All Zone 5 (or hardier) Plants
Sort by:
379 products
379 products
Species: Hamamelis vernalis
History: Ozark Witch-Hazel is native to the Ozark Plateau in the United States for which it is named. It has been cultivated ornamentally for its strong scent and unique flowering time, blooming from mid/late winter into spring. The name comes form a misspelling of the English word 'wyche' which means 'pliable' and 'hazel' due to the shrub resembling hazelnut shrubs. Interestingly, 'water witches' in the area did use Ozark Witch-Hazel branches in their water-finding rituals to divine the best locations to dig wells.
Why We Grow It: Witch-hazels are a unique plant for any property, sprouting stringy yellow flowers in the winter when nothing else is flowering. They produce woody capsules that forcibly pop open, launching the hard, black seeds up to 10m away.
History: Little is known about Kermerrien aside from the fact it originated in the Quimplerlé region in France. It was exhibited by an orchardist at an event in 1896 and was described in a book on cider apples published in the same year, but it is unknown how old the variety is. It is commonly used to make traditional Breton cider.
Why We Grow It: This bittersweet cider apple produces a good single-variety cider with a nice golden juice. The tree is vigorous and starts bearing at a young age.
Why We Grow It: It is easy to see why growers were so eager to overlook Viking's scab susceptibility, its flavour providing a sweet-tart taste with notes of rose and lychee. It is an excellent all-purpose apple that can be used for cooking, baking, sauce, and cider. Its great flavour and utility is matched by its attractive appearance, the large fruit featuring dark red skin bordering on maroon. However, it does bruise easily and brown quickly and only stores for about a month at most.
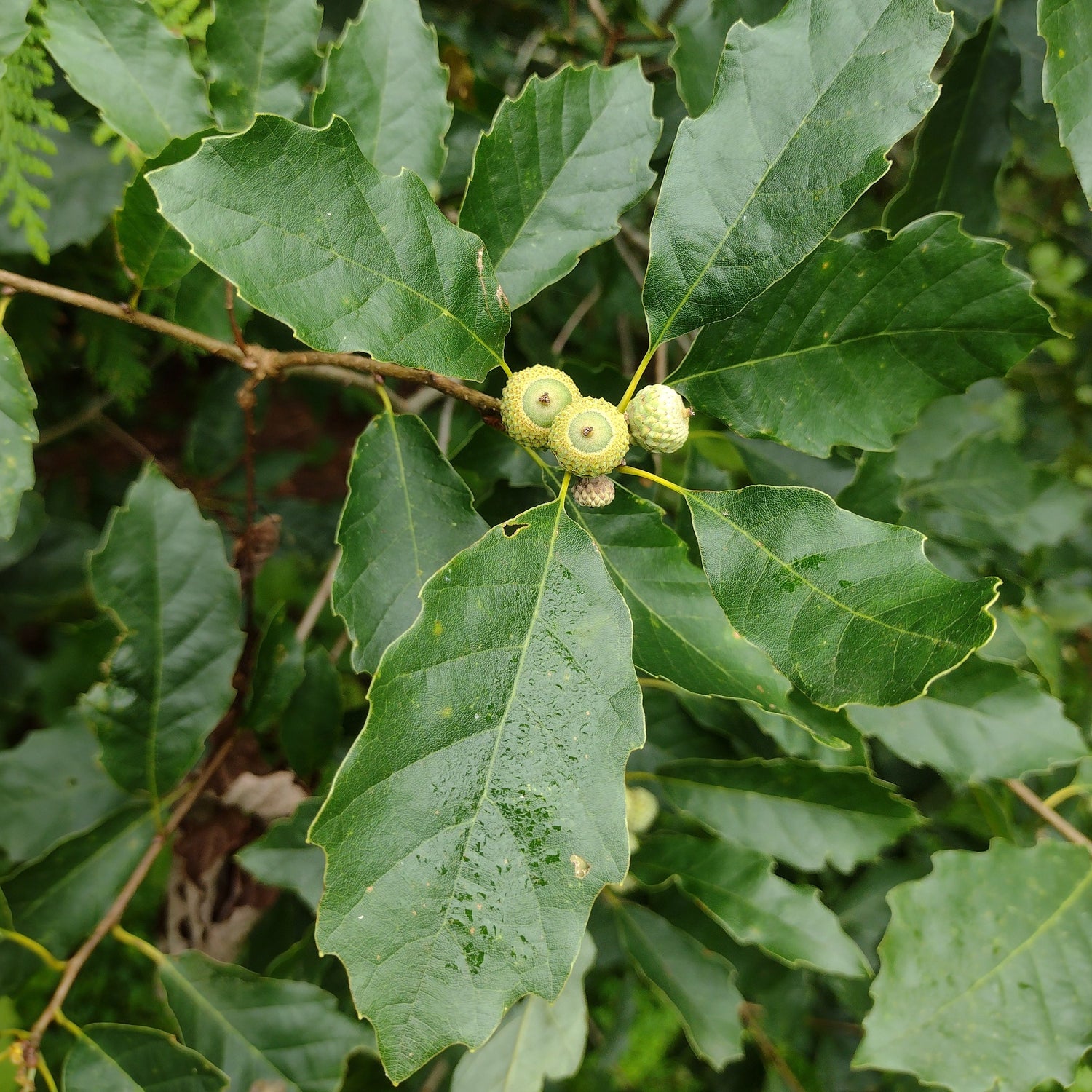
Species: Quercus prinoides or hybrid. Our seeds are collected from trees that may have been cross-pollinated by closely related species so the resulting seedlings may be hybrids.
History: Dwarf Chinquapin Oak (also spelled Chinkapin) is native to southern Ontario and much of the eastern and central United States. It was first described in 1801 by German botanist Karl Ludwig Willdenow but was likely well-known amongst indigenous groups in its range for its edible acorns.
Why We Grow It: Dwarf Chinquapin Oaks are most well known for producing mild sweet acorns that can be eaten raw or processed, making them popular with humans and wildlife alike. They are also quite quick to start producing acorns, only taking 3-5 years where some larger species may take decades.
History: The origins of Pomme Gris (translated as 'gray apple' from French) are a bit of a mystery. It may have originated in France in the 1600s as either a seedling or sport of the variety Reinette Gris which was then brought to Quebec by French or Swiss colonizers. Alternatively, it may have its origins in Quebec, perhaps being grown and propagated in Canada from the start. The first instance of this variety's documentation was by a William Forsyth in 1803 who believed the apple originated in Canada and made its way to Europe sometime in the 1700s. Regardless, this variety was grown in Quebec for centuries.
Why We Grow It: Pomme Gris is an excellent all-purpose apple! Although not the prettiest apple in the world, it is crisp, juicy, and aromatic with a nutty flavour and hints of vanilla. It was really a standout when our tree first produced fruit a couple years ago! The fruit can also be used for cooking and the apple would likely be a good addition to cider blends.
History: Kandil Sinap* originated in the early 1800s around the Black Sea, although it is debated whether it originally came from the Crimean Peninsula in the Ukraine or the Sinop Peninsula in Turkey. It was at one time commonly exported into Russia.
*There are different thoughts on what Kandil Sinap translates to, some say it is 'candle of Sinop,' others 'sweet apple of Sinap,' and it translates directly from Turkish as 'oil lamp'
Why We Grow It: Kandil Sinap's most prominent feature is the odd shape of the fruit, strangely oblong and conical, almost resembling a candle in appearance. The odd green fruit have a sweet, sprightly flavour and are quite aromatic, although they do bruise easily. The tree naturally stays smaller but produces heavy crops and is great for backyard orchards.
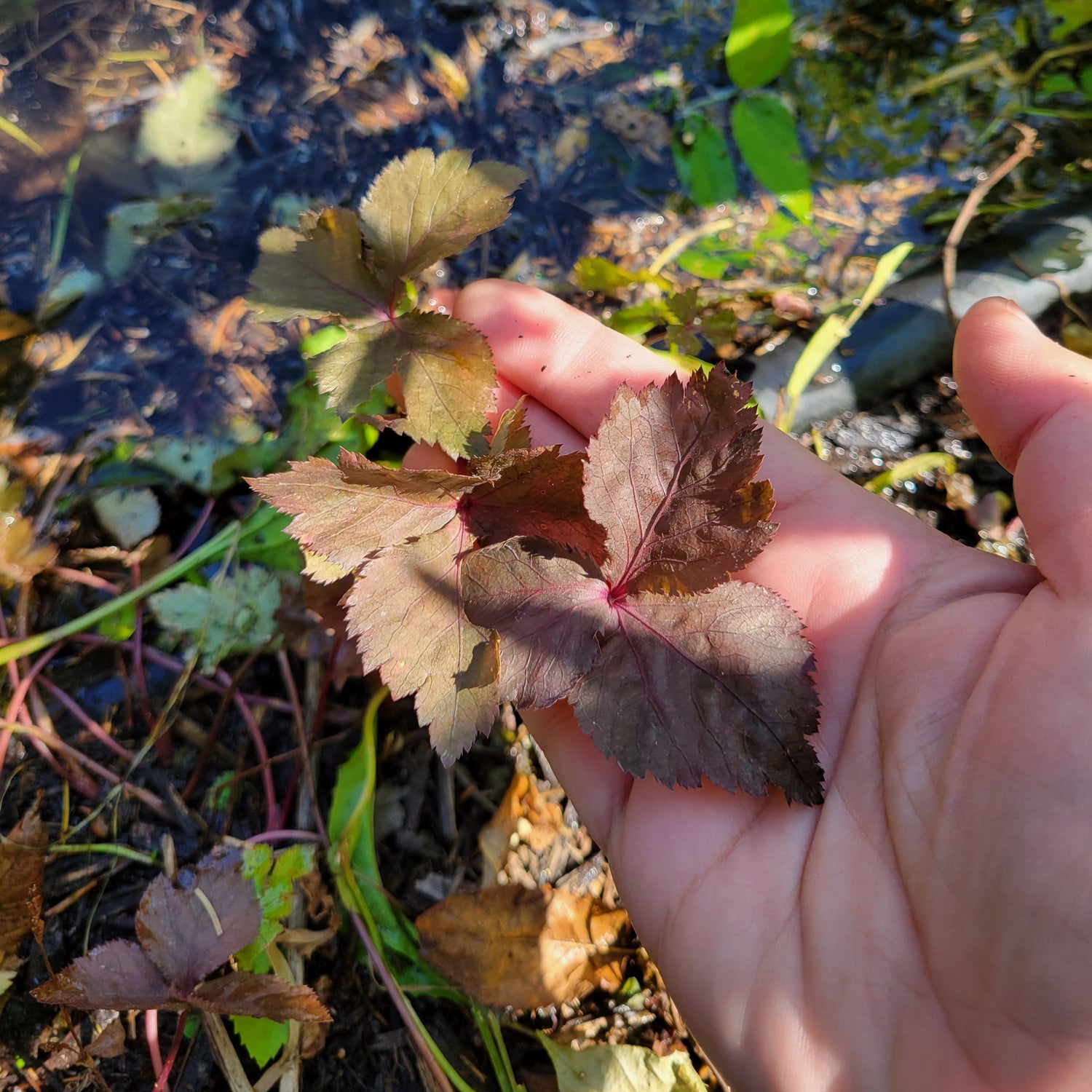
Species: Cryptotaenia japonica
History: Mitsuba is native to Japan, China, and Korea where it is used as a garnish, seasoning, and as a root vegetable. Mitsuba translates from Japanese as 'three leaves', referring to the way the plant grows leaves in groups of three. In Japan, it is also traditionally used at weddings where the stems of the plant are tied in knots to bring luck and symbolize the lasting relationship. It is also used in Japanese flower arrangement.
Why We Grow It: Mitsuba has a light, refreshing, vegetal flavour that is reminiscent of parsley and celery. It is also high in calcium and vitamin C. This variety boasts attractive purplish foliage (more green in shade and purple in full sun, see photos) and produces small, pinkish-white star-shaped flowers which add a nice ornamental touch to the garden.
History: Major dates back to potentially before the nineteenth century and was commonly grown on farms in Devon and Somerset in England. It remains a traditional English cider variety.
Why We Grow It: Major produces a lovely bittersweet juice that is good both in blends or on its own. It ripens relatively early so it is a nice apple for extending the cider pressing season.
History: Blakeney Red (aka Circus pear, Red pear, and Painted Lady) is believed to have originated in the English village of Blakeney, its birthplace and the prominent red blush on the fruit earning it its name. It may have been originally planted sometime in the 1700s but became better known starting around 1830 and was the most widely planted perry pear. It is still popular in the UK today and is gaining attention in North America as well. A yellow dye can also be made from this variety and it was used to dye khakis for British soldiers during WW1.
Why We Grow It: This perry pear produces small to medium yellow fruit with red blush and some russet. For those interested in perry, it's hard to ignore this variety's long history, although its quality can vary based on growing conditions.
History: Luscious was developed at South Dakota State University as a cross between Ewark and South Dakota 31 in 1954. This goal was to create trees suitable for areas like the Northern Great Plains. Luscious was introduced in 1973, likely selected for its cold-hardiness and excellent flavour.
Why We Grow It: Luscious produces small to medium yellow fruits with an attractive red blush. The fruit is quite sweet, great for fresh eating and cooking/baking! This is an excellent option for fans of Bartlett who are looking for a versatile and cold hardy variety! Luscious also has value as an ornamental tree, producing white blooms and glossy green leaves that turn a nice red in the fall.
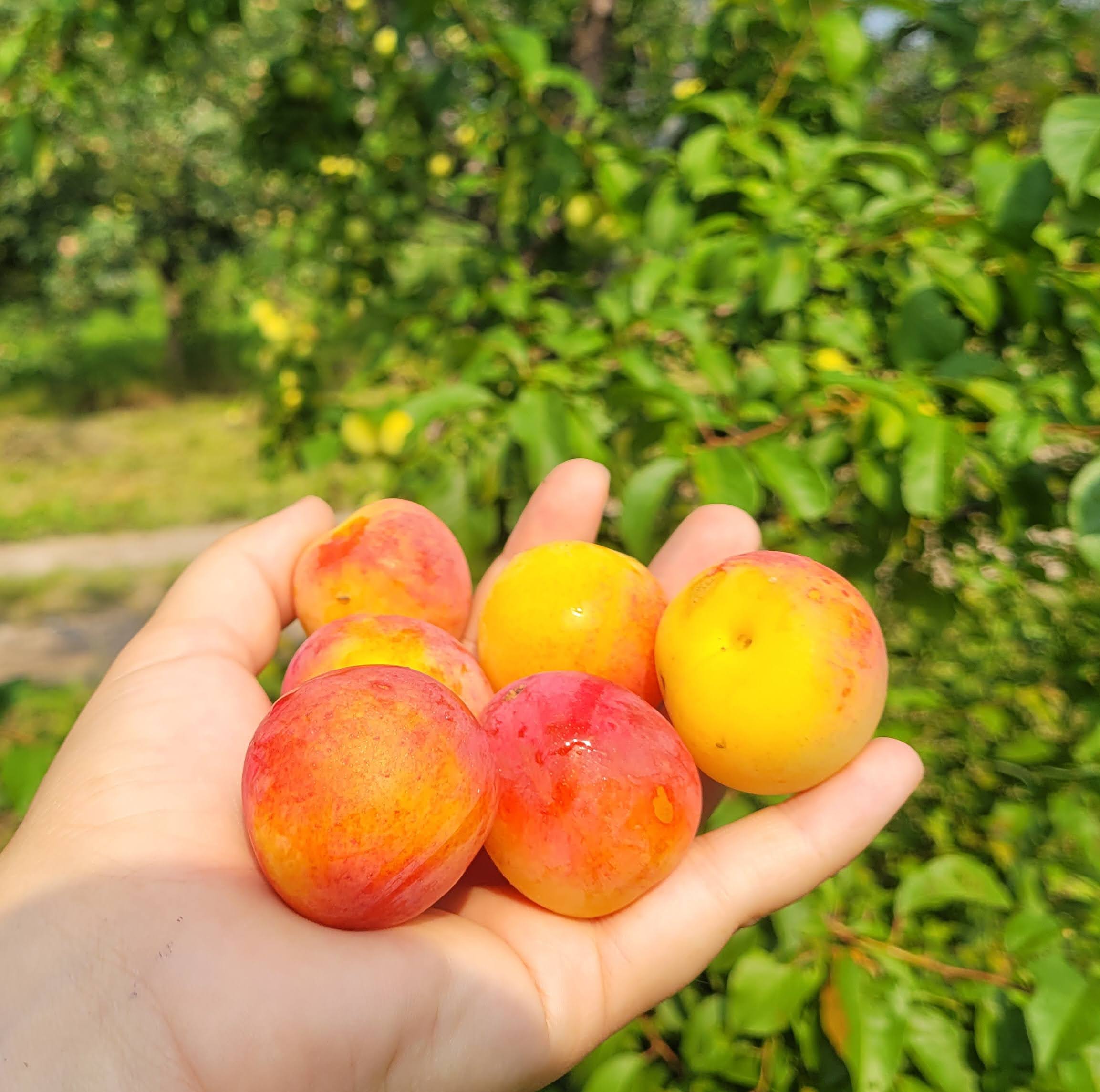
History: The origins and history of this variety are unknown based on our current research.
Why We Grow It: This variety produces a medium-sized freestone plum with purple-pink skin and yellow flesh that is sweet and juicy. It is one of the hardiest European plums around, making it a good choice for our colder climate!
Species: Rubus idaeus
History: Tulameen was bred at the Pacific Agri-Food Research Centre in 1980 and released in 1990. It was selected for its disease resistance, long ripening period, large fruit, and excellent flavour and quality. The name likely comes from either the Tulameen River or the town of Tulameen in BC, although it also means 'red earth' in Nlakaʼpamuctsin.
Why We Grow It: Tulameen is a summer-bearing variety that is known for producing large crops of huge red raspberries that are very sweet! The exceptionally tall canes may require some trellising but have very few thorns which makes handling them much easier than other varieties.
History: Golden Sentinel was developed at the Pacific Agri-Food Research Centre in Summerland, BC. It was first bred in 1986 as part of a breeding program to create high quality columnar apples. It underwent further testing until 1997, after which it was eventually released.
Why We Grow It: Golden Sentinel is wonderful for a variety of reasons! It produces attractive, large yellow apples with a sweet flavour reminiscent of Golden Delicious. The fruit can be eaten fresh or used for baking. Its columnar growth habit means it stays quite thin, making it a great option for container growing and/or those with limited space. This variety is also quite disease resistant.
History: Miki* Life was bred in Hirosaki City, Japan in 1981 by Seiichi Kudo and patented in 1996. It is a cross between two popular Japanese varieties: Tsugaru and Senshu.
*without knowing how the name is written in Japanese, it is difficult to say what 'miki' translates to but it could be 'beautiful tree'
Why We Grow It: Like many other Japanese varieties, Miki Life is a lovely red apple that is all sweetness with no acidity. These juicy apples can also be used to help bulk up cider and add alcohol by adding more sugars.
History: Mindemoya was discovered growing along the shores of Lake Mindemoya on Manitoulin Island along with Mindemoya Maroon. Wayne Kuntze happened upon these trees in 2020 while vacationing with his family. The good size and pinkish striping on the fruit caught his eye, and the sweet flavour sealed the deal! Now in 2023, we are happy to introduce this variety to the world!
Why We Grow It: Always on the search for new varieties, we are happy to grow and offer something that Wayne discovered! Mindemoya is an attractive whitish apple with pinkish-red stripes. It has a pleasantly sweet flavour and plenty of juice, along with a soft texture that may make it good for applesauce along with fresh eating.
This is a brand new variety and we're still learning about it! For any avid apple growers who decide to plant these out, feel free to keep us updated on how it grows, what you use the fruit for, etc, so we can provide as much information as possible!
Species: Cornus mas
History: Cornelian Cherry (aka Cornel) is a dogwood species native to parts of Europe and Asia. The berries were traditionally used mainly in cooking and to make jams and alcohol and have also been used in traditional Chinese medicine along with the leaves. The wood is quite dense (it sinks in water!) and has been used to make tool handles, machine parts, weapons in Ancient Greece, and the sticks traditionally carried by the mounted herdsman in the Maremma region. In the UK there was some interest in its use as a garden plant starting in the mid 1500s but interest has mainly grown in the last century or so.
Why We Grow It: A novelty among the dogwoods, Cornelian Cherries produce small, red fruits that resemble cherries. The acidic fruit can be eaten fresh when they're quite ripe but are primarily used for cooking and preserves, similar to cranberries. They are also attractive ornamental plants, producing clusters of bright yellow flowers very early in the season.
History: Whitney crabapples were grown from seed by nurseryman A.R. Whitney around 1865 at Whitney Nursery in Illinois, US. It became popular for its excellent cold hardiness and productivity and in the 1900s the state of Montana recommended it as one of the best crabapple varieties to grow.
Why We Grow It: These large (for a crabapple) yellow and red apples boast a sweet-sharp flavour with some astringency and juicy, crispy flesh. They are a truly multipurpose fruit and can be eaten fresh (if you like some astringency to your apple) or used for cooking, sauce, cider, and jelly. The trees are very cold hardy and boast good disease resistance as well.
Why We Grow It: It is hard to turn down an apple that sounds as wonderful as Sundance! It is crisp and juicy with a spicy, citric flavour. Along with being great for fresh eating, the fruit also holds its shape well when baked. As an added bonus, this variety is resistant to many common apple diseases and stores quite well so you'll have plenty of high quality apples to easily last you through the winter.
History: Holstein was discovered in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany in 1918 and became one of the most popular varieties in the country. It is possibly a seedling of Cox's Orange Pippin.
Why We Grow It: This popular German variety sports attractive yellow skin with an orange/red blush. The flesh is firm, juicy, and aromatic in a way that is reminiscent of Cox's Orange Pippin. In general, this variety is easy to care for and grows vigorously.
History: Little is known about this variety aside from that it originated in the Brittany region of France in the 1800s. The variety is held in high esteem as a traditional French cider variety. Translated from French, its name means 'Queen of Apples.'
Why We Grow It: Reine des Pommes produces a bold, fragrant flavoured bittersweet cider that is quite unique. It is good both as a single-variety cider and in blends. The tree is fairly vigorous and produces good crops.
Why We Grow It: The saying 'big things come in small packages' holds true for Chinook. Although the fruit is on the smaller side, it boasts a lovely red skin, excellent sweet-tart flavour, a nice aroma, and crisp and juicy flesh. Fans of this variety will be happy to hear that the fruit can be enjoyed well through the winter, it is an excellent keeper and can last 6-7 months in storage. On top of that the tree grows fairly vigorously, starts bearing fruit at a young age, and produces heavy crops (although thinning will be required).
History: Paula Red (sometimes written Paulared) was discovered in Michigan in 1960 by Lewis Arends near a ravine where apples were dumped. It was one of several wild apple seedlings that had sprouted up from the discarded seeds. Likely pleased by its attractive red skin and flavour, Arends named it 'Paula Red' in honour of his wife Pauline. It is a cross between Duchess and McIntosh.
Why We Grow It: Paula Red produces medium to large red apples with small yellow/green patches that are juicy and firm with a nice sweet/tart flavour. The flavour has strong vinous and strawberry notes. It is also slower to brown. This early-ripening variety tends to soften relatively quickly which means it does not store very long, but it is great for making applesauce. The tree produces heavy crops although tends to bear every other year as a result.
Species: Prunus avium
History: These seedlings are grown from Hedelfingen seeds from sweet cherries sourced in Ontario. First discovered in Germany in 1850, Hedelfingen has become a popular variety in Ontario.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! The parent variety, Hedelfingen, is well-regarded due to its great flavour and later bloom time which makes it more tolerant of late spring frosts.
Please Note: Since sweet cherries tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
History: Jalander is a little-known apple with a unique history. Eric Hambly, owner of Siloam Orchards, and his wife visited one of New York's experimental farm stations in the 1980s shortly before it shut down. Hundreds of newly developed disease-resistant apple varieties were slated for destruction, so the couple gathered as much material for propagation as possible and grafted the trees back in Ontario. In the end, five of these trees were chosen for their disease-resistance and taste. One of them was Jalander and it is Hambly's favourite apple among all disease-resistant varieties.
Why We Grow It: For those interested in growing truly rare and unique apples, check out Jalander! On top of its disease-resistance, this apple boasts a sweet-tart taste with character (according to Hambly), and is also crisp and juicy.
History: Not to be confused with Stembridge Cluster, Stembridge Jersey was introduced in Somerset, England, in the 1950s. To this day it remains a popular variety in UK cider orchards.
Why We Grow It: The good-quality bittersweet juice produced by this variety explains why it is still popular in the UK. Although Stembridge Jersey suffers from a tendency to only produce fruit every other year, it does produce good crops in those alternate years and is relatively disease resistant.
History: Brown's Apple was discovered in Devon, UK, in the early 1900s and is considered a traditional English cider apple. It remains quite popular in the area.
Why We Grow It: This traditional variety boasts cold-hardiness and a resistance to scab. It is great for making cider thanks to being simultaneously high in both acid and sugar, an uncommon feature in most apples. Brown's Apple presses to a fragrant, vintage quality juice.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
Species: Prunus persica
History: These peach seedlings are grown from peach seeds from the very trees we have in our orchards! The parents will be a mix of the Harrow Diamond, Redhaven, Reliance, Veteran, and seedling peaches from True Root Nursery.
Why We Grow It: Peach seedlings tend to stay fairly true to type so odds are you're going to get a pretty solid peach tree once they mature and it is hoped that growing them from seed here will make them a littler hardier! For those who prefer the certainty that comes with getting a named variety, these trees would also be great for grafting as rootstock, feeding wildlife, or planting along a fence line.
Species: Prunus avium
History: These seedlings are grown from seeds from Sandra Rose sweet cherries sourced in Ontario. Sandra Rose was developed at the Summerland Research and Development Centre in BC.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! Sandra Rose, the parent variety, produces large dark cherries with excellent flavour.
Please Note: Since sweet cherries tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
History: Nonpareil originated in France although no one is sure quite how old it is or what its exact origins are. We do know that it was brought over to England sometime in the 1500s where it gained more popularity due to its pear-drop flavour. It can still be found at markets, farmgate sales, and in gardens in England to this day and is believed to be the ancestor of the popular European variety Ashmead's Kernel.
Why We Grow It: Nonpareil is not much to look at with its dull yellow-green russet skin but it packs a flavourful punch: sweet-sharp with notes of pear-drops. The fruits hangs onto the tree well and stores for several months. It is mainly used for fresh eating but can be added to cider blends as well. The tree is naturally more compact and has moderate vigour.
History: Airlie's Red Flesh originated on the farm of Lucky and Audrey Newell in Airlie, Oregon who sold the property in the 1960s. Two decades later in the 1980s, a Louis Kimzey was walking through the old orchard, bit into an apple from the tree, and was amazed at its stunning pink flesh. This was also known as Newell-Kimzey to reference those who found it and Airlie's Red Flesh as a reference to its place of origin and pink flesh. It also goes under a separate brand name.
Why We Grow It: This small, slightly conical apple has yellow skin that belies a bright pink interior that whitens near the core. Not only is it pretty, the fruit has a very sweet flavour with some mild astringency and the flesh is slow to brown. Along with the attractive fruit, the tree boasts bright pink blossoms that gives it an extra ornamental appeal.