresh eating, canning, preserving, and baking. The tree itself is adaptable and the blossoms tolerate unpredictable spring weather better than most.
Grafted Peach Trees
We are very pleased to be able to offer peach trees to our customers. They are both challenging and rewarding plants to grow. However, due to the unique challenges of growing peach trees, and the increased care required for their success, we regrettably cannot offer our standard 90 day guarantee on peaches. Please inspect your peach trees to your satisfaction when you pick them up at the nursery, or immediately upon arrival if they are shipped. For shipped trees, make your claim within 7 days of receipt of the trees. After 7 days of receipt, you will have been deemed to have accepted the trees in as-is condition.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
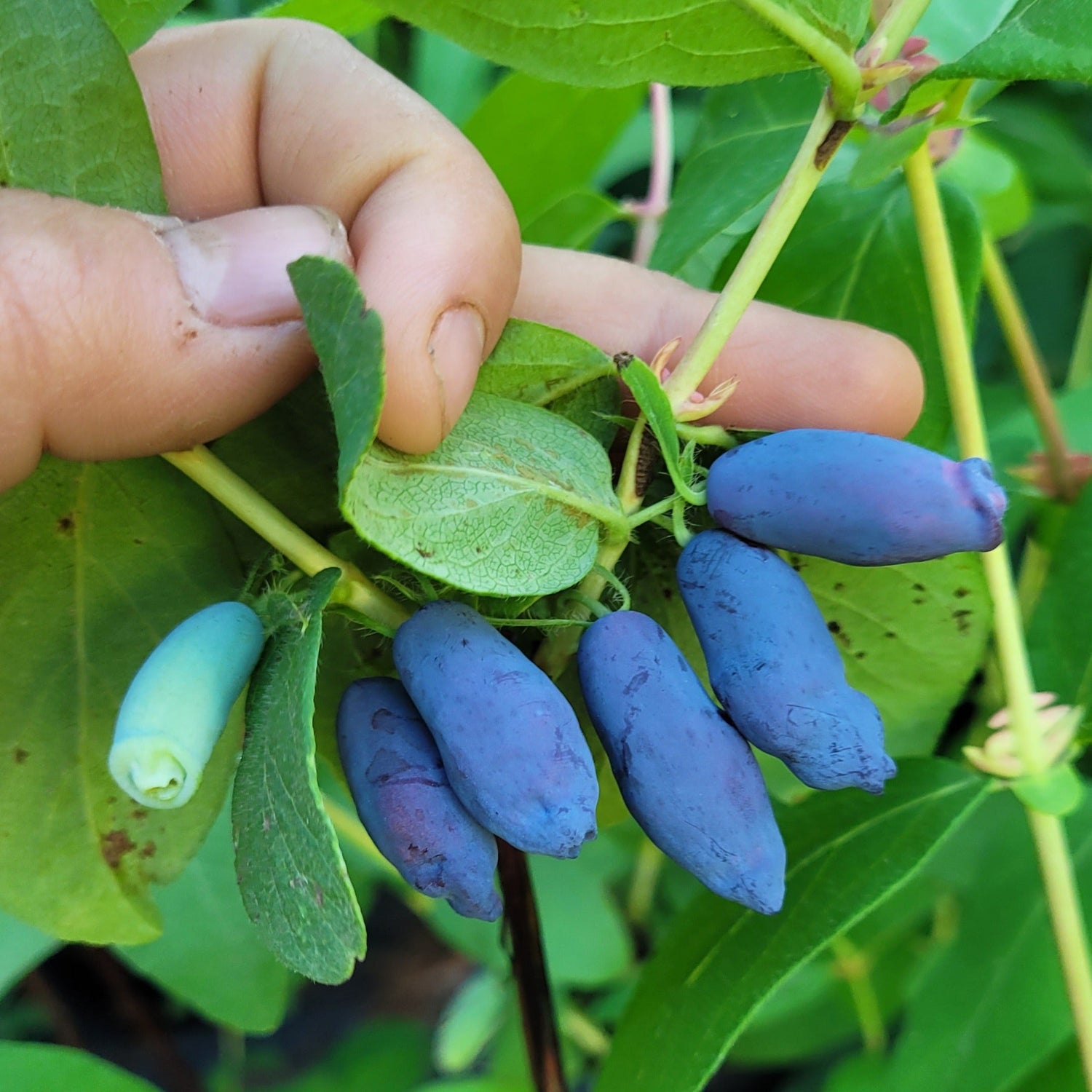
Species: Lonicera caerulea
History: Indigo Gem was bred by Bob Bors at the University of Saskatchewan as part of the Indigo Series, a series of five varieties that all share the same parents. They were bred sometime in the mid to late 2000s and released around 2010/2011. Indigo Gem is the most productive variety of the series.
Why We Grow It: Indigo Gem produces fairly round berries that are sweeter and smaller than most haskaps, although they still have that characteristic tartness to them! It is considered one of the better options for fresh eating and like other haskaps is also great in baking, making preserves, etc.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Lindera benzoin
History: Spicebush is native to eastern North America, although in Canada it can only be found in Ontario. It has been used medicinally by several indigenous peoples and early land surveyors used it to find good agricultural land due to its propensity to grow in good soil. It remains a popular ornamental plant along with its uses for spices and teas. Spicebush is also the only host plant for the spicebush swallowtail.
Why We Grow It: If you want to source your own spices locally, try this aromatic, native shrub! The leaves and berries can be used as substitutes for cinnamon, nutmeg, and allspice. It is attractive to butterflies and the early bloom time means it is a good source of pollen in the spring. The shrub is also quite pretty in autumn when its leaves turn a bright yellow.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
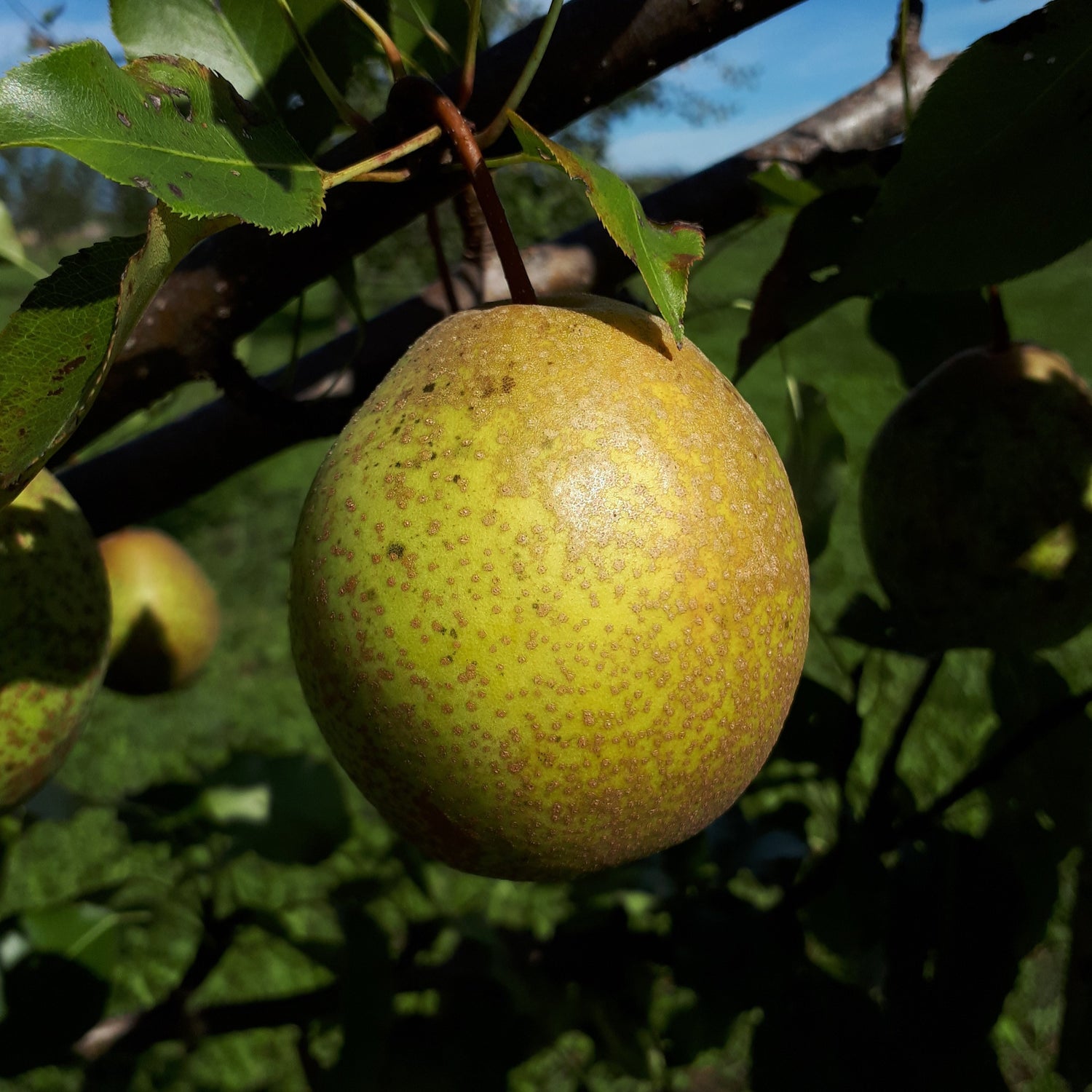
History: Mishirasu is an Asian pear from Japan.
Why We Grow It: Mishirasu is a popular variety since the fruit are extra large with a sweet, mild flavour and a nice crunch. The skin is brown and russeted, and the fruit have a roundish shape that is reminiscent of European pears.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Meigetsu is an Asian pear that originated in Japan. The word 'meigetsu' roughly translates to 'beautiful moon' or 'grand moon.' Its name could also be a shortened version of 'Chushu no Meigetsu,' the Japanese name for the harvest moon in September.
Why We Grow It: Meigetsu Asian pears are pleasantly sweet with the flavour and aroma being compared to pineapples, watermelon, and butterscotch. The flesh is somewhat softer than other Asian pears, making the texture more akin to that of European pears.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: In 1817 Joel Gillet accidentally received Rome Beauty as a seedling in a shipment of nursery trees. His son planted the seedling along the Ohio River in Rome Township. When it began producing lovely red apples, Gillet's cousin started a nursery to propagate and promote it. Originally named Gillet's Seedling, the name was later changed to Rome Beauty in 1832 to honour the township. The original tree collapsed in the 1850s due to bank erosion but the variety still remains popular in the United States today.
Why We Grow It: The fruit is deep red, large, and slightly conical with cream coloured flesh. It has a mild flavour compared to something with more character like a russet, though still an excellent snacking apple. It makes a good cooking apple too since it keeps its shape when cooked. It also stores exceptionally well, lasting all winter long.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Vicar of Winkfield was discovered growing as a wild seedling in the woods near Villiers-en-Brenne in France around 1760. It was originally named Curé (translated from French as 'priest') among other names but became known as Vicar of Winkfield when a vicar of the English village Winkfield named Rev. W.L. Rahm introduced the variety to England. It is a heritage cooking pear and can still be found in old French orchards today.
Why We Grow It: This long, yellowish-green pear is best known for its use in cooking and baking due to its uniquely dry flesh and more tart flavour. Vicar of Winkfield can be stored for several months and will develop a sweeter flavour over time. It is generally recommended to store the pear until after Christmas for fresh eating! The tree is vigorous and produces abundant crops.
History: Pine Golden Pippin's exact origins are unknown, but it is quite an old variety that either originated in northern England or in Scotland. It was first formally described by nursery worker Thomas Rivers in A Descriptive Catalogue of Fruit Trees in 1863. In 1875, Robert Hogg claimed that Pine Golden Pippin was one of the best fresh eating apples around in his book The Fruit Manual.
Why We Grow It: Robert Hogg was correct about Pine Golden Pippin! Despite the small size of the fruit, it makes up for it with crisp and juicy fruit with a sweet/sharp flavour that has a hint of pineapple and resin. The fruit is great for fresh eating and can also be used in cider blends. It tends to be slower growing but produces good crops.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Caragana arborescens
History: As the name implies, Siberian pea shrubs are native to Siberia but also parts of China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan. They came to the US with Eurasian immigrants who used the pods as a source of food while traveling. It has been planted ornamentally and as bonsai, and can be used as erosion control. It is also unfortunately invasive in some parts of the US.
Why We Grow It: A classic permaculture plant! Siberian pea shrubs are nitrogen fixing, very hardy, disease and drought resistant, and, above all, edible. The flowers and young pods can be eaten fresh while the older pods are cooked. The plants are also attractive to pollinators.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Symphytum sp.
History: Comfrey plants are native to various continents around the world including Europe, Asia, and North America. Common names such as boneset and knitbone and its genus name referencing the Greek 'symphis' meaning 'growing together of bones' indicates it may have been used medicinally for mending bones. Comfrey is now popular as a permaculture plant.
Why We Grow It: This classic permaculture plant grows incredibly deep tap roots, mining rich nutrients from deep below the soil surface. It's a living mulch that 'molts' 3-4 times each season. It's used in traditional medicine and creates a healthful compost tea full of calcium and potassium. It grows up to 70 cm tall, before molting down, and spreads slowly over the years.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
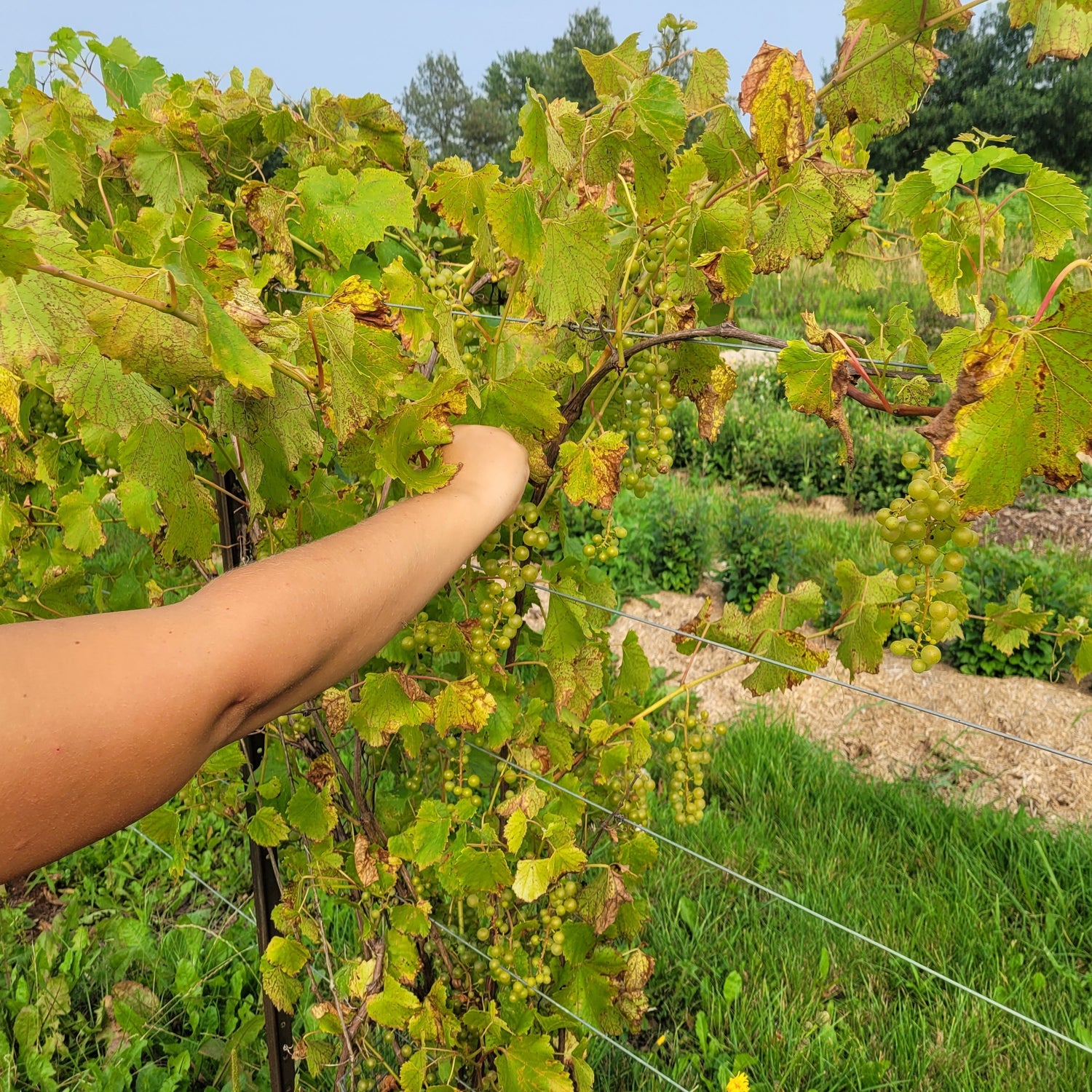
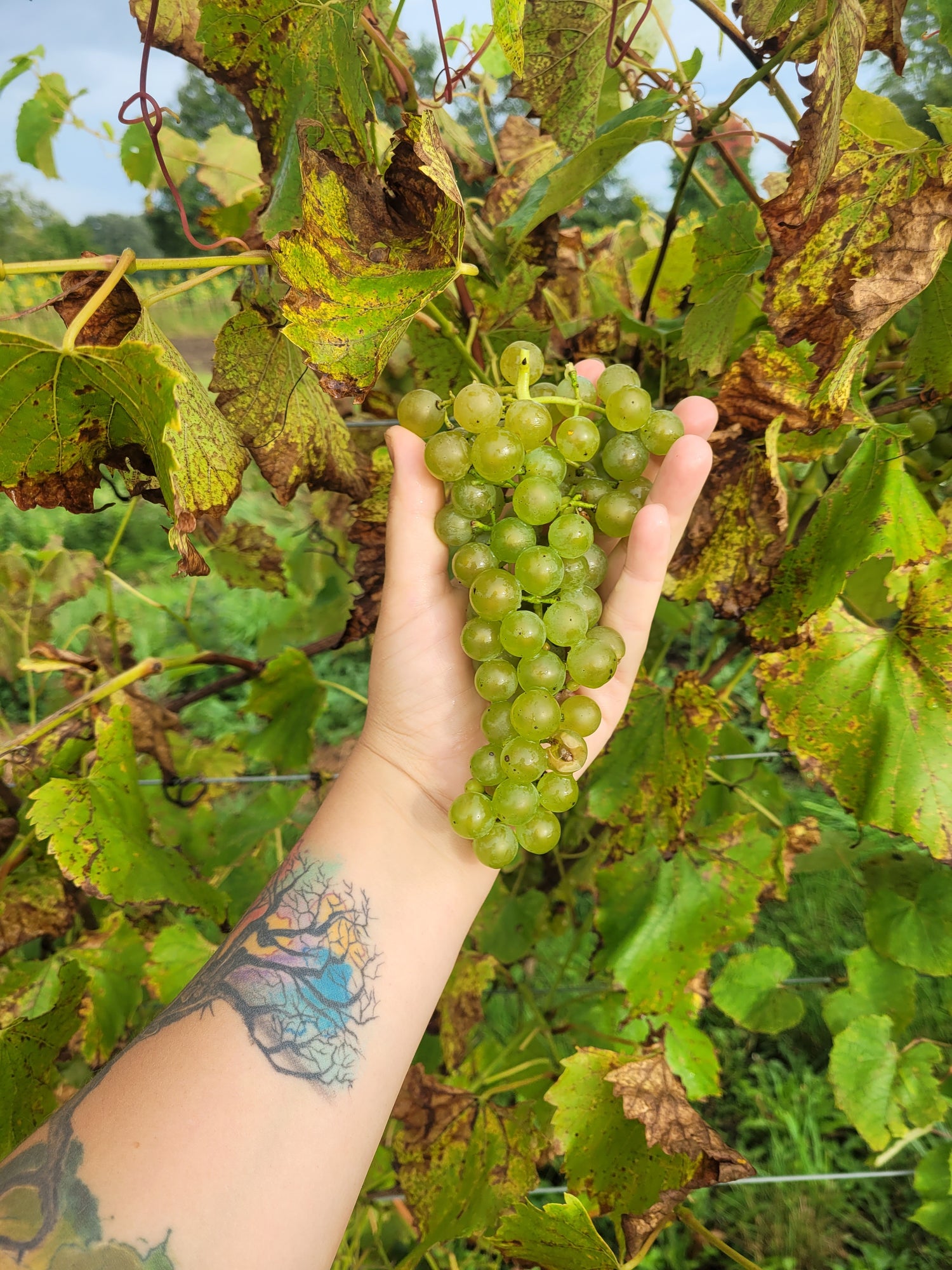
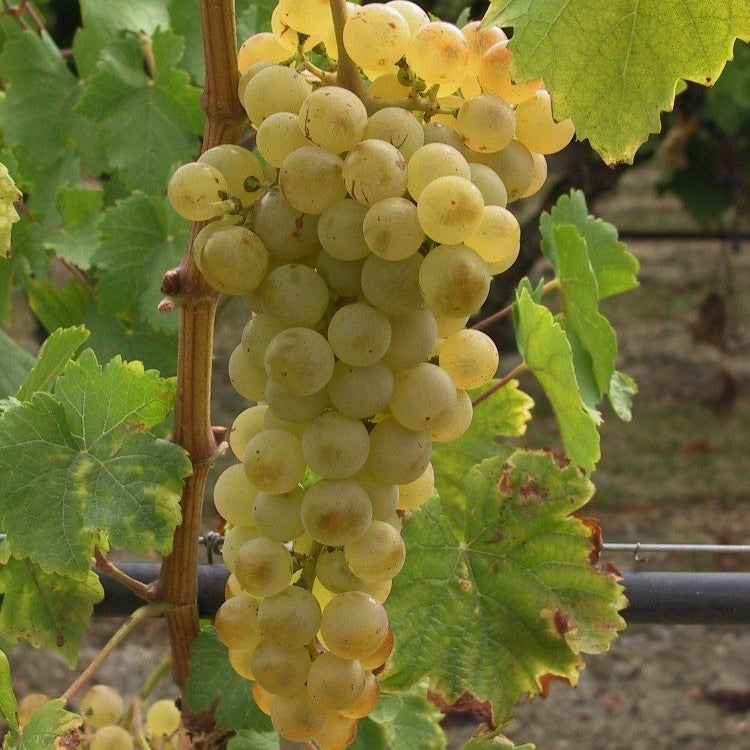
Species: Vitis labrusca x Vitis riparia x Vitis vinifera, and small amounts of other Vitis species from North America
History: Bred by Elmer Swenson in Wisconsin, Somerset is one of numerous varieties he created for growing in our cooler North American climates. This cultivar has become increasingly popular in recent years and has good potential for commercial growing. The variety was released in 2002.
Why We Grow It: One of the hardiest, highest quality seedless grape varieties out there, this is an excellent table grape: sweet, spicy, with strong notes of strawberry. The grapes have beautiful pink flushed skin and are most decadent if allowed to sit on a sunny window sill for a week or so after harvest. Although the fruit is on the smaller to medium end of the scale, the vines produce large, heavy clusters that more than compensate for the size of the individual grapes. The grapes have a firm texture with some crunch.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Actinidia kolomikta
History: September Sun is a Russian variety that was selected for its ample crops of large fruit. Its Russian name is Sentyabraskaya which translates to 'September' in English with a bit of a feminine sound to the name.
Why We Grow It: September Sun is known for producing good-size crops of large, sweet fruits. These grape-like kiwis are a delightful treat for any yard, especially for growers in a colder area! It is also a great ornamental plant, featuring pinkish-white and green variegated leaves.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Alnus incana (likely subsp. rugosa)
History: Native to large portions of the Northern Hemisphere including parts of North America, Europe, and Asia, this widespread tree is often divided into six subspecies. We likely offer Alnus incana subsp. rugosa but with seedlings it is hard to say for sure. Indigenous people have used these trees for medicine and dyes, and they can also be used for erosion control. This subspecies in general is unique for its cold hardiness and ability to fix nitrogen, making it a useful companion plant in permaculture settings.
Why We Grow It: Named for the white lenticels that dot the reddish-gray bark, Speckled Alders can make a useful addition to a permaculture with their ability to fix nitrogen. However, keep an eye on this tree as it tends to spread via suckering (sending up new shoots) and layering (branches rooting into the ground) and can form dense thickets.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Anjou is an older variety of pear that likely originated in France or Belgium in the mid-1800s. They were originally called 'Nec Plus Meuris' but at some point adopted the name Anjou (or d'Anjou or Beurre d'Anjou) after the French region when introduced to England or the US. Anjou pears are still quite popular and are one of the most commonly grown pears in the United States.
Why We Grow It: Anjou is a popular pear due to its good eating quality and flavour. The skin is greenish yellow, and the flesh is firm and sports a hint of yellow. The fruit keeps well and the tree is vigorous and hardy.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Honeycrisp apples were developed by the University of Minnesota in the 1960s and released in 1991. It is one of almost thirty varieties created by the university's breeding program since it began in 1888. The excellent flavour of Honeycrisp has allowed it to become one of the most popular apples in North America and in 2006 it became the state fruit of Minnesota.
Why We Grow It: Honeycrisp is popular for a reason. The apples are large and attractive with good flavour under favourable growing conditions. However, they are not an apple for beginner growers due to issues with some diseases especially in storage, but with diligent care you can produce these crunchy sweet apples in your own backyard/orchard.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: xSorbopyrus irregularis (Pyrus communis x Sorbus aria), also referred to as xSorbopyrus auricularis although this name is no longer correct
History: Shipova is a unique cross between European pears and Common Whitebeam* (Sorbus aria) which readily hybridizes with many other fruiting plants in the rose family. As a surprise hybrid, the history of Shipova is a little foggy. This cross supposedly appeared, or was perhaps planted, at Bollwiller Castle in France in the 1600s and was called Bollwiller Pear. It was cultivated in gardens in the late 1700s and early 1900s. It may have also originated in Yugoslavia and is popular in Eastern Europe today. Shipova was first brought to the US in 1959 and was imported from Yugoslavia. Today, it appears to remain something of a novelty in North America.
Why We Grow It: Shipova is a truly unique fruit tree and it is a shame that it is not grown more commonly. They are quite cold hardy and relatively disease-resistant. The trees produce clusters of small, round fruit that resemble pears. They are dense and crisp with a sweet flavour reminiscent of tropical fruits.
*Many places list Shipova as a cross between European pears and Mountain Ash. More precisely, the genus Sorbus is the Mountain Ash genus and the specific tree that is the parent of Shipova is the species Sorbus aria, commonly known as Common Whitebeam
These grapes got mixed up and are either Brianna or Osceola Muscat, but you won't know for sure until they bear their delicious fruit! Unfortunately it's too hard to tell the distinct difference with young plants, so we're offering them at a great discount to those who enjoy a little mystery!
Species: Vitis vinifera x V. rupestris x V. ripraria x V. labrusca (Osceola Muscat) OR Vitis riparia x Vitis labrusca (Brianna)
History: Both Osceola Muscat and Brianna grapes were bred by renowned grape breeder Elmer Swenson in an effort to develop grapes that grow well in cooler climates.
Why We Grow It: Both of these grape varieties are seeded green grapes. Osceola Muscat produces loose clusters of seeded, intensely aromatic grapes with notes of peach and apricot. Meanwhile, Brianna boasts excellent complex fruity flavour that has hints of grapefruit and pineapple. Both varieties are relatively vigorous and hardy, and you can't go wrong with either one!
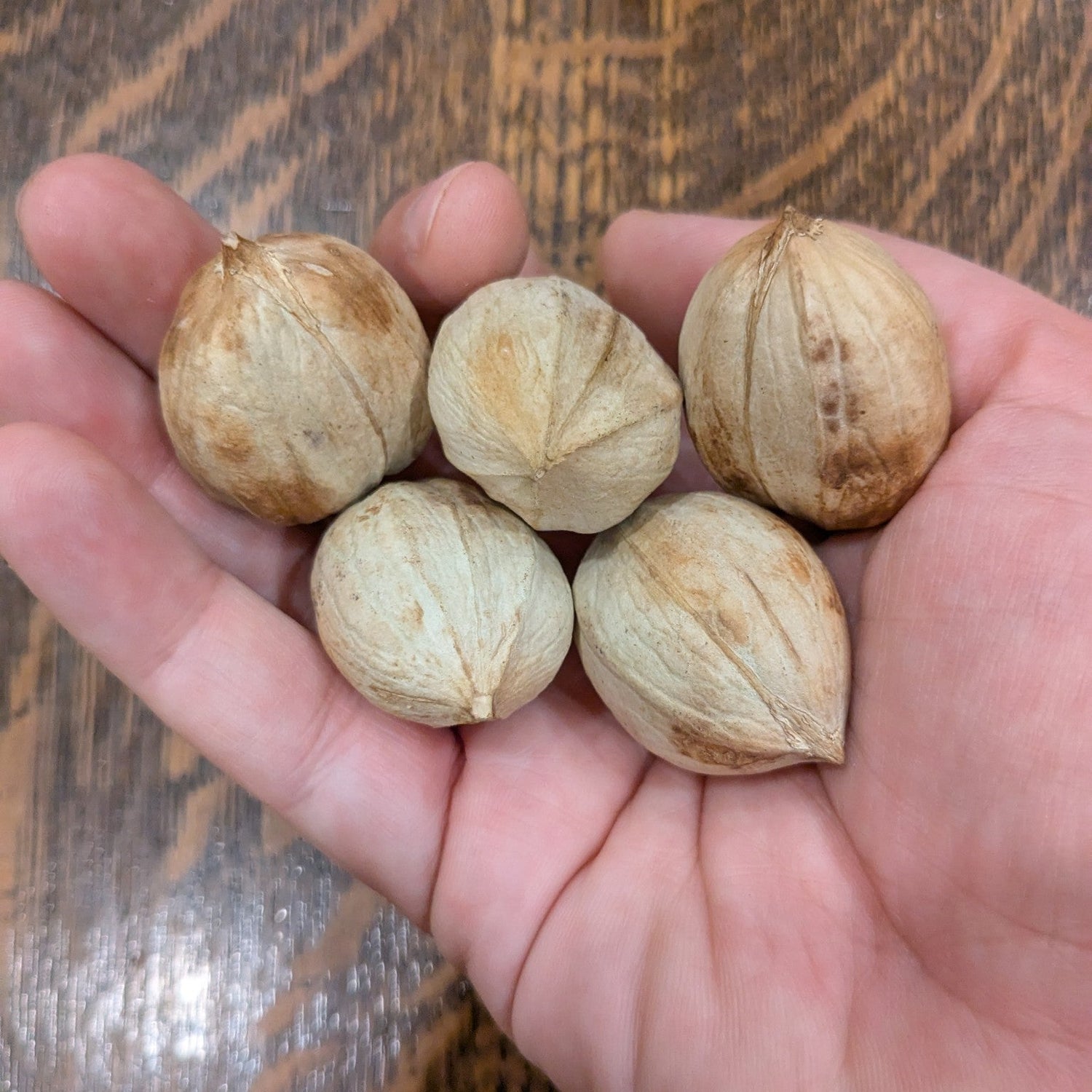
Species: Carya ovata
History: These are seedlings of Weschke Shagbark Hickories, a variety that was discovered in Iowa by Carl Weschke and named in 1926. It was selected for its excellent flavour.
Why We Grow It: While these seedlings will vary from their parents, the goal is that the excellent qualities of Weschke Shagbark Hickories will be passed along to its offspring! Weshcke Shagbark Hickories are known for having excellent flavour and thin shells that are easier for cracking.
History: Alkmene, aka Early Windsor, was developed by M. Schmidt and H. Murawski at the Kaiser-Wilhelm-Institut für Züchtungsforschung in Müncheberg, Germany in the 1930s.* It was named after Hercules' mother Alcmene. After the chaos of WW2, it took about 30 years for Alkmene to be introduced to the rest of the world. It was released in 1962 and given the name Early Windsor for better marketability. It remains a popular apple in Europe today.
Why We Grow It: Alkmene produces a medium-sized crisp, juicy apple that has yellow skin overlaid with red stripes. The aromatic fruit is known for its rich flavour that is both honeyed and notably sharp. The tree is known to be quite a heavy cropper!
*While the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute was heavily involved with the Nazis during WW2, at the time of Alkmene's development the institute's president was Max Planck, a scientist who staunchly defended his Jewish colleagues. The institute was renamed in his honour following WW2. That is to say, we're not selling a Nazi apple.
History: White Lady was created by Zaiger Genetics in California as part of their fruit breeding enterprise. It was selected for its unique white flesh, reddish skin, and overall excellent fruit quality. The variety was introduced in 1986.
Why We Grow It: White Lady is a unique variety featuring red blush over white skin and firm, white flesh. This freestone peach has quite low acidity giving it a very sweet flavour and it is great for fresh eating, canning, preserving, and baking. The tree itself is adaptable and the blossoms tolerate unpredictable spring weather better than most.
Grafted Peach Trees
We are very pleased to be able to offer peach trees to our customers. They are both challenging and rewarding plants to grow. However, due to the unique challenges of growing peach trees, and the increased care required for their success, we regrettably cannot offer our standard 90 day guarantee on peaches. Please inspect your peach trees to your satisfaction when you pick them up at the nursery, or immediately upon arrival if they are shipped. For shipped trees, make your claim within 7 days of receipt of the trees. After 7 days of receipt, you will have been deemed to have accepted the trees in as-is condition.