All Zone 5 (or hardier) Plants
Sort by:
488 products
488 products
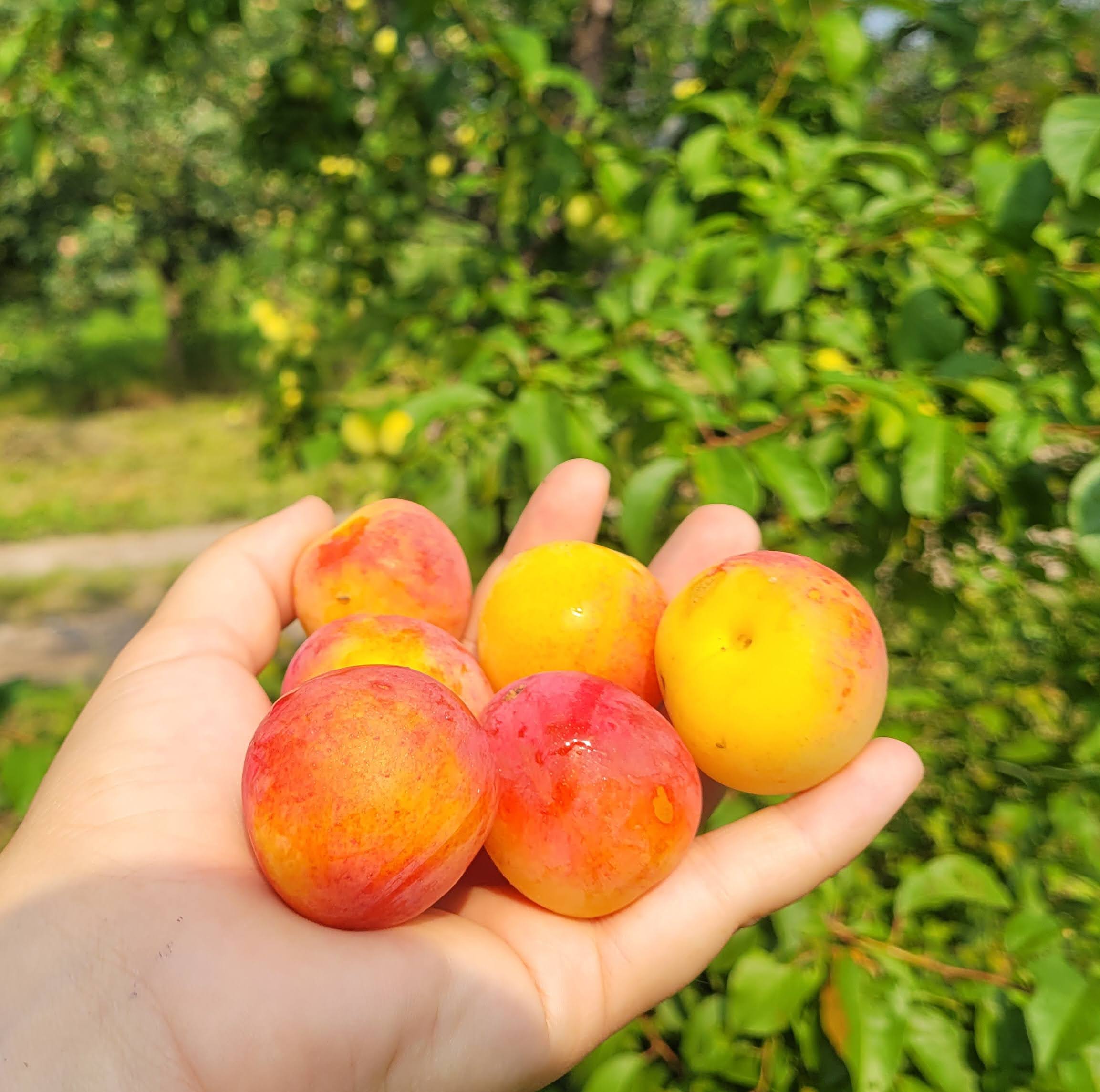
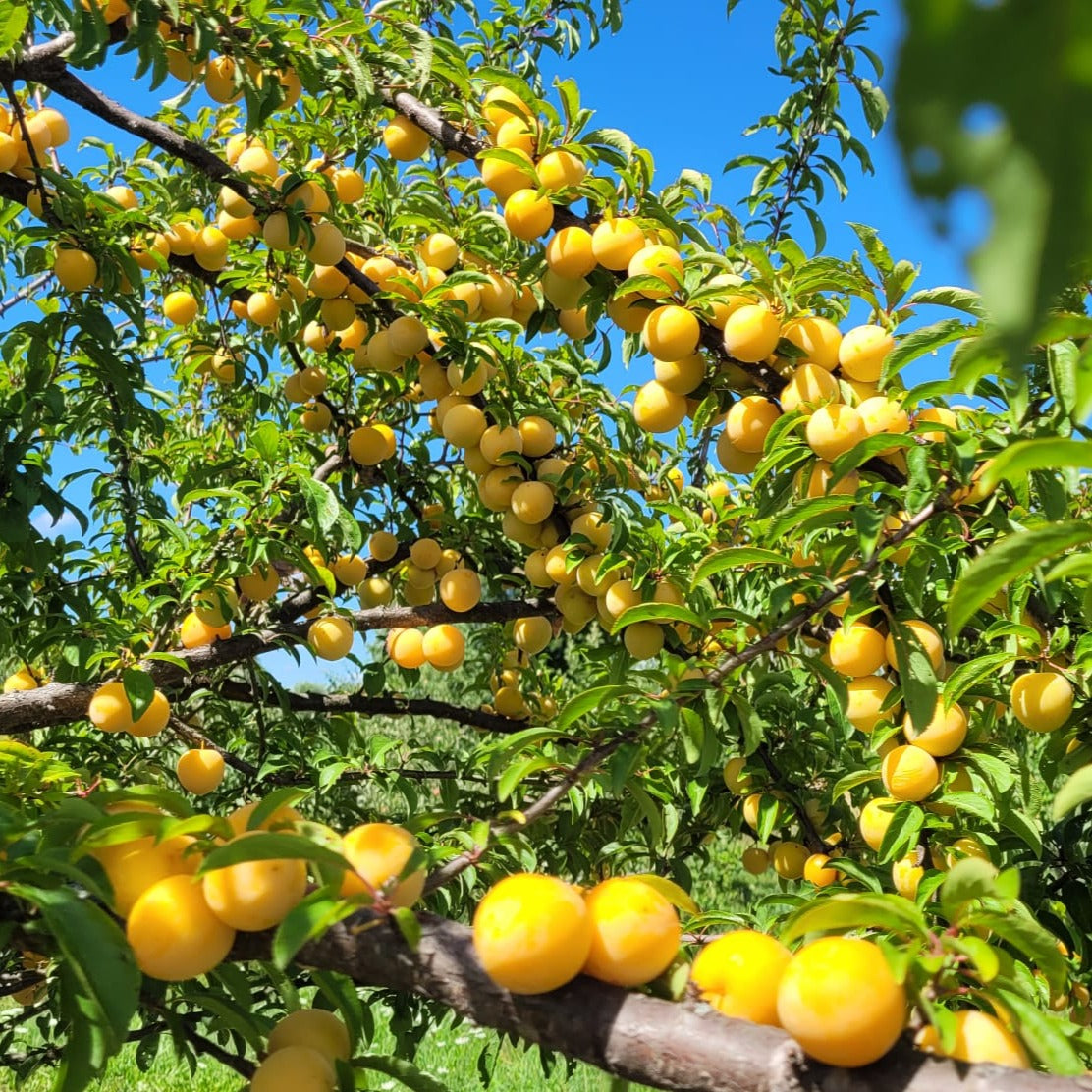
Species: Prunus sp
History: These seedlings are grown from Shiro plum seeds collected from our orchard and a Niagara orchard. Shiro plums (translated from Japanese as 'white') were developed in California and introduced in 1899.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! The parent variety, Shiro, has yellow skin and flesh that is juicy and sweet.
Please Note: Since plums tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
Species: Prunus cerasus
History: These sour cherry seedlings are grown from Juliet seeds we've collected here at Silver Creek Nursery from our own trees! Juliet, is one of the members of the Romance Series released in 2004 from the University of Saskatchewan.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! The parent variety, Juliet, has a sweet/tart flavour that some enjoy for fresh eating and is great for processing. A naturally dwarfing and bush-like variety. For a full description, see our Juliet page here.
Please Note: Since sour cherries tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
Species: Prunus sp
History: These seedlings are grown from plum seeds collected from our orchard. We missed labelling this particular batch, but we know their parents are a blue prune plum similar to German and Late Italian plums.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! The seedling of a classic prune plume like German or Late Italian, these plums will be good for fresh eating but great for baking, drying, etc.
Please Note: Since plums tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
History: Barnet's history is somewhat of a mystery although we know it likely originated in Gloucester, England in the 1800s and was distributed by the Long Ashton Research Station in the 1900s. It is a traditional perry pear that is known by many names including Barn, Brown Thorn, and, adorably, Hedgehog. The last name is speculated to come from the fruit's resemblance to baby hedgehogs (aka hoglets) nestling in the grass.
Why We Grow It: Barnet produces small, brown russetted fruit that are quite juicy. The juice is quite mild since it is low in both tannins and acidity, making it a good choice for adding to perry blends. The ripe fruit is easily shaken from the tree for ease of harvest.
History: Fresco, also known by the brand name Wellant®, was developed through a fruit breeding collaboration between Inova Fruit and the Applied Plant Research at the Wageningen University and Research Center in the Netherlands. The goal was to create an apple variety that better aligned with changing consumer tastes. It was bred in the late 1900s and named Fresco during the years it underwent various tests before being released in 2004 under the brand name Wellant®. It is primarily grown and sold in Europe.
Why We Grow It: Fresco produces a large, deep red fruit that is crunchy with a strong flavour high in both sweetness and tartness. It is excellent for fresh eating and can be used in baking and cooking as well. An excellent multi-purpose apple!
History: Woolbrook Pippin originated in 1903 at Woolbrook Nursery in the UK. It was discovered by J.H. Stevens and Son. It is a Cox's Orange Pippin seedling and received an Award of Merit from the Royal Horticultural Society in 1929.
Why We Grow It: Woolbrook Pippin produces a greenish apple overlaid with bright red stripes that is excellent for fresh eating. The fruit is firm, crisp, and juicy with a sweet, aromatic flavour balanced by a bit of tartness. This is a great choice for fans of Cox's Orange Pippin!
History: Mother was first officially introduced to the world in an 1844 edition of the "Magazine of Horticulture." We know it came from General Stephen Gardner's farm in Massachusetts in the US but do not know any other details about its origins. It faded from popularity in the US during the 1900s but remained popular in the UK.
Why We Grow It: Mother produces medium-sized apples with yellow skin that turn deep red where exposed to the sun. This crisp, juicy apple is sweet with hints of pear and vanilla making it an excellent choice for fresh eating. It is also a popular option for baking pies! The fruit stores well, the blooms are tolerant of late spring frosts, and the tree tends to start producing at a young age. It is also susceptible to several common apple diseases, but we believe its other qualities outshine that fact.
History: Goodland was developed at the Morden Research Station in Manitoba as part of an effort to breed cold hardy apples for the prairies. It is a seedling of Patten Greening that was selected in 1925 and the variety was introduced commercially in 1955.
Why We Grow It: The cold hardy Goodland produces a medium to large yellow apple with red striping. This crisp, juicy apple has sweet/tart flavour that is great for fresh eating, cooking, and sauce. Unlike most early ripening varieties, Goodland will store well for several months.
Species: Amelanchier x wiegandii (likely a hybrid of A. arborea and A. sanguinea)
History: There is little information on the origin of Isaac although it is believed to be a cross between the Common Serviceberry (A. arborea) and the Roundleaf Serviceberry (A. sanguinea). It was likely selected for its large, sweet berries.
Why We Grow It: Isaac produces very large berries with a lovely sweet flavour. Like other serviceberries they are great for fresh eating, cooking, baking, and preserving. Isaac makes a nice ornamental shrub with its rounded shape and white blooms in the spring. It is generally an adaptable and cold hardy plant as well!
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Oops, we had an inventory mishap and don't know what variety these sweet cherries are! We're happy to offer these wonderful plants at a discount to any adventurous growers who don't mind a bit of mystery. These will be full-size sweet cherry trees.
Why We Grow It: While we don't know what variety these trees are, they'll certainly produce a deliciously sweet cherry that is a great summer treat! We recommend these mystery trees for customers with plenty of space since sweet cherries get quite tall and who already have sweet cherries on or near their property. Since these are mystery trees, we do not know if they require a pollination partner to produce fruit.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Oops, we had an inventory mishap and don't know what variety these dwarf sour cherries are! We're happy to offer these wonderful plants at a discount to any adventurous growers who don't mind a bit of mystery. They will be one of the Romance Series of dwarf sour cherries released from the University of Saskatchewan.
Why We Grow It: Dwarf sour cherries are self-pollinating and relatively compact, making them a great option for anyone with limited space! These productive bushes produce ample amounts of bright red sour cherries that are great for baking, preserving, etc. The bushes are also showy in the spring when covered in white blossoms and are quite cold hardy.
Check our our blog post with some tasty sour cherry recipes!
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Vaccinium corymbosum x V. angustifolium
History: Northblue was bred by the University of Minnesota as part of a hybrid blueberry breeding program that started in 1967. The goal of the program was to cross highbush and lowbush blueberries in order to create high-quality cold hardy varieties. Of the three varieties initially created in this program, Northblue was noted for having the largest fruit and highest productivity. Northblue was introduced to the public in 1983.
Why We Grow It: Northblue produces nicely sized, firm blueberries that store well. The berries have a good sweet flavour akin to that of wild blueberries and are great for a variety of uses. The compact shrub is quite productive and cold hardy.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Vaccinium corymbosum x V. angustifolium
History: Northcountry was bred by the University of Minnesota as part of a hybrid blueberry breeding program that started in 1967. The goal of the program was to cross highbush and lowbush blueberries in order to create high-quality cold hardy varieties. Northcountry itself was created in 1968 and was introduced in 1986.
Why We Grow It: Northcountry produces small to medium blueberries with a sweet flavour akin to that of wild blueberries. For those looking to enjoy fresh blueberries as soon as possible each year, this variety is an excellent choice since it ripens quite early. The compact bush is also quite cold hardy and productive!
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
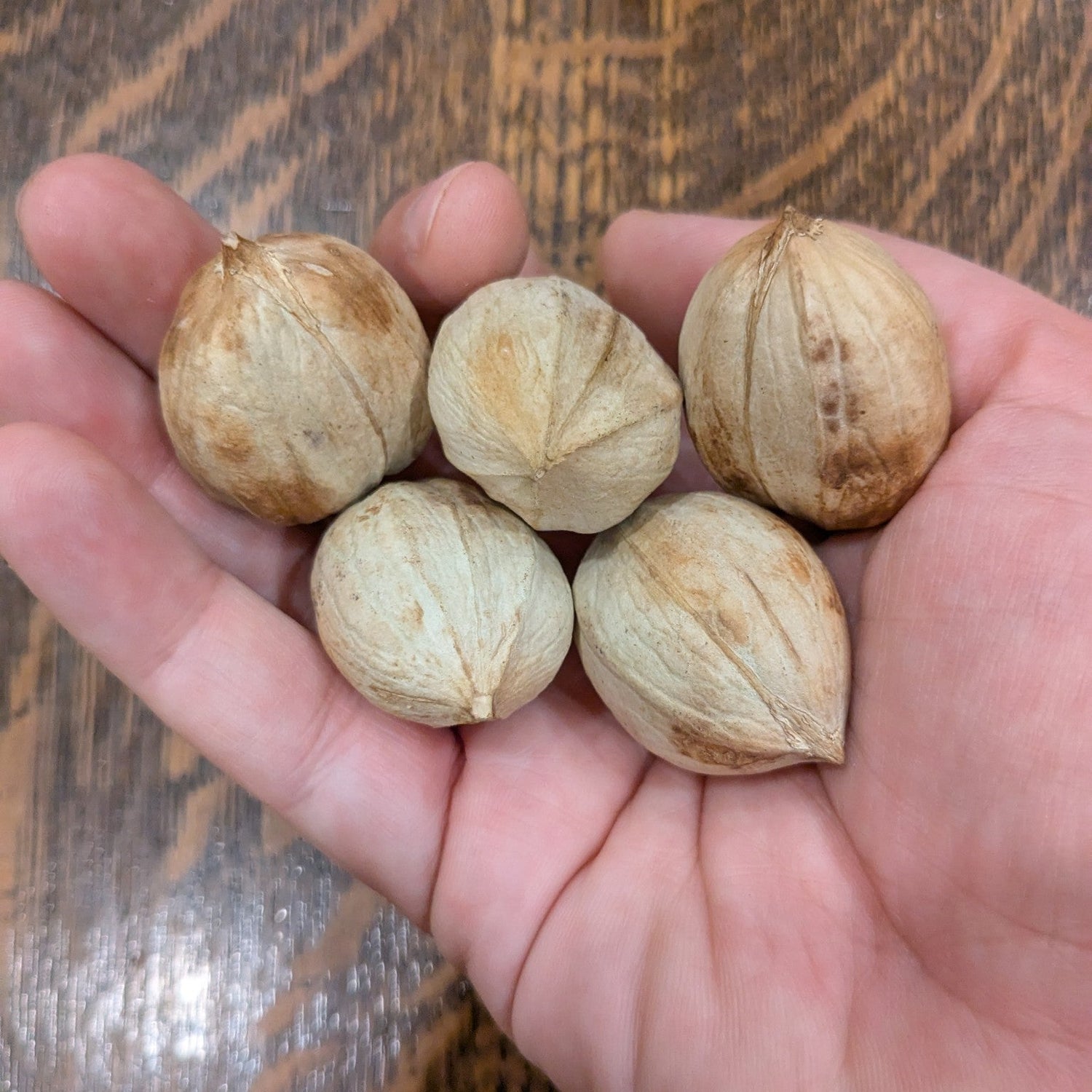
Species: Carya ovata
History: Shagbark Hickory is native to parts of southern Ontario and much of the eastern United States. Much more common than the Shellbark Hickory, Shagbark Hickory is an important source of food for many species. Indigenous peoples also used the nuts as a food source and made the kernel milk into various dishes, along with using the wood to make bows. The strong wood is also used to make items such as tool handles and drumsticks that require extra durability. Check out this blog post by one of our customers to learn more cool history about these trees.
Why We Grow It: Shagbark Hickory produces an abundant crop of small hickory nuts every year and the sap can also be boiled for a unique flavored syrup (we haven't tried this yet, but would love to hear about it if you have!). The tree gets its name from the unique peeling bark, adding extra visual appeal wherever the tree is planted.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Picea abies
History: Norway spruce, aka European spruce, is native to Northern, Central, and Eastern Europe. It is one of the most commonly planted spruce trees in the world, used as an ornamental landscape tree and as a Christmas tree. In fact, the Norwegian capital Oslo sends large Norway spruce trees as the central Christmas display in London, Edinburgh, and Washington DC every year as thanks for aid during WW2. The shoot tips have been used in traditional European medicines.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
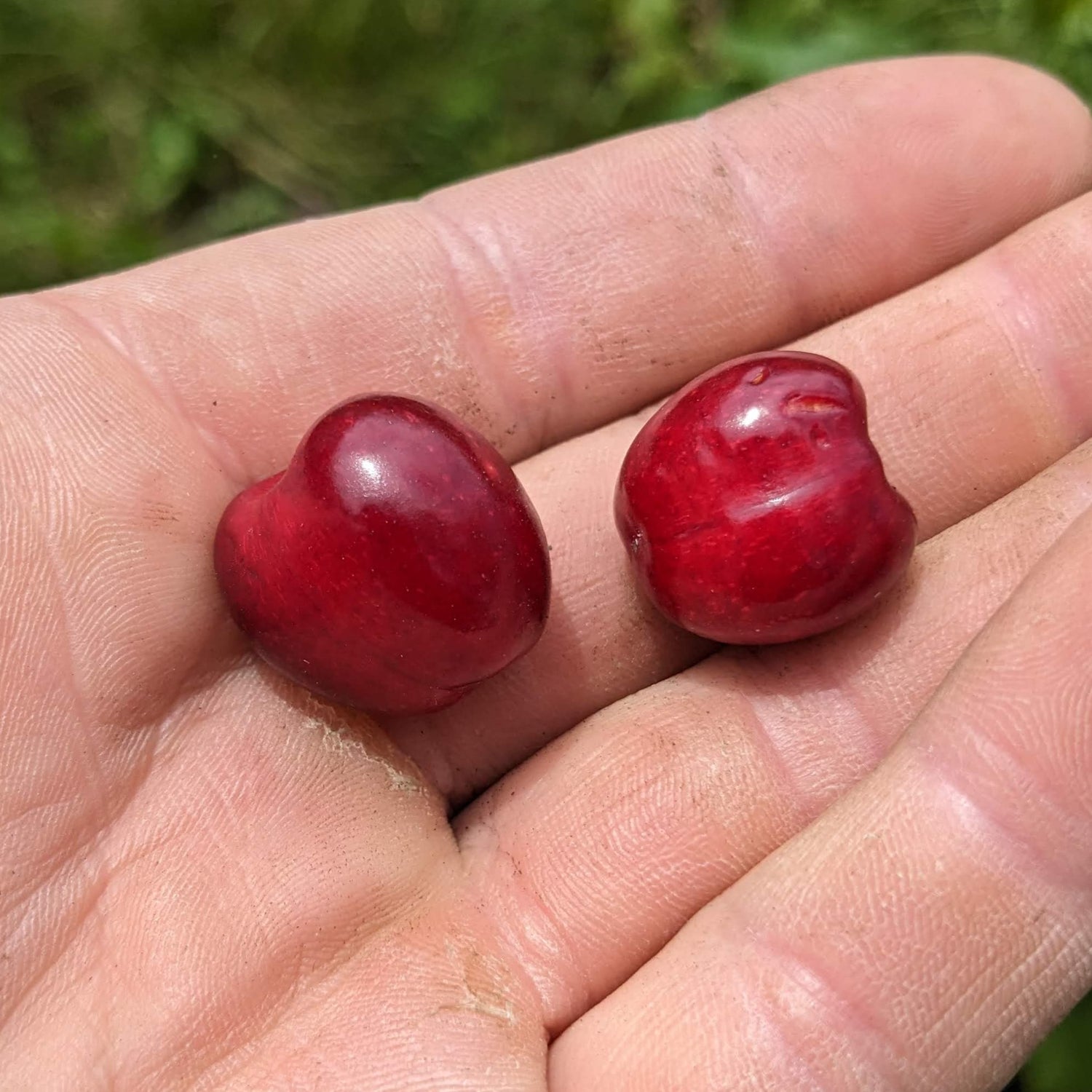
History: Van was developed at the Summerland Research Station in BC and was the first variety released by their breeding program. It originated as an open-pollinated cross with Empress Eugenie in 1936 and was introduced in 1944. Van was named after J.R. Van Haarlem, a pomologist at the Horticultural Experiment Station in Vineland, ON. The variety initially enjoyed great popularity, but has faded out of commercial favour since it is not self-pollinating. It can still be found being grown on a small scale and in backyards.
Why We Grow It: Van produces firm, dark red cherries with an excellent flavour similar to Bing. They have a sweet/tart flavour that makes them great for both fresh eating and baking/cooking. The tree itself is vigorous, hardy, starts bearing fruit at a young age, and produces heavy crops. It also flowers prolifically, making it a lovely tree in the spring and a great pollination partner for other sweet cherries.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Rainier sweet cherries were created by Harold Fogle at the Washington State University research center in 1952 and released in 1960. They were named after Mount Rainier, the tallest mountain in the state. Due to their delicate nature, Rainier cherries tend to be a bit more expensive than other commercial varieties.
Why We Grow It: Rainier are delicious yellow-skinned, yellow-fleshed sweet cherries. Some say they are the best tasting of all yellow cherries, and perhaps the best tasting cherry in general. Along with being great for fresh eating, they are also suitable for uses such as canning.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Bing sweet cherries originated near Salem, Oregon in 1875 as a cross between Black Republican and another sweet cherry variety. It was named after Ah Bing who worked as a nursery foreman for Seth Lewelling, the person who made Bing cherries into the top variety in the US. It is uncertain if Ah Bing himself developed the variety or if Lewelling simply named it after him as thanks for the 35 years he worked for him.
Why We Grow It: There are many reasons why this classic black sweet cherry has become the most commonly grown cherry in the US and the standard by which all other sweet cherries are measured. It produces large heart-shaped fruit with meaty purple-red flesh that is juicy and sweet. It has a semi-cling stone that is easy to remove, making it great for fresh eating and preserves. The tree is a heavy cropper, producing bountiful amounts of these lovely sweet cherries.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Little is known about this particular variety aside from that it's a Damson plum that originated in Sweden. 'Krikon' is the Swedish word for 'damson.'
Why We Grow It: Although its history is a bit of a mystery, we can certainly tell you that this is the best plum variety for very cold regions. It produces small round deep purple fruit that are good for cooking, preserving, and making jam. The flesh has a spicy, sweet flavour although some do not find it that great for fresh eating. Compared to regular Damson's Krikon Damson is a bit smaller, and more flavourful.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Strawberry Pippin is another variety whose history we know little about. All we know is that it likely originated in England where it was first recorded in 1874. The 'pippin' in its name indicates that it was grown from seed by chance.
Why We Grow It: While we may not know much about its past, we do know why we are happy to grow it! Strawberry Pippin has an attractive red striped fruit which is quite firm and sweet. Its excellent flavour is best enjoyed picked fresh right off the tree. In our experience, Strawberry Pippin does well with minimal care, and is an excellent choice for the backyard.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Royal Gala is a natural sport (mutation) of the Gala apple that was patented by Stark Bro's Nurseries in 1977. It boasts a deeper red colouring than the original Gala which makes it more visually appealing. In New Zealand, where the Gala apple originated, it has been almost entirely replaced by the Royal Gala in commercial growing operations.
Why We Grow It: Like the Gala apple, Royal Gala is popular for a reason. It is juicy and crisp with a sweet flavour and the fruit stores quite well.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
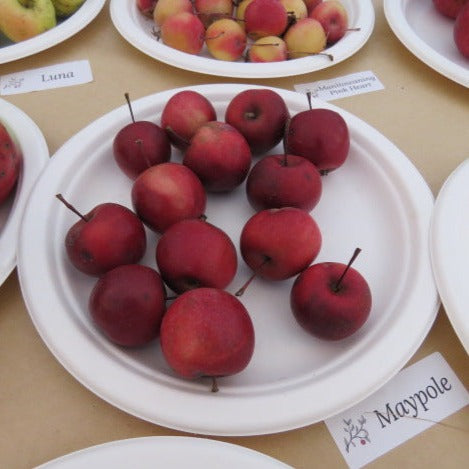
History: Maypole was developed in 1976 by Plant Breeding International at the East Malling Research Station in the UK as a cross between Wijcik Spur McIntosh and Baskatong. Wijcik Spur McIntosh originated as a mutation discovered on a McIntosh tree in 1962 in the Wijcik Orchards in British Columbia, the branch growing oddly straight with little branching. Several varieties were deliberately bred to have this mutation and now Maypole, released in 1986, is one of six columnar varieties developed at the station. This series of trees is known as Ballerina in the UK but due to that name being unavailable in the US, they are known as Colonnade in North America.
Why We Grow It: Not only is Maypole unique as a columnar apple, this crabapple also boasts lovely red flesh, bronze coloured leaves, and pretty pink blossoms in the spring. This makes it overall a lovely ornamental tree to have, whether planted in the yard or in a pot. The fruit is also excellent for jelly, apple butter, and cider, adding a red hue to each. It can also be eaten fresh although it tends to be quite acidic with a touch of sweetness.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Liberty was developed by the New York State Agricultural Experiment Station in Geneva, NY, in 1955 and released in 1978. It is a cross between Macoun and a Japanese crabapple (Malus floribunda), bred in hopes of achieving the disease resistance of the Japanese crabapple.
Why We Grow It: The creators of Liberty were highly successful in their goal, creating one of the most disease-resistant varieties. Liberty is a favourite for organic production as a result. The fruit is bright red with sweet, creamy flesh and it stores well.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Also known as Red Fuji, Fuji BC #2 is a sport (mutation) of the original Fuji apple that has redder skin. Although little can be found on the exact origins of this sport, its name suggests it originated in BC where it tends to be the most popular.
Why We Grow It: Along with the great sweet flavour and juiciness of the original, Fuji BC #2 also boasts redder skin, making it more appealing for those who prefer red apples.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Fireside apples originated in 1943 from a breeding program at the Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station. They are one of nearly 30 varieties that have been introduced by the university's breeding program since it began in 1888.
Why We Grow It: Fireside stands as an icon of toughness in the world of apples, thriving in cold northern areas. But don’t let this image fool you—Fireside has a warm heart! The flesh is amazingly sweet and very juicy.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Prunus pumila var. besseyi (Western sandcherry) x P. salicina (Japanese Plum)
History: Manor was developed at the Morden Research Station in Manitoba and released in 1945.
Why We Grow It: Manor produces a small plum with skin that is nearly black when ripe and purplish-red flesh. When ripe, the fruit is quite sweet and good for fresh eating! Some prefer to pick it when it is still a little unripe and a bit firmer since it is more astringent and lends itself well to uses such as baking, preserving, and making wine. The shrub stays smaller than other chums but starts bearing fruit at a young age and is known for being quite productive.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Ernie's Favourite was grown as a seedling on a homestead in Mt. Pleasant, ON. It is believed that the seed came from Eastern Europe but it has thrived in our climate for decades and been a family favourite for the original growers. When we asked the farmer what he wanted to call the variety, he requested we name it 'Ernie's Favourite' after his father.
Why We Grow It: Ernie's Favourite produces a medium-sized quince with good flavour. It has dependable crops and does well in our climate - a good, tried-n-true variety!
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
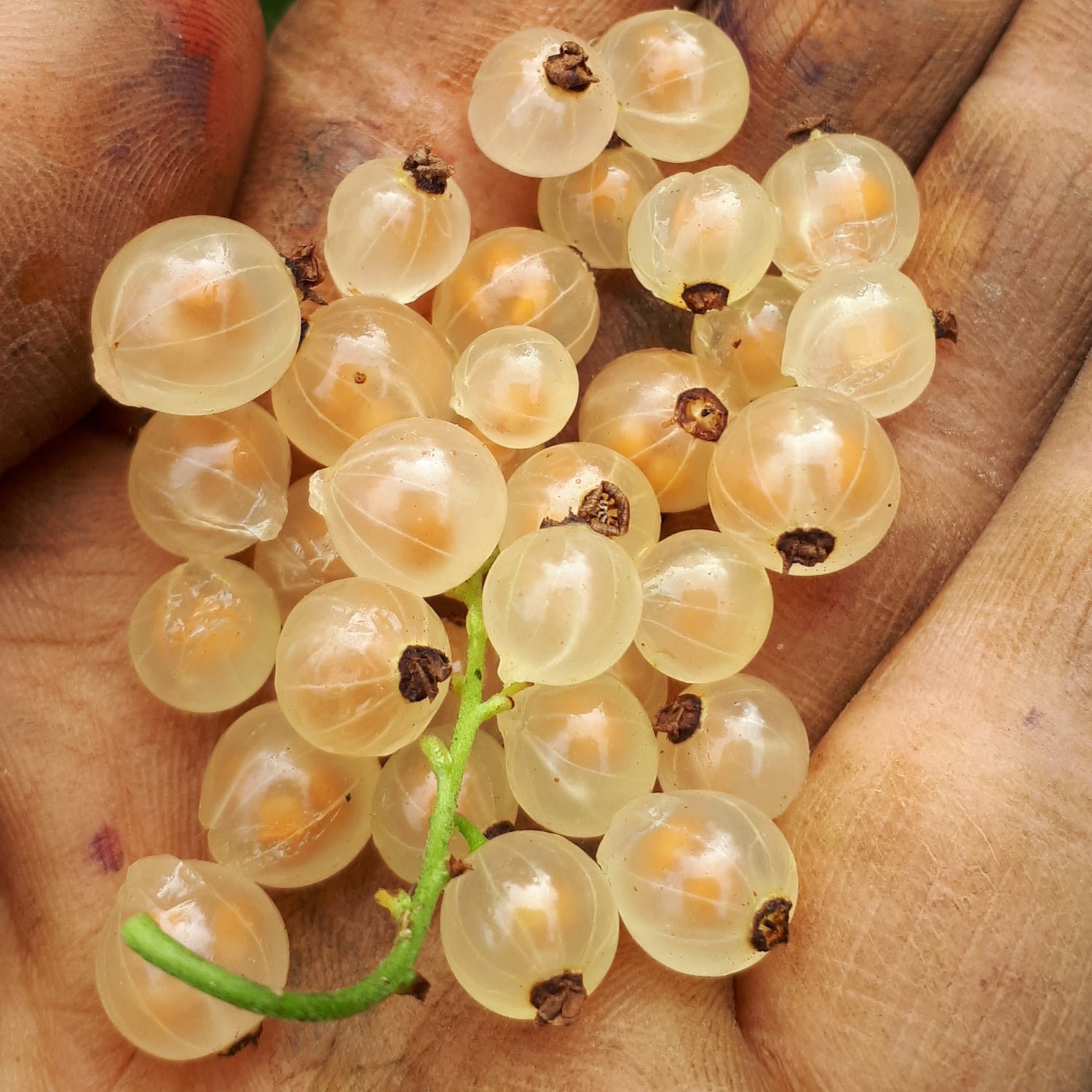
Species: Ribes rubrum
History: Developed in Holland, White Pearl currants, like all white currants, are actually an albino mutation of red currants. This variety has been popular in Europe for quite some time, although aside from its place of origin it appears there is little information on how it came to be.
Why We Grow It: These delicate translucent berries are white with a pinkish-gold hue, making them delightful to see growing in the garden. They have sweet and mild flavour that is slightly floral. The plant itself is quite cold hardy and bears prolific crops.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
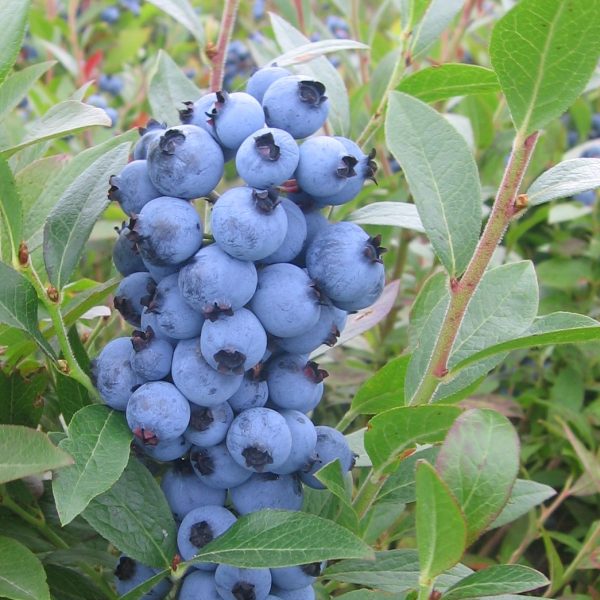
Species: Vaccinium corymbosum
History: Toro is a cross between Earliblue and Ivanhoe bred by USDA blueberry breeder Arlen Draper in Maryland. It was selected for its productivity, firmness, and flavour and introduced in 1987. It was named Toro ('bull' in Spanish) due to its strong and stocky structure, however this dense canopy structure prevented Toro from achieving true commercial success due to the added difficulty of pruning and harvesting it at a commercial level.
Why We Grow It: Toro produces large blueberries that are quite sweet and firm. They tend to produce heavy crops that ripen all at once, making mechanical picking easier. Like other blueberries, Toro is great for eating fresh, baking, and preserving!
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
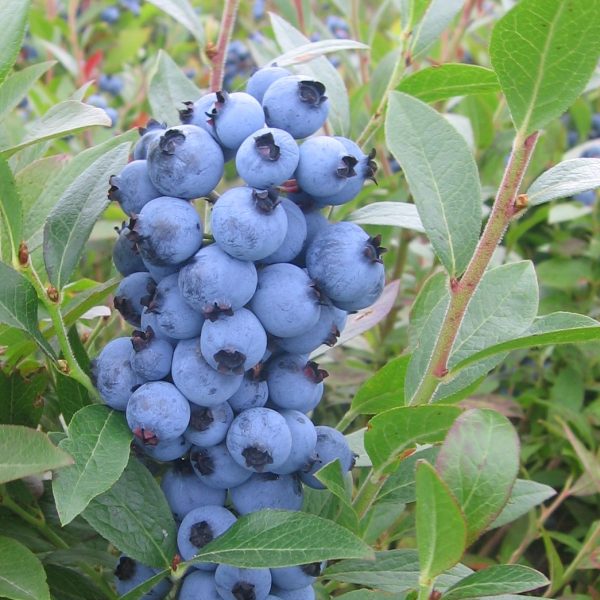
Species: Vaccinium corymbosum
History: Patriot was developed by the USDA and Maine Agriculture Experimental Station where it was first bred in 1954. It was selected for its cold hardiness and resistance to root rot. Patriot was released in 1976 and given its name to mark the 200th anniversary of the signing of the Declaration of Independence.
Why We Grow It: Patriot produces large berries with excellent flavour that are a bit on the softer side. The fruit ripens early in the season and is great for fresh eating, baking, preserving, and freezing! It is more tolerant of the cold and of wet soils than other blueberries and can be grown even in a clay soil.