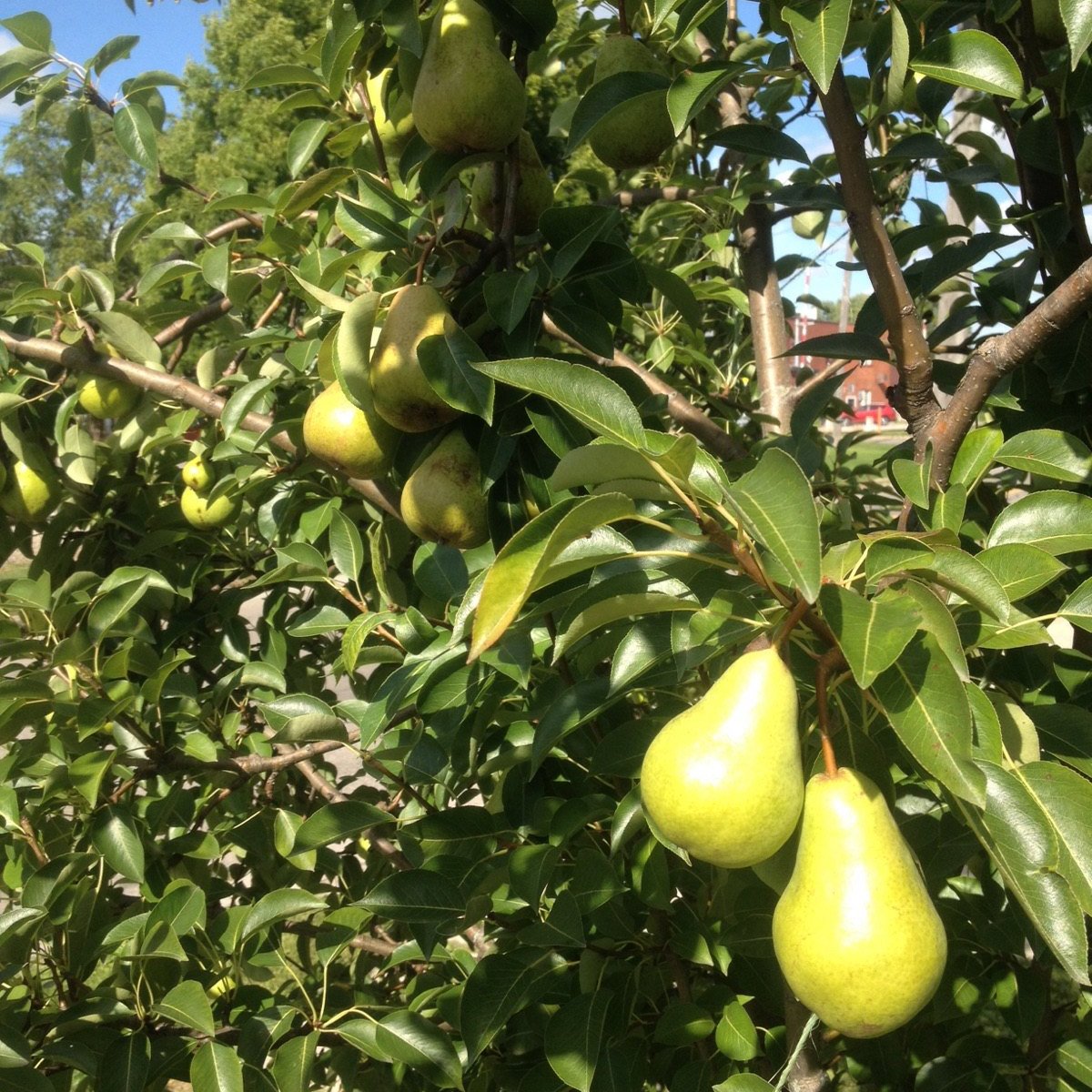
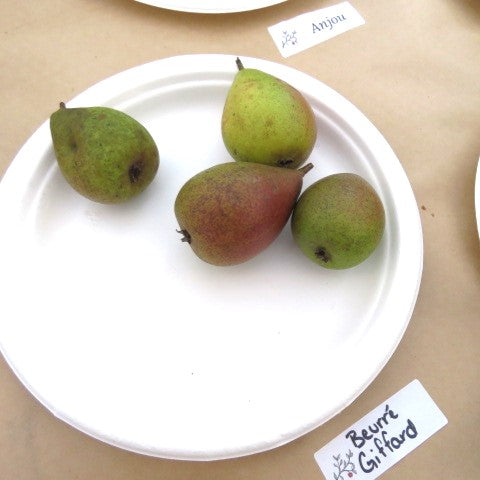
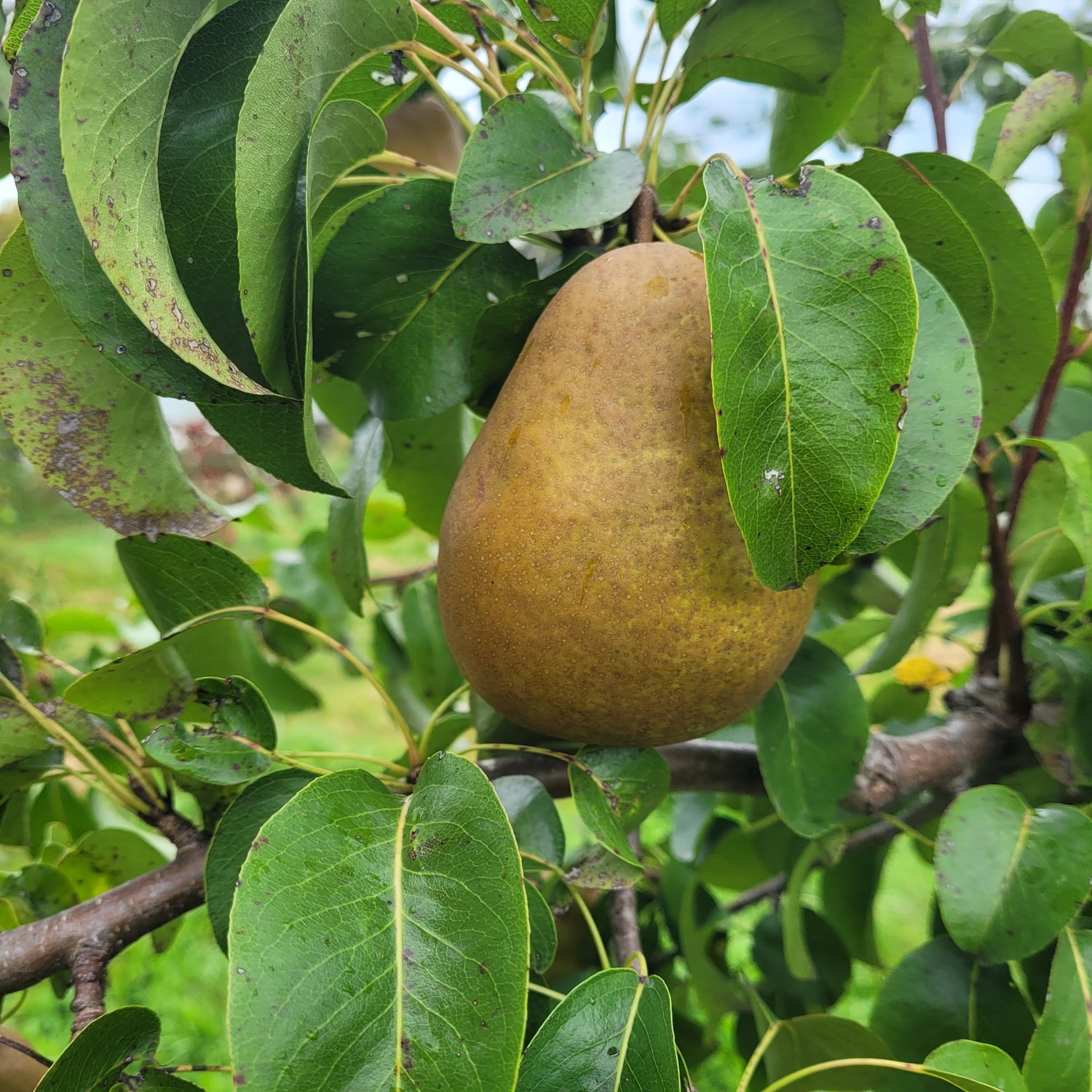
Pear Trees
European Pear Trees
Pyrus communis
A pear tree is an excellent addition to the backyard or orchard. Although slow to start bearing, pears are hardy and reliable producers requiring less attention than other types of fruit trees. Each of these varieties requires a pollinator.
Asian Pear Trees
Pyrus pyrifolia
Resembling their more-familiar European cousins, Asian pears are distinct in their texture and mild flavour. The fruit is often larger, and sometimes round in shape like an apple. Each variety requires a pollinator.
Sort by:
33 of 44 products
33 of 44 products
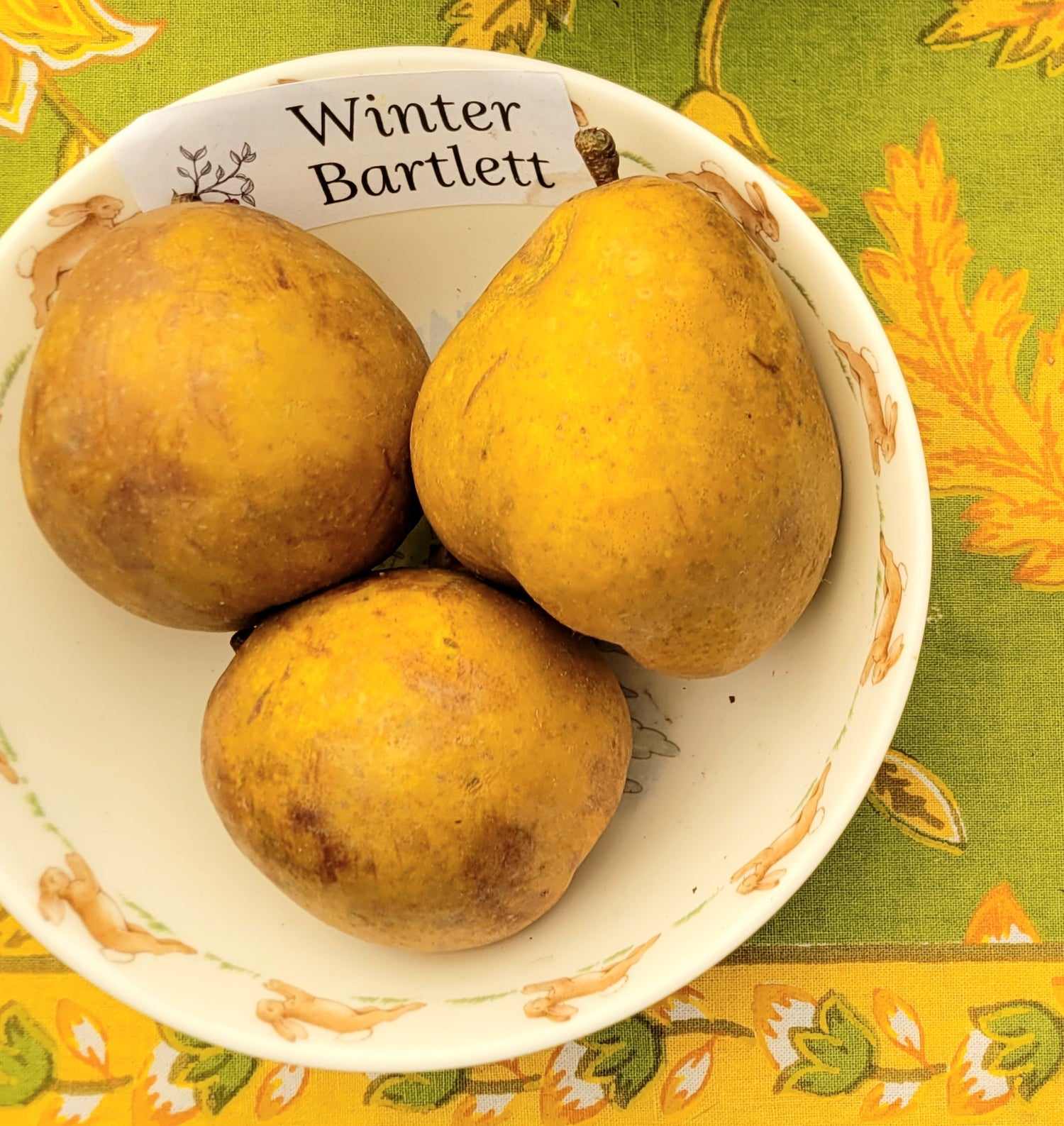
History: Winter Bartlett pears originated on the western coast of the United States, likely in Eugene, Oregon. They were introduced by D.W. Coolidge in 1880 but it is believed the variety may have existed for some time before that. It earned its name from it's resemblance to the Bartlett pear in taste and shape and it's designation as a winter pear.
Why We Grow It: As opposed to summer pears which are meant to be eaten shortly after picking, winter pears are supposed to be allowed to ripen for months in cold storage and enjoyed during later seasons. It is worth the wait for this variety, which produces a medium to large fruit with golden-yellow skin covered in patches and dots of russet and red streaks. It has a sweet and slightly subacidic flavour paired with firm, coarse, juicy white flesh. It is also great for cooking.
History: Although its exact origins are unclear, it is believed that Barland comes from Bosbury in England. It was already well known by the late 1600s and its perry was believed to have medicinal properties. This perry pear has stood the test of time and is still widely grown in the UK.
Why We Grow It: Barland remains one of the most popular perry varieties. This bittersharp perry pear can be made into a good single-variety perry or added into blends.
History: Gin pears were first recorded in England in 1886. It was said the perry made from this pear had a juniper flavour, hence the name 'Gin.' It it still quite popular in parts of England.
Why We Grow It: The small fruit of this pear are used chiefly for perry, producing a good quality juice of medium tannins and acidity. The harvested fruit can be kept up to a month until pressing.
History: Little is known about this variety aside from the fact it originated in France and was widely grown in Austria. It has historically been popular in both countries. Its name translated from German means Normandy Cider Pear, which may point to its place of origin or at least where it was most popular in France.
Why We Grow It: Normannischen-Ciderbirne produces small, russeted pears that are a greenish-yellow. The fruit produces high quality juice for perry.
History: Winnal's Longdon was raised by a Mr. Winnall in the parish of Weston-under-Penyard, a village in England, around 1790. Despite being named after Winnall, Winnal's Longdon is now commonly spelled with only one 'L' after it was recorded incorrectly in the 1920s. This pear is still grown in small quantities in England.
Why We Grow It: This old English variety is a high quality perry pear. It was blended with Hendre Huffcap to form a perry which won the Long Ashton Perry competition many years in a row. The tree is known for its vigorous growth, heavy crops, and high resistance to scab which make it quite suitable for organic production.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Anjou is an older variety of pear that likely originated in France or Belgium in the mid-1800s. They were originally called 'Nec Plus Meuris' but at some point adopted the name Anjou (or d'Anjou or Beurre d'Anjou) after the French region when introduced to England or the US. Anjou pears are still quite popular and are one of the most commonly grown pears in the United States.
Why We Grow It: Anjou is a popular pear due to its good eating quality and flavour. The skin is greenish yellow, and the flesh is firm and sports a hint of yellow. The fruit keeps well and the tree is vigorous and hardy.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Harrow Delight, as the name suggests, was introduced from the pear breeding program at the Harrow Research and Development Center in Ontario in 1981. It is a cross between Bartlett and Purdue 80-51, making it a sibling to Harrow Sweet.
Why We Grow It: Harrow Delight pears are green with red blush when mature. They have sweet, juicy flesh and keep about a month. The tree boasts resistance to both fireblight and scab, making it a good option for anyone looking for a more disease resistant pear variety.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Ping Guo Li (translated from Mandarin as 'apple pear') was developed by Jilin Sheng in China and likely named for its round, apple-like shape. While its exact age is unknown, this pear is considered to be an old variety.
Why We Grow It: This Asian pear is nothing but sweet and juicy melting goodness! Its flavour is quite sweet and is comparable to that of a European pear. So far it has performed very well in our test orchard and displays good cold-hardiness.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Vicar of Winkfield was discovered growing as a wild seedling in the woods near Villiers-en-Brenne in France around 1760. It was originally named Curé (translated from French as 'priest') among other names but became known as Vicar of Winkfield when a vicar of the English village Winkfield named Rev. W.L. Rahm introduced the variety to England. It is a heritage cooking pear and can still be found in old French orchards today.
Why We Grow It: This long, yellowish-green pear is best known for its use in cooking and baking due to its uniquely dry flesh and more tart flavour. Vicar of Winkfield can be stored for several months and will develop a sweeter flavour over time. It is generally recommended to store the pear until after Christmas for fresh eating! The tree is vigorous and produces abundant crops.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Meigetsu is an Asian pear that originated in Japan. The word 'meigetsu' roughly translates to 'beautiful moon' or 'grand moon.' Its name could also be a shortened version of 'Chushu no Meigetsu,' the Japanese name for the harvest moon in September.
Why We Grow It: Meigetsu Asian pears are pleasantly sweet with the flavour and aroma being compared to pineapples, watermelon, and butterscotch. The flesh is somewhat softer than other Asian pears, making the texture more akin to that of European pears.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Mishirasu is an Asian pear from Japan.
Why We Grow It: Mishirasu is a popular variety since the fruit are extra large with a sweet, mild flavour and a nice crunch. The skin is brown and russeted, and the fruit have a roundish shape that is reminiscent of European pears.
Available only for pick-up at nursery.
History: Jules d'Airoles was first discovered by Leon Leclerc in Laval, France, in 1836. It was named after Jules de Liron d'Airoles, a notable French horticulturalist and pomologist. Confusingly, this pear shares its name with a Belgian variety grown about twenty years later by François-Xavier Grégoire-Nélis.
Why We Grow It: This pear develops in storage to a wonderful treat: very sweet and a touch tangy, semi-fine juicy flesh, with pleasant tannic notes depending on the terroir. Smooth, thick green skin with a lovely rose blush where the sun touches the fruit.
History: Barnet's history is somewhat of a mystery although we know it likely originated in Gloucester, England in the 1800s and was distributed by the Long Ashton Research Station in the 1900s. It is a traditional perry pear that is known by many names including Barn, Brown Thorn, and, adorably, Hedgehog. The last name is speculated to come from the fruit's resemblance to baby hedgehogs (aka hoglets) nestling in the grass.
Why We Grow It: Barnet produces small, brown russetted fruit that are quite juicy. The juice is quite mild since it is low in both tannins and acidity, making it a good choice for adding to perry blends. The ripe fruit is easily shaken from the tree for ease of harvest.
Collections
Pyrus pyrifolia
Asian pears are wonderful low maintenance trees! They are regular, prolific producers in our test orchards. Asian pears, sometimes called Apple Pears, are crunchy and sweet, with a mild flavour. While some pears are partially self fertile, we recommend planting at least two different cultivars for reliable pollination; European and Asian pears do cross pollinate.
Pyrus communis
A pear tree is an excellent addition to the backyard or orchard. Although slow to start bearing, pears are hardy and reliable producers requiring less attention than most other types of fruit trees. While some pears are partially self fertile, we recommend planting at least two different cultivars for reliable pollination; European and Asian pears do cross pollinate. Pears ripen from the inside out, and therefore typically should be picked when the fruit is still a bit hard. They then can fully ripen off the tree - especially important if it is a winter pear. A slight softening at the stem end will indicate the fruit ripe.
Similar to to cider apples, perry pears are pears that are best suited to making an alcoholic beverage known as perry or pear cider. While not a great option for fresh eating, many of the pears here are heirloom varieties that have stood the test of time for perry production. Pears generally require two varieties for pollination.
Juice Classification
- Bittersharp: acidity TA >4.5g/L, tannins >2g/L
- Bittersweet: acidity TA 2-6g/L, tannins >2g/L
- Medium: acidity TA 2-6g/L, tannins <1.5 g/L
- Sweet: acidity TA <2 g/L, tannins <1.5 g/L