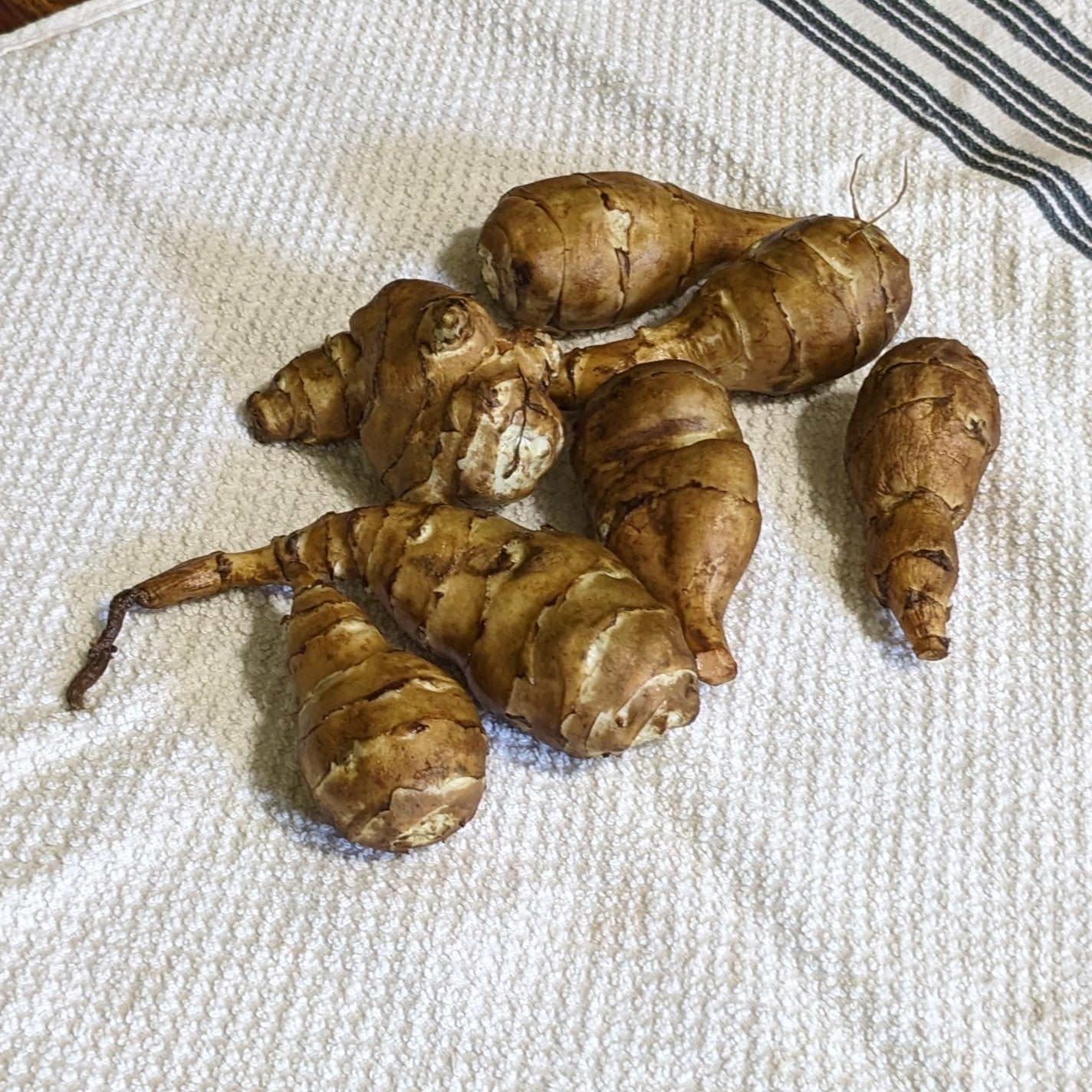All Zone 5 (or hardier) Plants
Sort by:
379 products
379 products
History: Noël des Champs (translated from French as 'Christmas Field') emerged in the Normandy region of France in the 1800s. It has remained a well-regarded apple and is one of thirteen apples prized for cider production in the Pays d'Auge region.
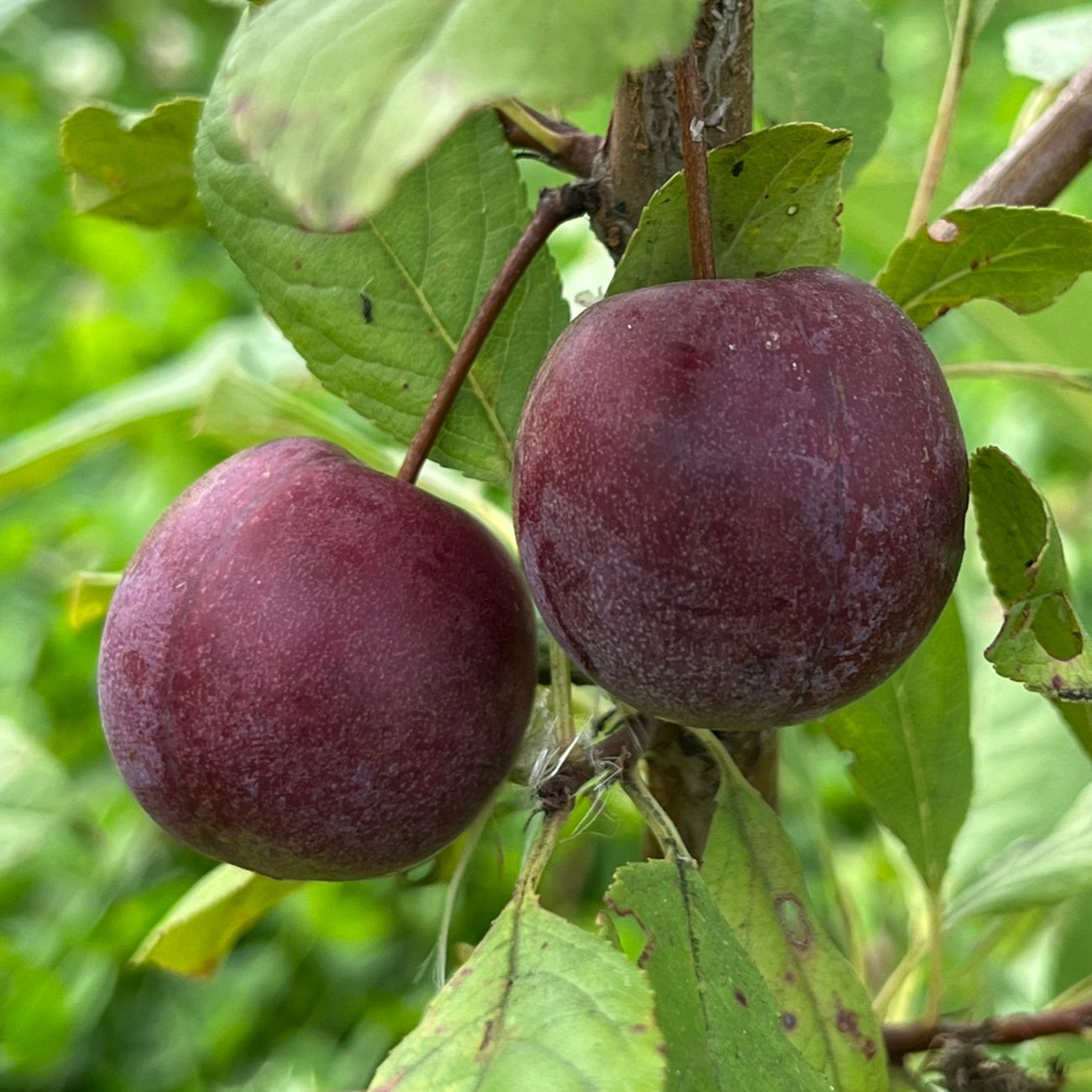
Why We Grow It: This rare cider apple is bittersweet with small, flattish fruits. They are dark red with some striping. As its prestige suggests, this is a good quality cider apple. The tree tends to start bearing fruit at a young age.
Species: Asparagus officinalis
History: The parent of these seedlings, Precoce d'Argenteuil (translated from French as 'early Argenteuil'), is an heirloom French variety that has been grown since either the 1700s or 1800s depending on the source. It was first listed in 1885 and is a selection from the Giant Dutch Purple variety of asparagus, along with the middle and late Argenteuil varieties which were all likely named after the commune in Paris. It is still commonly used in French dishes to this day. The variety is also sometimes called White Gold if grown without exposure to light, causing the plants to remain white. These seedlings may vary from their parents but should bear similar traits!
Why We Grow It: We love offering seedlings as a way to add some diversity to the plants being grown! The parent variety Precoce d'Argenteuil may not be as productive as modern varieties, but its excellent flavour more than makes up for it! Living up to its name, this variety produces thick shoots quite early in the season as well.
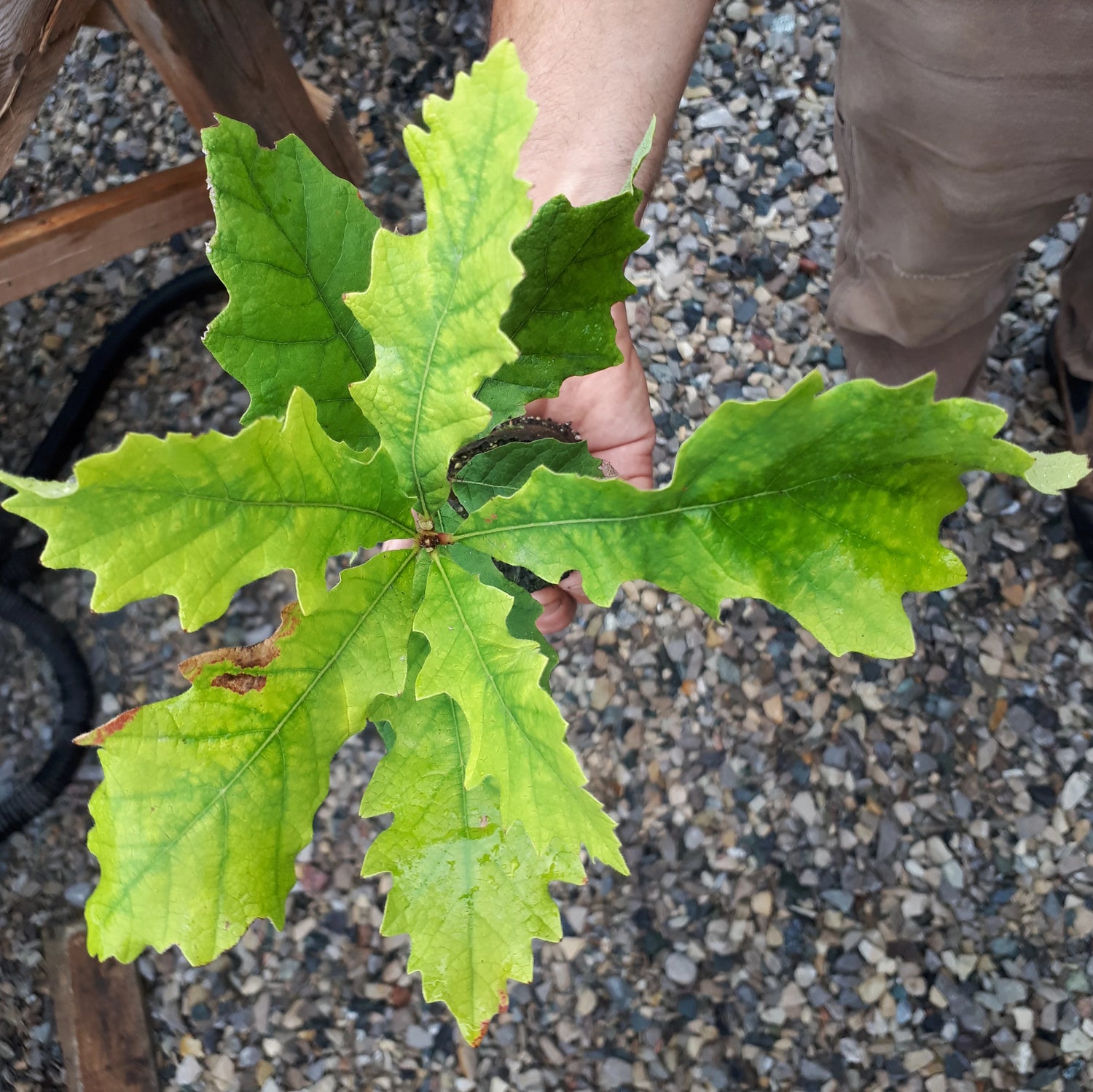
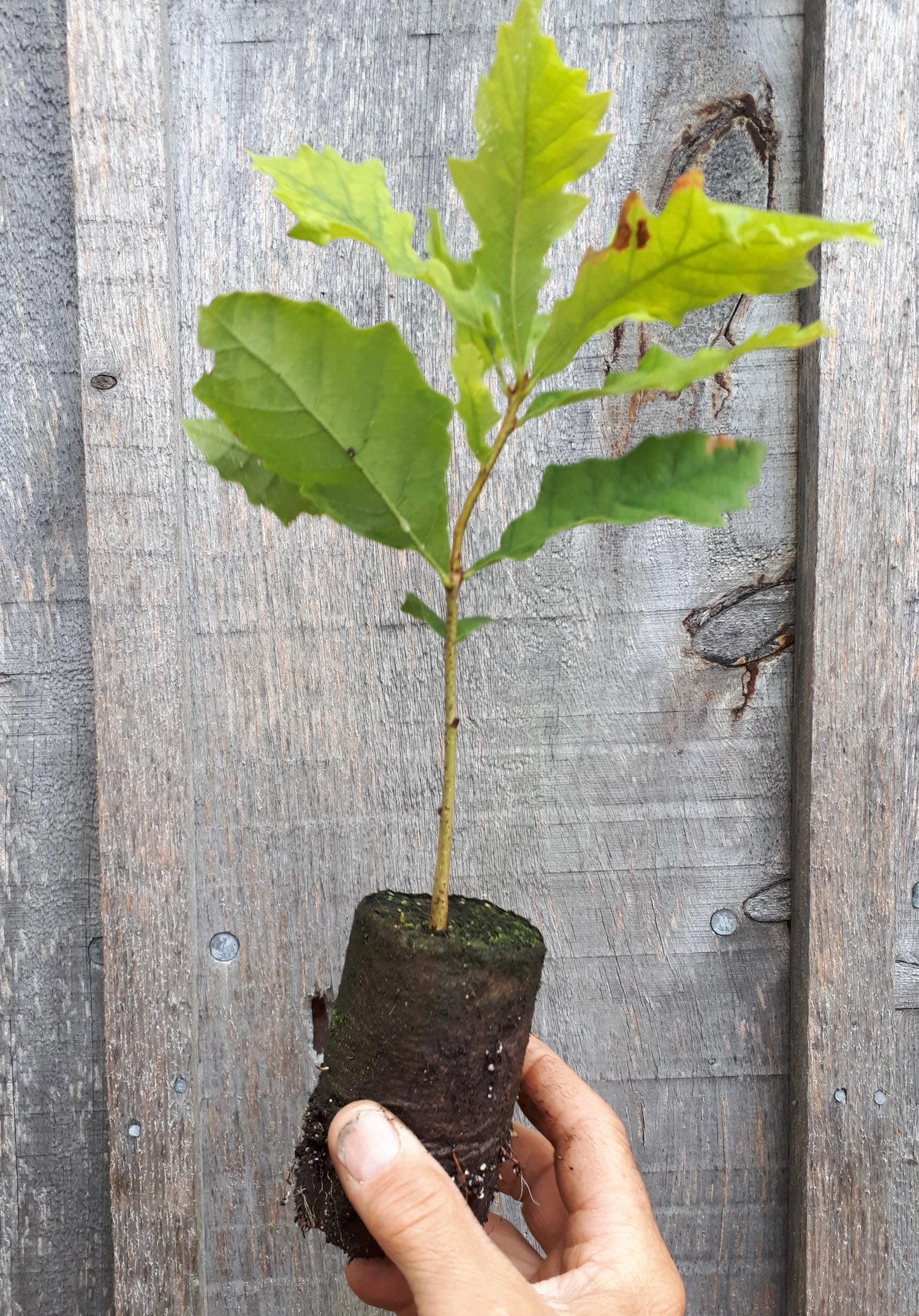
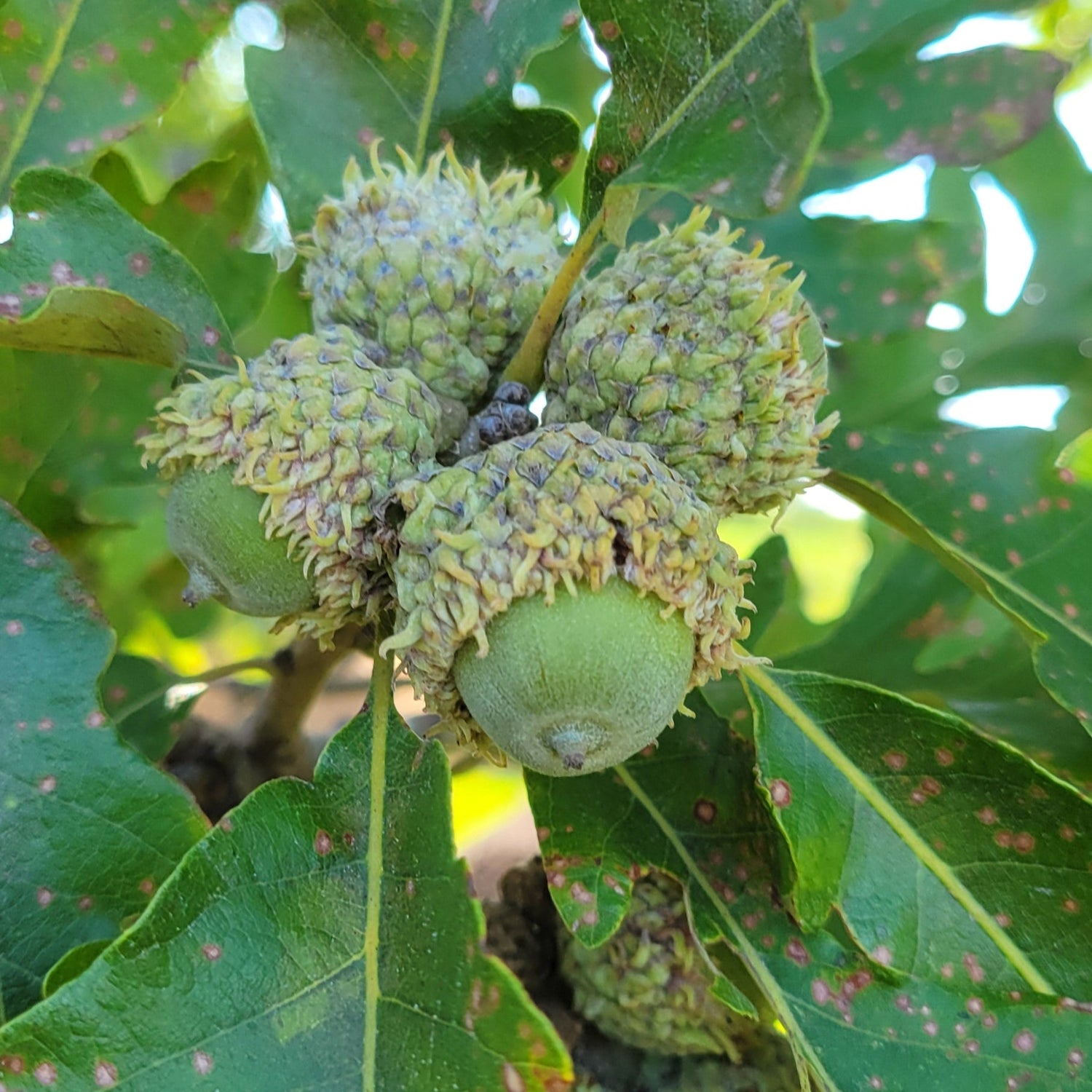
Species: Quercus macrocarpa or hybrid. Our seeds are collected from trees that may have been cross-pollinated by closely related species so the resulting seedlings may be hybrids.
History: Burr Oaks are native to much of the central United States with populations in Canada stretching from Alberta to New Brunswick. The tree has been planted ornamentally across North America and the durable wood has uses such as flooring and barrels. The acorns, the largest in North America, are a source of food for many animals and indigenous peoples use the bark medicinally. Numerous towns and a book of poetry are named after this tree.
Why We Grow It: The Burr Oak's acorns have slightly less tannins than other oaks, making it the preferred choice for eating. It still requires processing to remove tannins, but once done, the nuts can be toasted, and/or made into flour and used in baking. It is one of the largest oaks in North America, making quite the specimen when full grown.
History: Parkland apples were variety created at the Morden Research and Development Centre in Manitoba and released in 1979. Like other varieties developed there, Parkland was designed to withstand the harsh prairie winters and is especially cold hardy. It has become the most commonly grown apple in Alaska after it was brought over in 1985 in an effort to determine which Canadian varieties could survive in the northern state.
Why We Grow It: Parkland is a very satisfying early season apple - sweet and crunchy. It's excellent snacking or applesauce although the fruit is small (about 2" diameter) with creamy flesh and red skin. The tree is quite hardy.
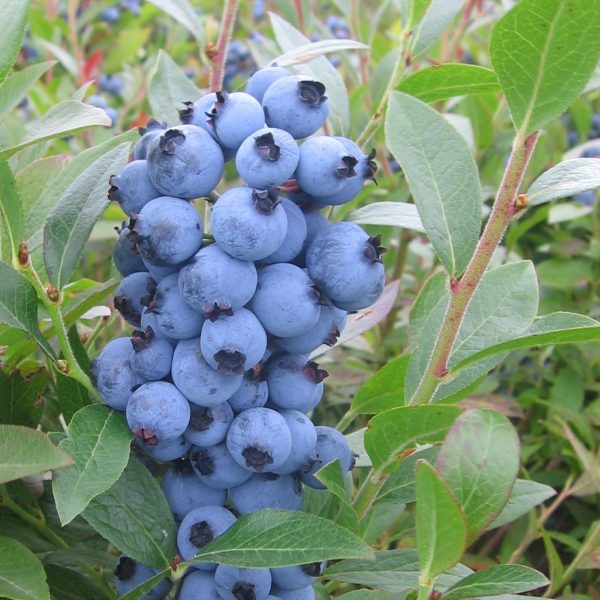
Species: Vaccinium corymbosum, hybridized with V. ashei and V. darrowi
History: Draper blueberries were developed at Michigan State University by renowned plant breeder James Hancock who has also developed several other notable blueberry varieties and other fruits such as the Redhaven peach. He worked with Arlen Draper, a blueberry breeder from the US Department of Agriculture, for 14 years to breed and test different varieties for commercial use, picking Draper due to its many excellent qualities. Named for Arlen Draper, this variety has quickly become an extremely popular commercial variety due to the size and quality of the fruit.
Why We Grow It: Draper produces large, firm fruit with an excellent sweet flavour. They are great for eating fresh or can be used in baking, jams, etc like other blueberries! The large size of the berries makes them good for u-pick orchards and the bushes stay slightly smaller than other highbush varieties! They also store better and longer than other blueberry varieties and ripen at the same time.
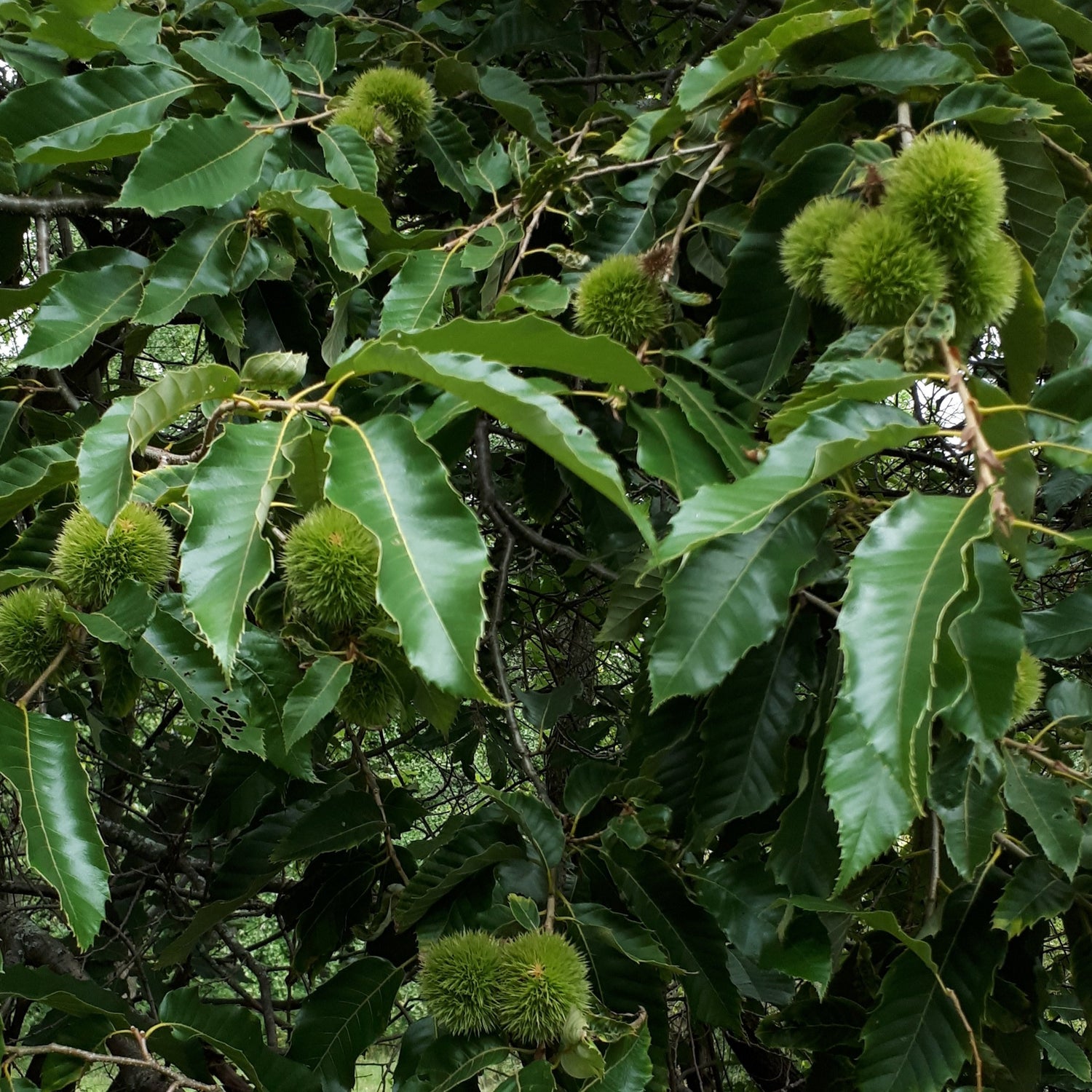
Species: Castanea dentata x mollissima
History: These seedlings are a cross between Chinese chestnuts and American chestnuts grown from seed from Grimo Nut Nursery. As a hybrid of Chinese and American chestnuts, these seedlings have blight resistance along with good cold hardiness.
Why We Grow It: This tree has incredible potential as a truly sustainable food source for humans. High in vitamins and starch, the nuts can be used to make a flour food staple, or pressed for oil to be made into bio fuel. For more inspiration and ideas in growing sweet chestnuts as a crop, we recommend the book Restoration Agriculture: Real-World Permaculture for Farmers by Mark Shepard.
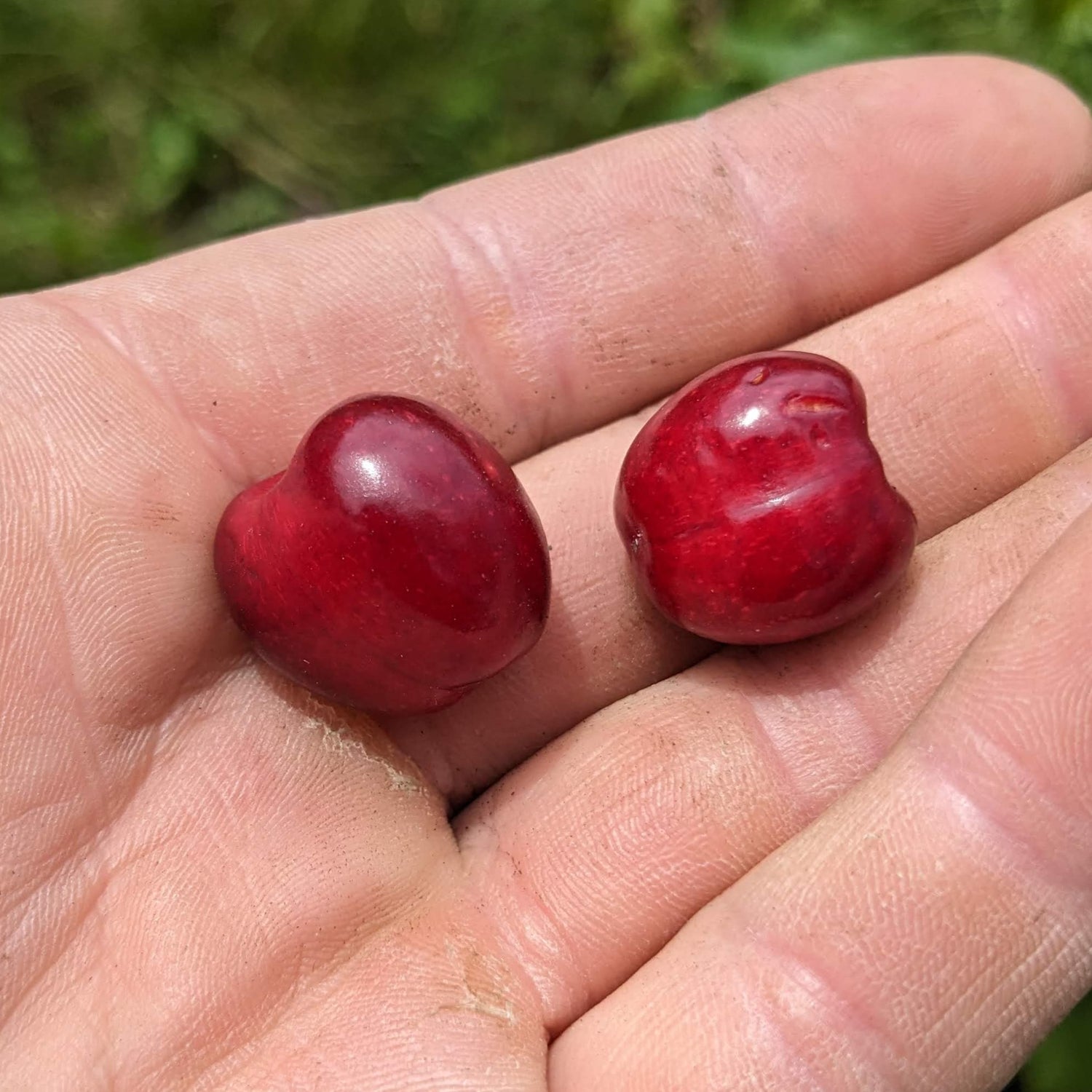
History: Bing sweet cherries originated near Salem, Oregon in 1875 as a cross between Black Republican and another sweet cherry variety. It was named after Ah Bing who worked as a nursery foreman for Seth Lewelling, the person who made Bing cherries into the top variety in the US. It is uncertain if Ah Bing himself developed the variety or if Lewelling simply named it after him as thanks for the 35 years he worked for him.
Why We Grow It: There are many reasons why this classic black sweet cherry has become the most commonly grown cherry in the US and the standard by which all other sweet cherries are measured. It produces large heart-shaped fruit with meaty purple-red flesh that is juicy and sweet. It has a semi-cling stone that is easy to remove, making it great for fresh eating and preserves. The tree is a heavy cropper, producing bountiful amounts of these lovely sweet cherries.
History: Redfree is one of the apples developed under the collaborative PRI disease-resistant breeding program run by Purdue University, Rutgers University, and the University of Illinois. It was bred in 1966 and officially introduce to the public in 1980.
Why We Grow It: Redfree apples are great for fresh eating with a pleasant, mildly sweet flavour and softer yet crisp flesh. The fruit does not ripen all at once, allowing a longer eating season. As its name would suggest, it has decent resistance to several common apple diseases.
History: Lady apples are one of, if not the oldest, apple varieties in existence with a verifiable history. It is said to have originated in the Brittany region of France before 1628 and was grown during the reign of King Louis XIII. This apple goes by several other names as well. It is also known as Api or Pomme d'Api, named after the Forest of Api in France where it is believed this apple may have been discovered. This particular name is similar to Appia, an apple variety popular in Ancient Rome, which some believe is the same apple as Lady. Lady apples are also known as Christmas apples due to their use in adorning Christmas wreaths and trees.
Why We Grow It: It's hard not to be interested in an apple with such a long history as this one. The fruit is small but attractive: red flushed over yellow. The crisp, sweet fruit maintains its good quality all winter in storage.
History: Wagener apples come from a seed that was planted by George Wheeler in the Finger Lakes area of New York in 1791. In 1796, Abraham Wagener purchased Wheeler's property and planted the seedling on his own property in Penn Yan village where the tree was known for producing attractive, tasty fruit in abundance every year. The variety was named after Wagener and became popular for its excellent storage qualities.
Why We Grow It: Wagener is ideal for the self-sufficient homesteader who values a late keeper, lasting until April in an ordinary cold cellar. When first picked they have a sharp, acidic taste and are great for cooking. In storage, they mellow to an excellent sweet, crisp apple that is perfect for fresh eating.
History: Shizuka (translated as "quiet" or "calm") was created at the Aomori Apple Experiment Station in Japan in the 1930s. It is a cross between Golden Delicious and Indo, the same parentage as its sister apple Mutsu.
Why We Grow It: Although it resembles Mutsu with its large yellow-green fruit, sometimes featuring a reddish-orange blush, Shizuka is sweeter and less acidic. This is an excellent fresh-eating apple for farm gate sales and it also keeps well. It is also great in salads due to its slow browning.
History: Meigetsu is an Asian pear that originated in Japan. The word 'meigetsu' roughly translates to 'beautiful moon' or 'grand moon.' Its name could also be a shortened version of 'Chushu no Meigetsu,' the Japanese name for the harvest moon in September.
Why We Grow It: Meigetsu Asian pears are pleasantly sweet with the flavour and aroma being compared to pineapples, watermelon, and butterscotch. The flesh is somewhat softer than other Asian pears, making the texture more akin to that of European pears.
Species: Helianthus tuberosus, Sunchokes are also known as Jerusalem Artichokes or J Chokes
History: Little is known about the origins of Clearwater aside from the fact that it originated in Maine, possibly as a wild plant found in 1988.
Why We Grow It: Clearwater produces smooth, white tubers with a mild flavour that some say borders on sweet. This is a productive variety and the smoothness of the tubers generally makes them easier to clean. Sunchokes can be prepared and eaten in much the same way potatoes can, making them a very versatile food.
History: Harlayne apricots were developed at the Harrow Research and Development Centre in Ontario and released in 1980. It is one of several specifically bred to survive in a southern Ontario climate and of the Harrow apricots it was the most cold hardy.
Why We Grow It: Harlayne is a cold hardy variety that can tolerate temperatures of -30°C. It is a medium-sized apricot and freestone. The skin is a bright orange with an attractive red blush and the flesh is sweet, making it great for fresh eating along with canning or preserving. Unlike most of our apricots, Harlayne requires a pollinator.
History: Westland apples were developed at the Alberta Special Crops and Horticultural Research Centre in Brooks, Alberta and introduced in 1979.
Why We Grow It: This medium sized pie apple is cold hardy, excellent for the prairies and northern regions. The fruit is large and a pale yellow-ish green with red flush and stripes.
History: This cold-hardy apple was developed in the prairies and is for growing in colder, northern areas.
Why We Grow It: This unique apple produces a yellow fruit with red stripes. It is a rather uncommon variety and is great for sauce. It has begun producing reliably in our test orchard the last few years, and always has a bountiful crop.
History: This heirloom sweet cherry originates from Arkona, Ontario where it was developed and grown by Ed Richter.
Why We Grow It: As an Ontario bred and raised sweet cherry, Richter cherries are well-suited to growing in our local conditions. We were fortunate to acquire this variety just before the removal of some very old Richter trees.
Special Note: We take special care to grade out (remove) any of these seedlings that are showing visible thorns when we dig them in the fall. This increases the likelihood (although we cannot make any guarantees) that you will not have thorns develop on your Thornless Honey Locust Seedling. If you don't mind thorns on your Honey Locust, the ones we grade out are available here at a lower pricepoint.
Species: Gleditsia triacanthos
History: Thanks to its ability to tolerate a host of adverse conditions that would hinder or kill other trees, Honey Locusts have been cultivated for us as ornamental, urban trees. As a result, several thornless varieties have been developed including the mother tree for these seedlings.
Why We Grow It: Honey Locust has many benefits for permaculture and now growers do not need to worry about popping tires with thorns thanks to these thornless trees - though they are seedling so some may develop thorns though most will not; these can be top grafted with a thornless type if needed. Reaching 30 meters tall, this native nitrogen fixing tree benefits many including bees, wildlife, and even humans: we can use the sweet (honey flavoured) pulp inside their pods in baking, tea or for brewing beer. The durable, rot-resistant wood has a variety of uses.
History: Norhey comes from the Morden Research Station, Agriculture Canada. It was created by Dr. C. R. Ure in the 60's to survive the harsh prairie winters. It was introduced in 1975.
Why We Grow It: It seems Dr. Ure was successful since this is about the hardiest apple we've come across. The fruit has green skin that turns yellow after picking. It's fair for fresh eating, good for cooking and juicing with sweet, sub acid flavours and creamy crisp flesh. The tree has consistent, heavy crops.
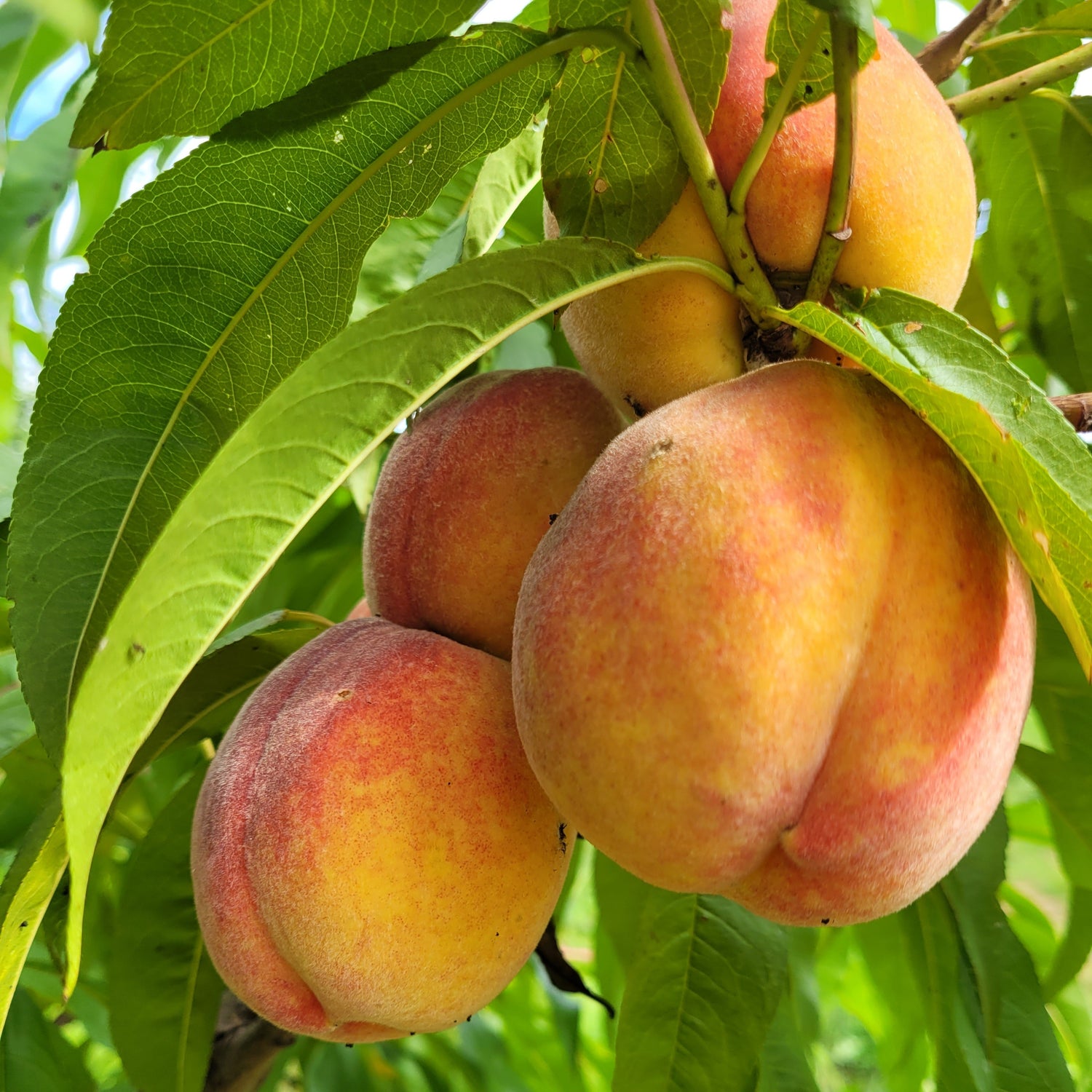
Species: Prunus persica
History: These seedlings are grown from Redhaven peach seeds collected from mother trees growing in Ontario. Redhaven was released from Michigan State University in the 1940s and has remained one of the most popular peach varieties in the world.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! We expect that seedling peaches will be even hardier trees than their parents! Redhaven has a stellar reputation due to its excellent flavour and attractive red skin. See our Redhaven product page here for more information.
Please Note: Since peaches tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
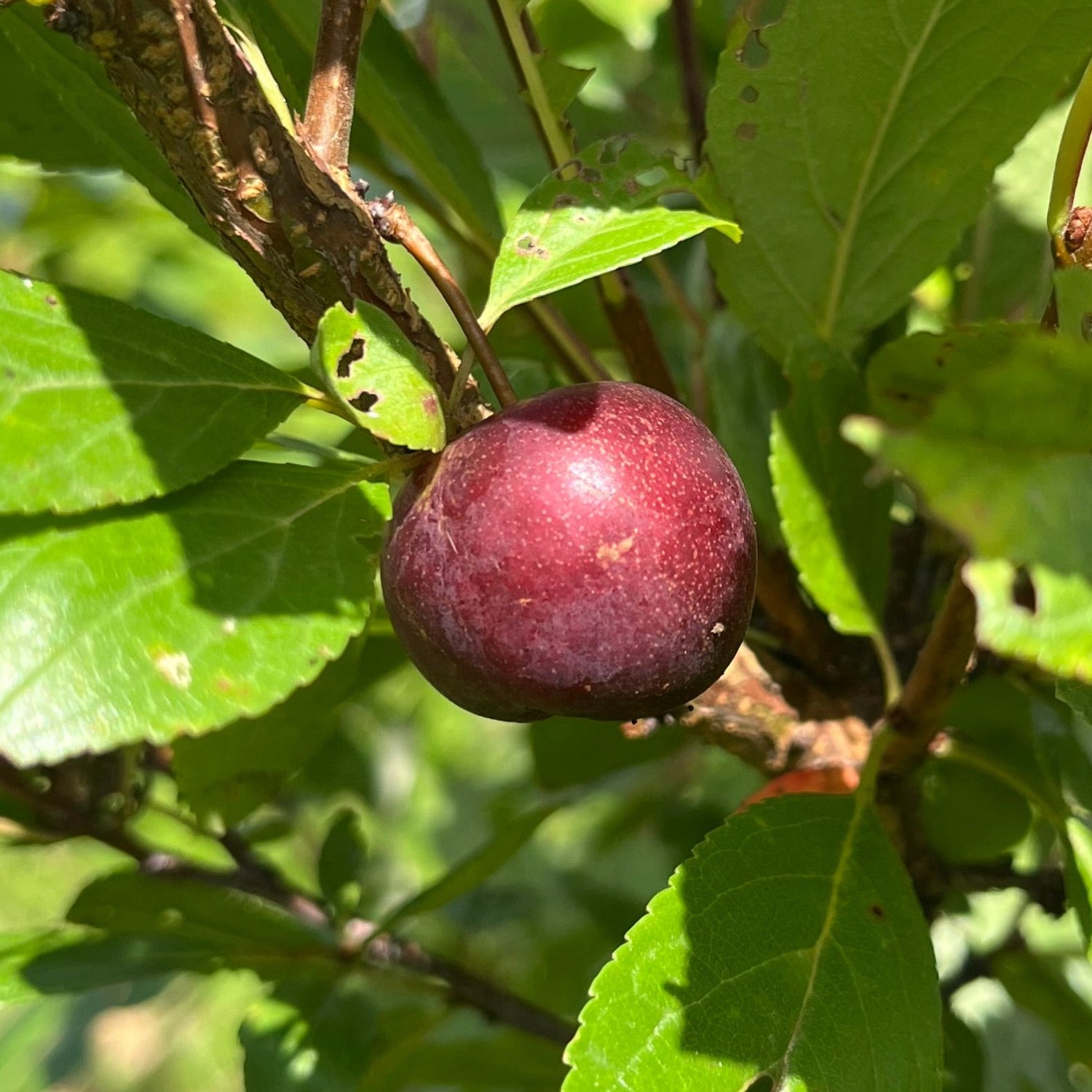
Species: Prunus pumila var. besseyi (Western sandcherry) x P. salicina (Japanese Plum)
History: Manor was developed at the Morden Research Station in Manitoba and released in 1945.
Why We Grow It: Manor produces a small plum with skin that is nearly black when ripe and purplish-red flesh. When ripe, the fruit is quite sweet and good for fresh eating! Some prefer to pick it when it is still a little unripe and a bit firmer since it is more astringent and lends itself well to uses such as baking, preserving, and making wine. The shrub stays smaller than other chums but starts bearing fruit at a young age and is known for being quite productive.
History: Vista Bella was created at Rutgers University in New Jersey in the 1950s and released in 1974. Although its poor keeping ability prevents it from being a commercial success, this early ripening variety is still a nice way to herald in the apple harvest season every year.
Why We Grow It: Vista Bella is the first red apple of the season. The flavour and texture are of better quality than other early apples, making Vista Bella an excellent choice for early farmer’s market sales and roadside stands. The flesh is crisp and juicy, although it softens quickly and, like other early apples, does not keep long.
Species: Alnus incana (likely subsp. rugosa)
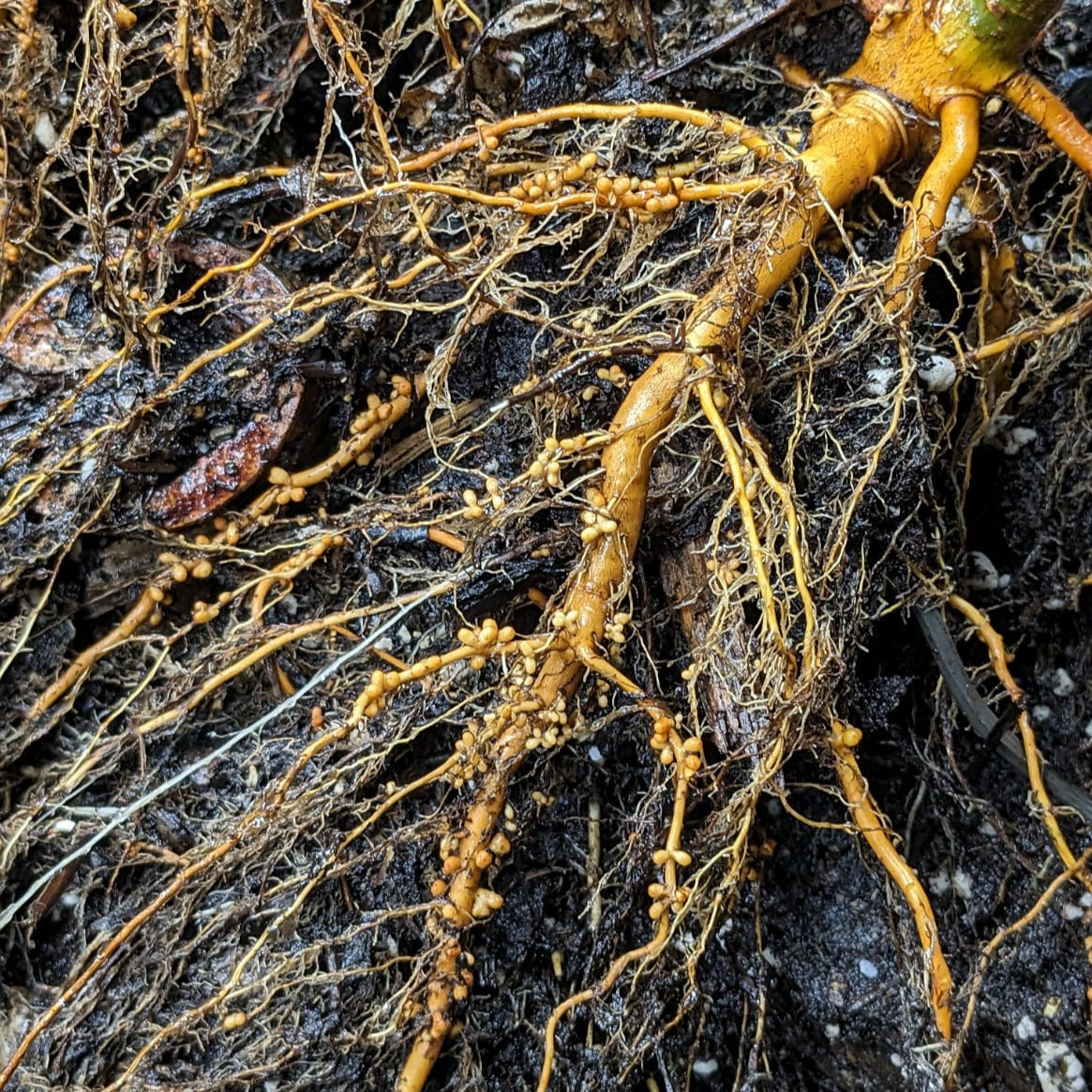
History: Native to large portions of the Northern Hemisphere including parts of North America, Europe, and Asia, this widespread tree is often divided into six subspecies. We likely offer Alnus incana subsp. rugosa but with seedlings it is hard to say for sure. Indigenous people have used these trees for medicine and dyes, and they can also be used for erosion control. This subspecies in general is unique for its cold hardiness and ability to fix nitrogen, making it a useful companion plant in permaculture settings.
Why We Grow It: Named for the white lenticels that dot the reddish-gray bark, Speckled Alders can make a useful addition to a permaculture with their ability to fix nitrogen. However, keep an eye on this tree as it tends to spread via suckering (sending up new shoots) and layering (branches rooting into the ground) and can form dense thickets.
Species: Prunus pumila var. besseyi (Western sandcherry) x P. salicina (Japanese Plum)
History: Sapa (translated as 'black' from Lakota) was developed at the South Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station in the US by renowned plant breeder N. E. Hansen and released in 1908. His goal was to create plants hardy enough to grow in the harsh, northern prairies and was one of the first people to start breeding chums. Hansen had a tendency to name his native plant crosses after words from indigenous cultures of the area, choosing the Lakota word for 'black' in this case due to the dark colour of the fruit.
Why We Grow It: This small, hardy shrub produces purplish fruit with mauve flesh that has a sweet flavour with some tartness. It is good for fresh eating along with a variety of other uses such as cooking, baking, and preserving. It is also quite productive and tends to start bearing fruit at a young age!
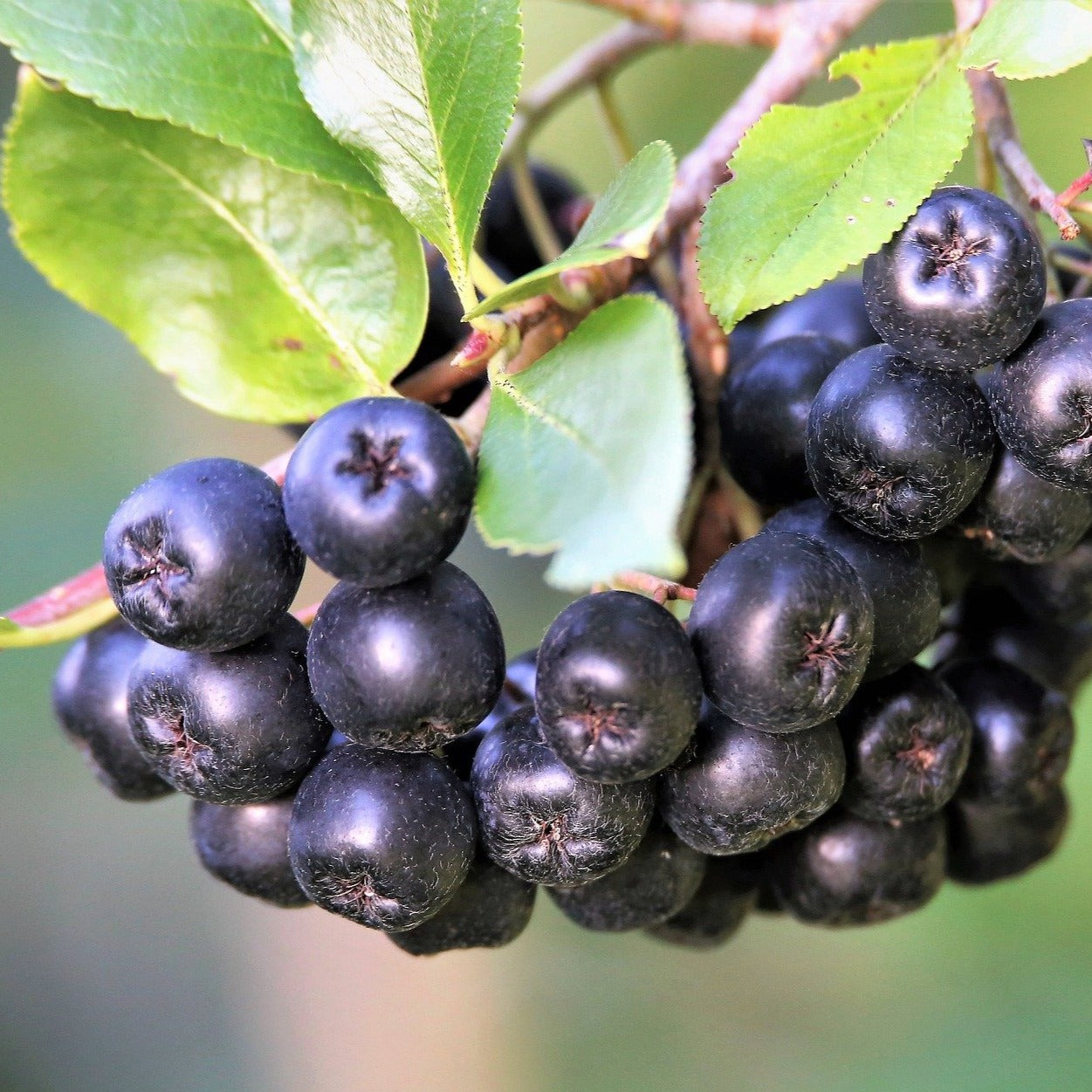
Species: Aronia melanocarpa
History: Galicjanka was developed in Poland where Aronia berries are a common agricultural crop. It is one of the most popular varieties grown there due to its suitability for commercial plantations.
Why We Grow It: This variety produces large berries with good flavour. While the berries ripen in August, they can hang onto the bush for a couple months and tend to sweeten over time. Despite its popularity in Poland, it is unfortunately not very common in North America.
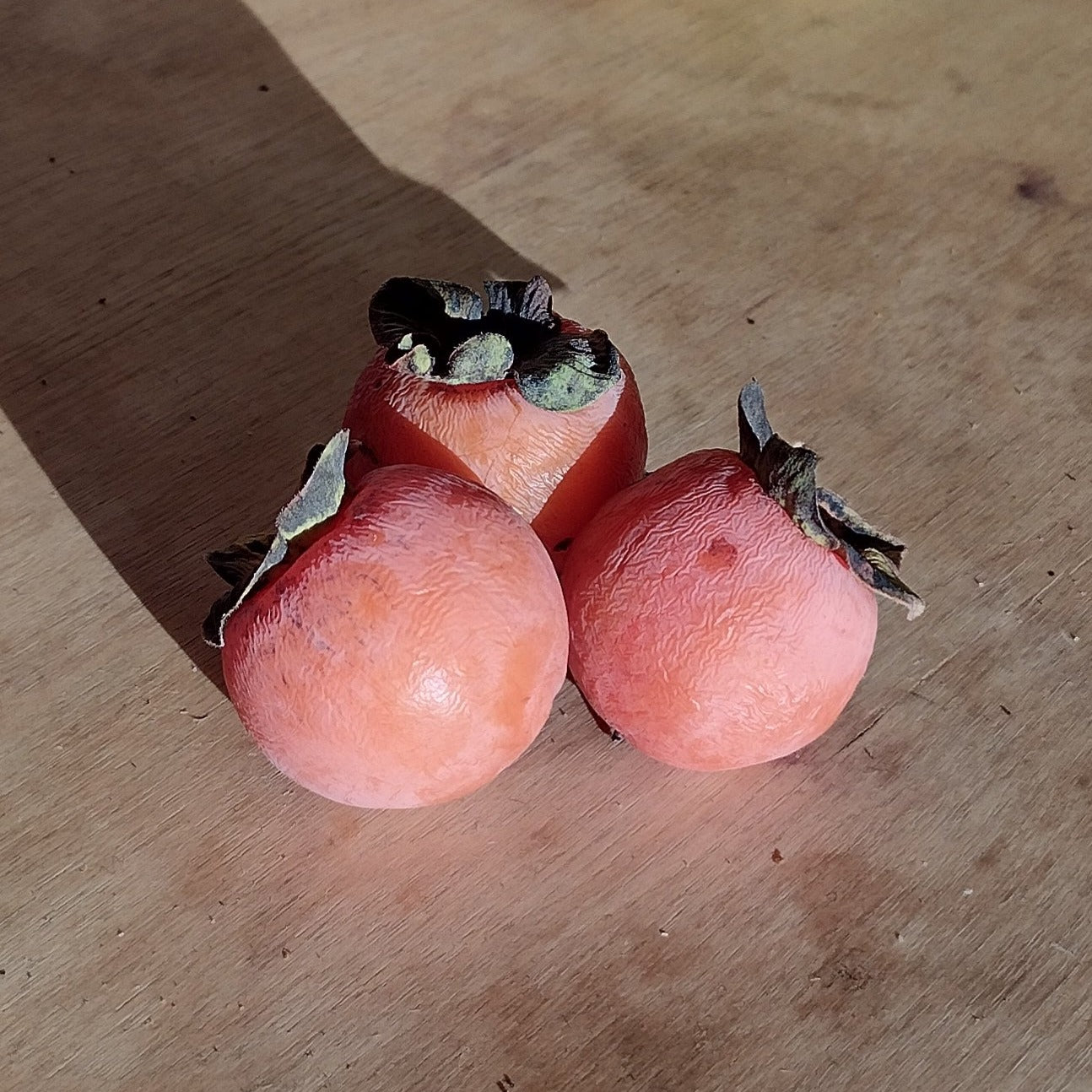
Species: Diospyros virginiana
History: Native to the southeastern and central areas of the United States, American Persimmon has had a long history of cultivation. The word 'persimmon' is an Anglicized version of the words 'putchamin,' 'pasiminan,' or 'pessamin,' which all mean 'dried fruit' in various Algonquin dialects, reflecting the fruits' usage. It is also common in southern states to trick the unwary into eating the unripe fruit which has an incredibly astringent flavour. Other historical uses for the American Persimmon include turning the seeds into buttons during the American Civil War and using the wood to make items such as pool cues and golf clubs.
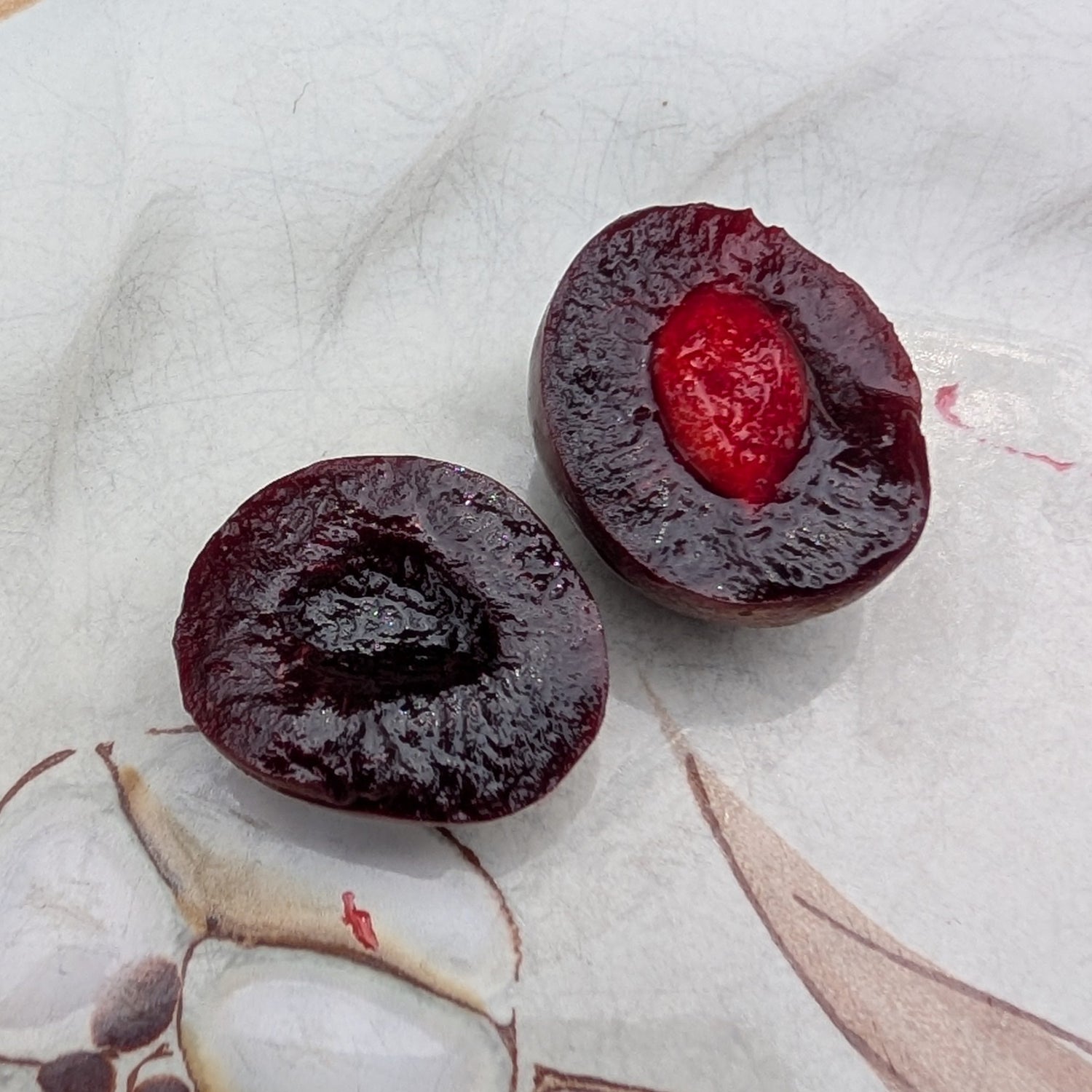
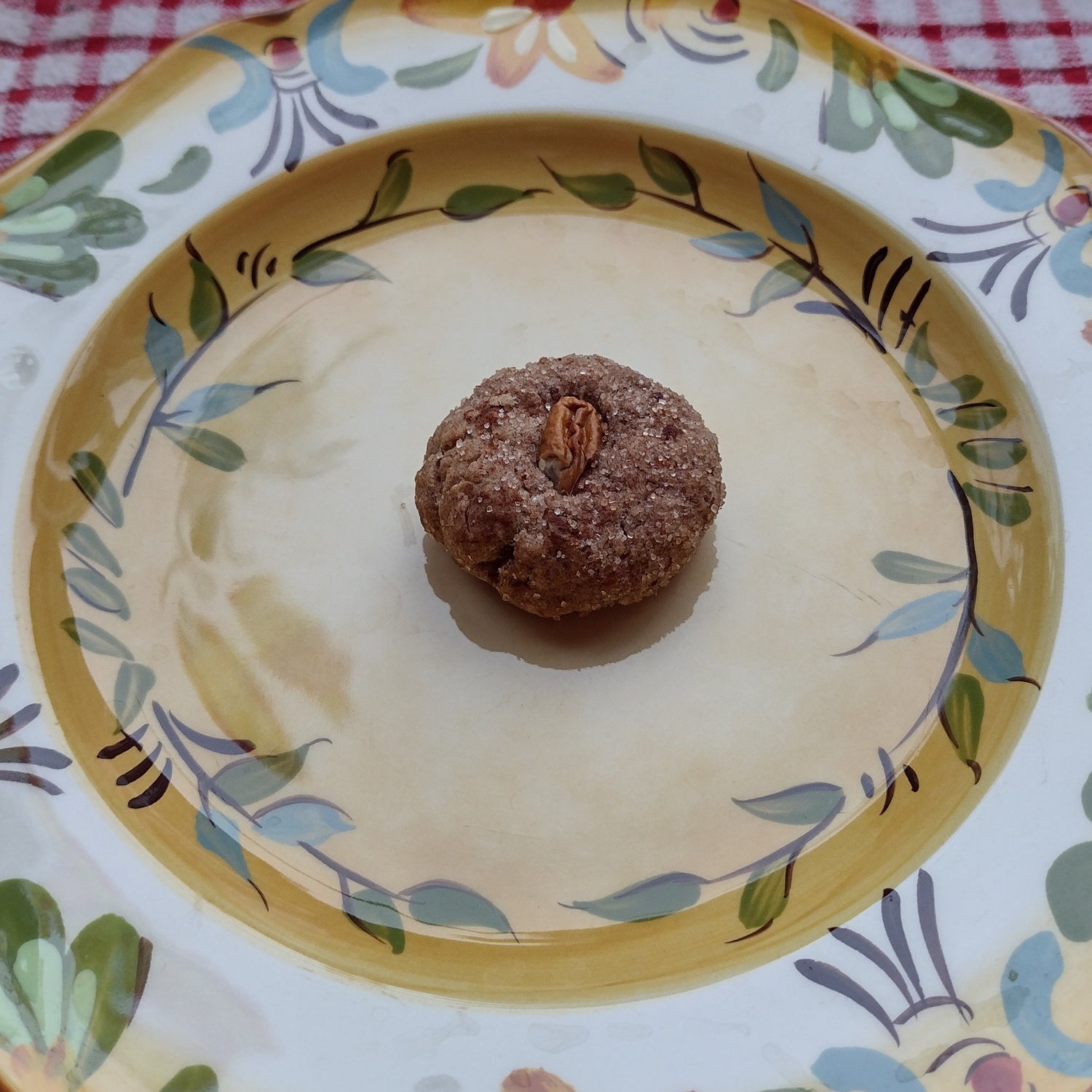
Why We Grow It: This unique fruit tree produces a succulently sweet orange fruit that must be extremely ripe before you can eat it. Although it ripens in the summer, the fruit can withstand freezing and hang onto the tree until December. The fruit can be used to make a variety of sweet and savoury dishes and are also very popular among wildlife. Steph has found them great for baking into sweets such as tarts or the pecan and persimmon cookies pictured here!
Pictured is a cookie made with our own American persimmons and pecans!
History: Domaine apples originated in France some time before the 1900s. In the Pays d'Auge region in Normandy, Domaine is one of the 13 cultivars prized for making hard cider (included in that 13 are Fréquin Rouge and Noël des Champs, which we also have available). This apple was brought to the United States in 1949 but remains relatively unknown outside of its country of origin.
Why We Grow It: This bittersharp cider apple is high in tannins and acid but low in sugar. Although not great for single-variety ciders, it can be an excellent addition when used in cider blends.
Why We Grow It: Another successful introduction from the PRI breeding program, Priscilla boasts resistance to most common apple diseases including fireblight and scab. The fruit is also quite attractive with a deep red blush over yellow skin with a sweet and subacid flavour.
History: White Jersey is another English cider apple whose origins are a little obscure. It was popular in the Somerset area of England during the 1800s where it was first recorded in 1895. It is still grown in modern cider orchards in the UK today.
Why We Grow It: Although it has been deemed an apple with 'average quality juice,' White Jersey is still worth checking out if you are interested in cider making. It does well in the Great Lakes area and it compensates for its average juice quality with good productivity and a tendency to start bearing fruit early.