Roots & Tubers
Roots and Tubers: Nature’s Underground Powerhouses
Roots and tubers aren't just food crops—they play a powerful role in improving soil health. With their deep-penetrating roots and nutrient-accumulating abilities, these plants help condition, aerate, and restore degraded or compacted soils.
Whether you're a home gardener or a regenerative farmer, incorporating roots and tubers into your planting system can boost long-term soil fertility and structure.
Sort by:
15 products
15 products
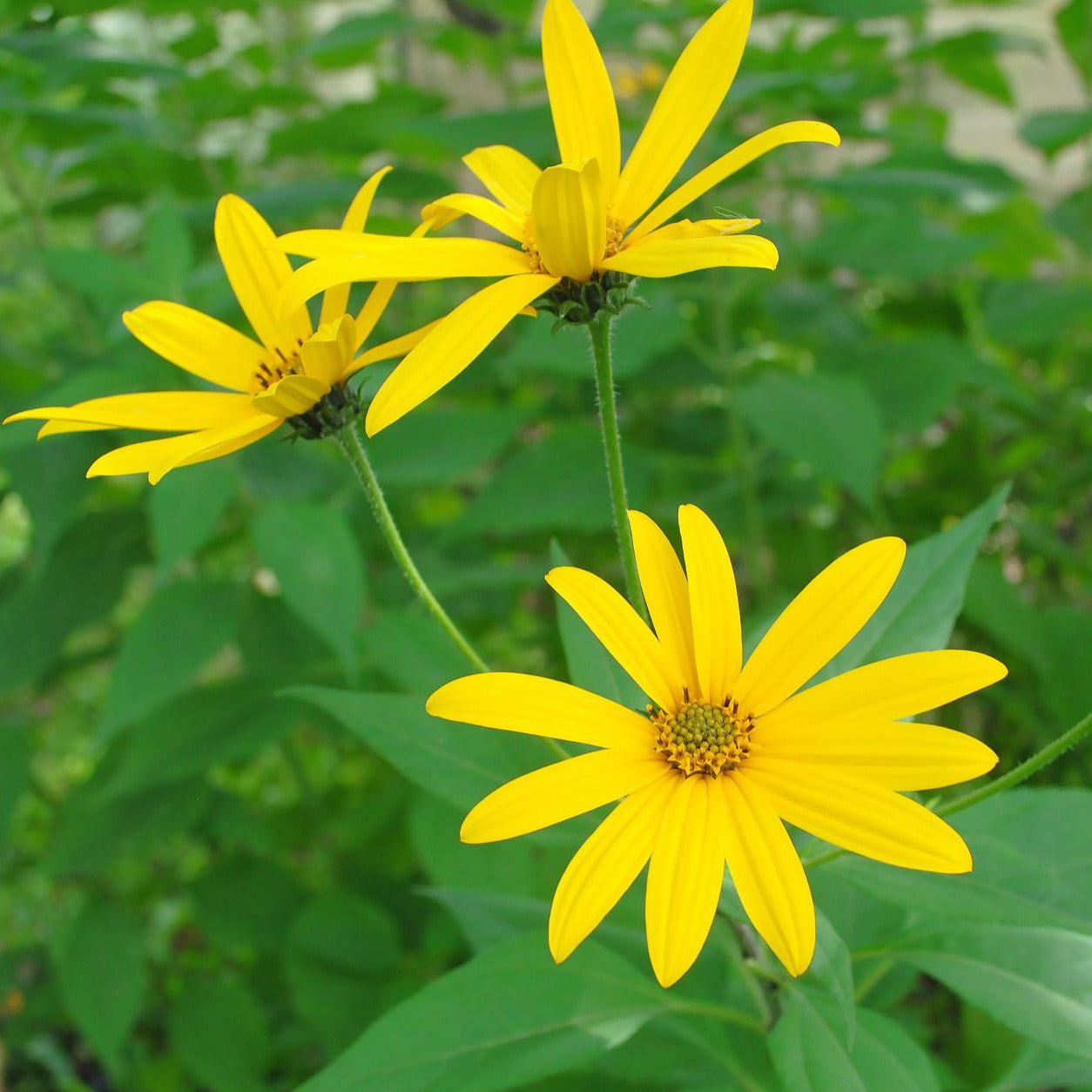
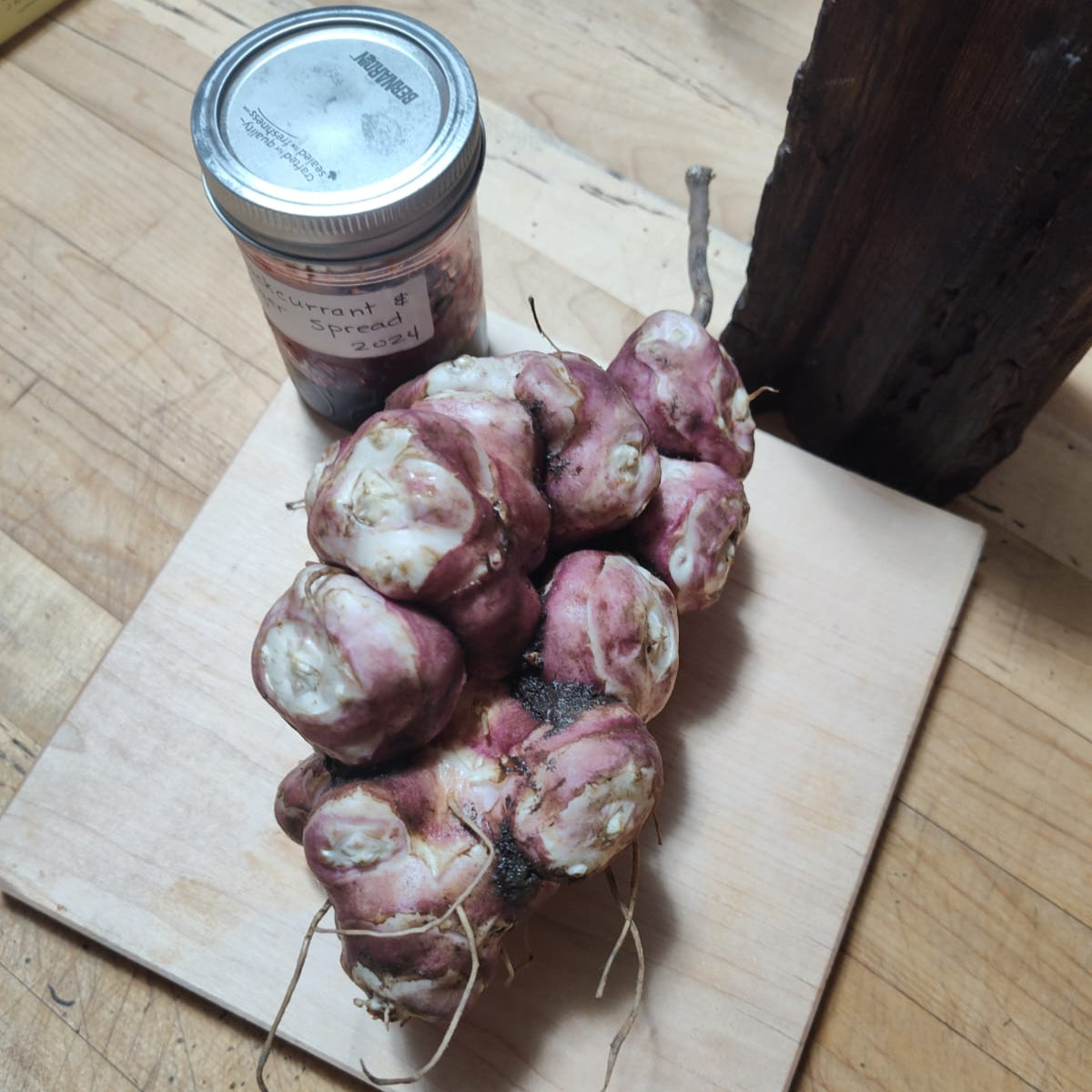
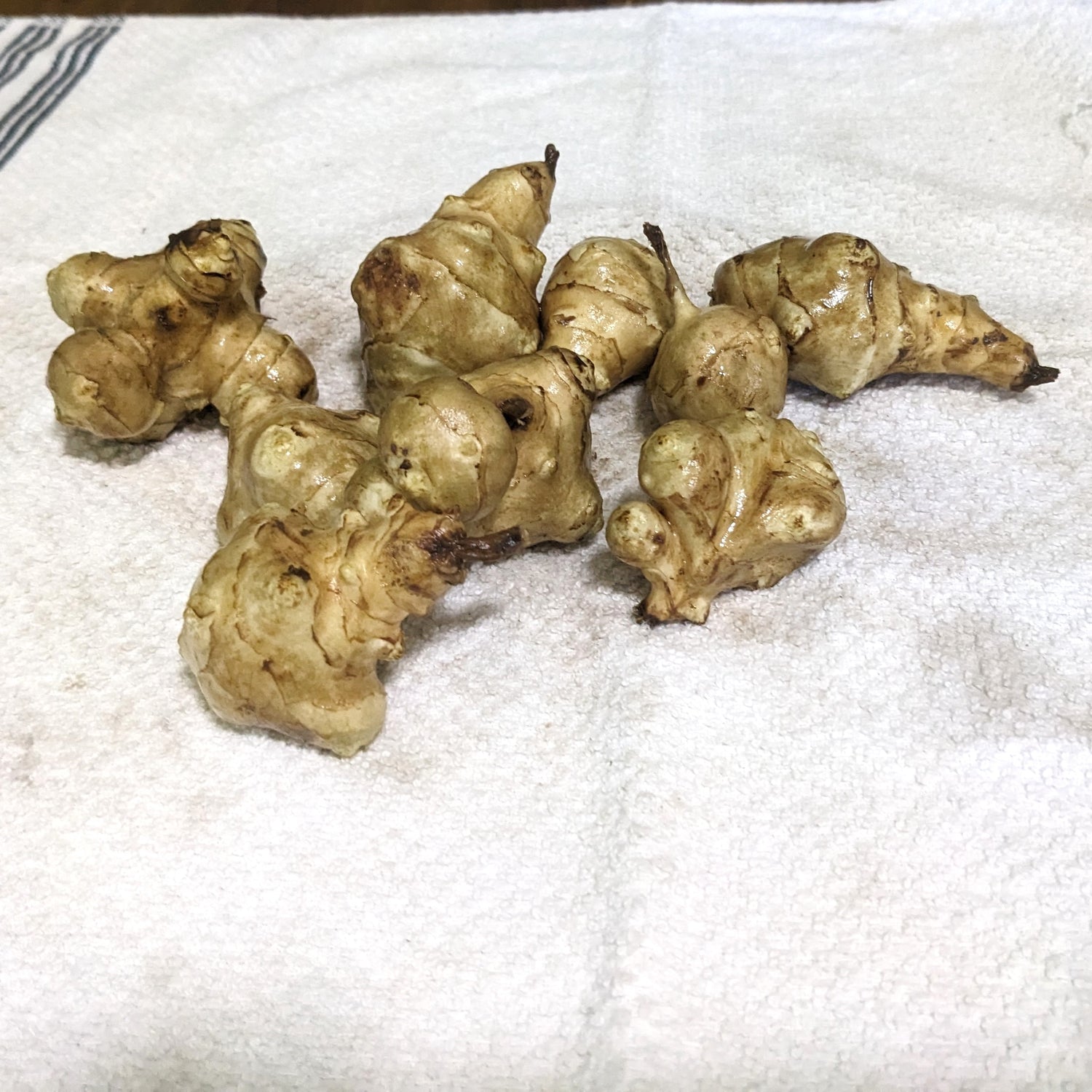
Species: Helianthus tuberosus, Sunchokes are also known as Jerusalem Artichokes or J Chokes
History: Corlis Bolton Haynes discovered a wild sunchoke growing on the farm her parents purchased in 1925 and then spent over sixty years selectively planting the biggest and smoothest tubers in order to improve on the plant. Corlis sadly passed away in 2003 but her family maintains the tradition of only replanting the biggest and best tubers.
Why We Grow It: This variety produces large, white, knobby tubers that like a potato can be prepared and eaten in a variety of ways! This variety is quite productive and the tall plants can be used as a temporary windbreak and/or privacy screen.
Species: Cryptotaenia japonica
History: Mitsuba is native to Japan, China, and Korea where it is used as a garnish, seasoning, and as a root vegetable. Mitsuba translates from Japanese as 'three leaves', referring to the way the plant grows leaves in groups of three. In Japan, it is also traditionally used at weddings where the stems of the plant are tied in knots to bring luck and symbolize the lasting relationship. It is also used in Japanese flower arrangement.
Why We Grow It: Mitsuba has a light, refreshing, vegetal flavour that is reminiscent of parsley and celery. It is also high in calcium and vitamin C. This variety boasts attractive purplish foliage and produces small, pinkish-white star-shaped flowers which add a nice ornamental touch to the garden.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Inula helenium
History: Elecampane is native from Spain all the way to parts of China and has become naturalized in parts of North America. It has traditionally served a variety of purposes including being used to treat snake and spider bites by the Ancient Greeks, to test if honey has spoiled by the Ancient Romans, as a candied snack in Medieval Europe, and to make absinthe. Throughout its long history it has provided various medicinal uses as well. It also has quite the storied past, with the species name referring to the myth that the plant sprung up from the tears of Helen of Troy while the Celts associated it with fairies and elves.
Why We Grow It: Although not commonly used medicinally today, it still provides some novelty to the garden. The small, yellow flowers resemble those of asters to which it is related. The flowers attract pollinators and the roots, like comfrey, are good at mining nutrients from deeper in the soil.
2025 Staff Favourite
Mavor Sunchokes are Zack's favourite this year! In his personal experience "the large tuber size of these sunchokes makes them a great potato substitute. They are great fried in beef tallow!”
All Staff Favourites are 20% off. The Staff Favourite Discount cannot be combined with other quantity discounts.
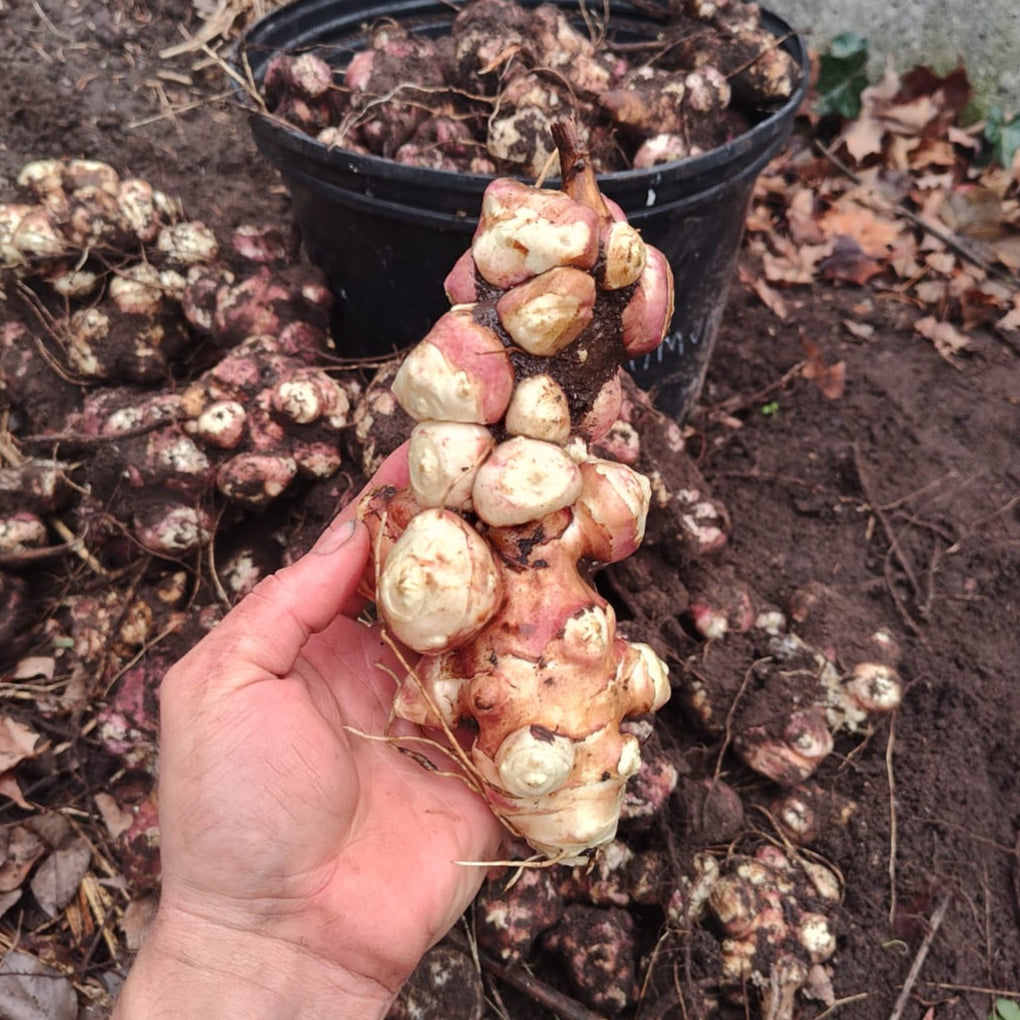
Species: Helianthus tuberosus, Sunchokes are also known as Jerusalem Artichokes or J Chokes
History: Mavor sunchokes are of unknown origin since they were kindly given to us by a local customer named A. Mavor. We were impressed with the large size and flavour of this variety and wanted to make them available to more customers, so are offering them under the name Mavor as thanks to the person who gave them to us.
Why We Grow It: Mavor sunchokes produce large, knobby tubers that are great for cooking in all the same ways you would cook a potato. At least in our soil, some of the tubers produce have a nice reddish tinge to the skin. The tubers store quite well in the fridge. It is a quick growing variety and, like other sunchokes, can spread quite aggressively if left unmanaged.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Symphytum sp.
History: Comfrey plants are native to various continents around the world including Europe, Asia, and North America. Common names such as boneset and knitbone and its genus name referencing the Greek 'symphis' meaning 'growing together of bones' indicates it may have been used medicinally for mending bones. Comfrey is now popular as a permaculture plant.
Why We Grow It: This classic permaculture plant grows incredibly deep tap roots, mining rich nutrients from deep below the soil surface. It's a living mulch that 'molts' 3-4 times each season. It's used in traditional medicine and creates a healthful compost tea full of calcium and potassium. It grows up to 70 cm tall, before molting down, and spreads slowly over the years.
Showing 15/15