Pear Trees
European Pear Trees
Pyrus communis
A pear tree is an excellent addition to the backyard or orchard. Although slow to start bearing, pears are hardy and reliable producers requiring less attention than other types of fruit trees. Each of these varieties requires a pollinator.
Asian Pear Trees
Pyrus pyrifolia
Resembling their more-familiar European cousins, Asian pears are distinct in their texture and mild flavour. The fruit is often larger, and sometimes round in shape like an apple. Each variety requires a pollinator.
Sort by:
20 of 34 products
20 of 34 products
History: Anjou is an older variety of pear that likely originated in France or Belgium in the mid-1800s. They were originally called 'Nec Plus Meuris' but at some point adopted the name Anjou (or d'Anjou or Beurre d'Anjou) after the French region when introduced to England or the US. Anjou pears are still quite popular and are one of the most commonly grown pears in the United States.
Why We Grow It: Anjou is a popular pear due to its good eating quality and flavour. The skin is greenish yellow, and the flesh is firm and sports a hint of yellow. The fruit keeps well and the tree is vigorous and hardy.
History: Bartlett pear, better known as William's Bon Chretien (translated from French as William's Good Christian) or William's pear in Europe, has a long history with unknown origins. What we do know is that in 1483 King Louis XI summoned holy man Francis of Paola to his deathbed and Francis offered the king a pear seed from his birthplace of Calabria in Italy. The name 'Good Christian' was given to the pear as a result. In 1799, this variety was brought to Roxbury, Massachusetts where it was planted and eventually renamed 'Bartlett' by Enoch Bartlett who was unaware of its origins. The mistake was not realized until 1828, by which time "Bartlett" pears were already popular in North America and the mistake could not be undone.
Why We Grow It: Bartlett is the most commonly grown pear in North America and with good reason. Not only is it productive and easy to grow, but it produces large yellow fruit with a delectable flavour.
Note: We graft our Dwarf Bartletts with an Old Home interstem to maintain compatibility between Province Quince rootstock and Bartlett.
History: Beurré Giffard was discovered as a chance seedling by Nicolas Giffard in 1825 in France. "Beurré" translates from French as "butter-like," referring to the smooth, juicy flesh that was typical of pears developed at this time in France and Belgium. It was later introduced to the United States in 1850.
Why We Grow It: This French heirloom pear is one of the earliest ripening pears we offer. Its sweet, melting yet crisp flesh is similar to Bartlett with an excellent flavour.
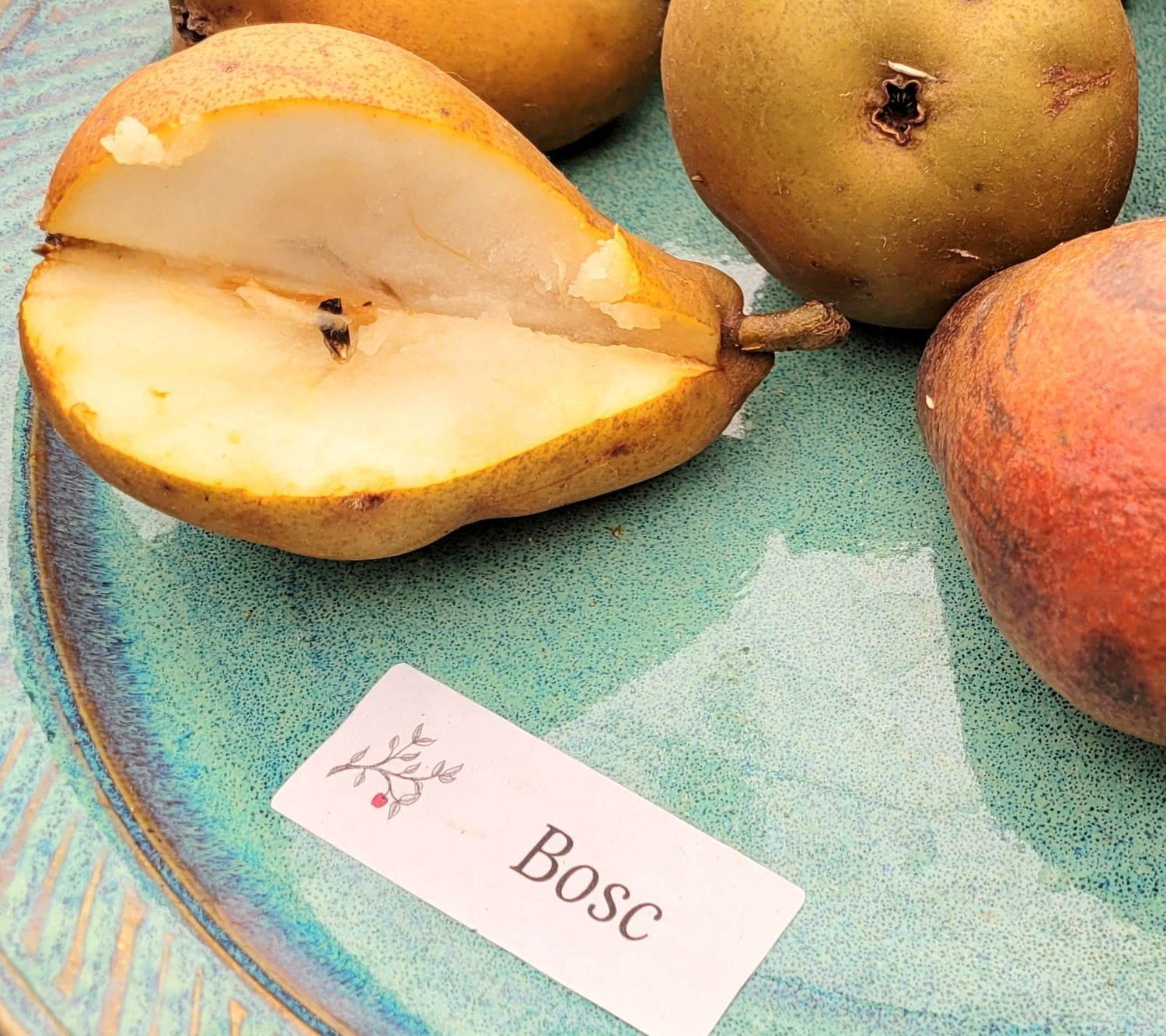
History: Bosc pears have an unclear history, either originating from Belgium or France. Some say that an M. Bosc in Belgium grew it from seed around 1807 while others believe it was found as an old tree in France in the 1830s and named after horticulturalist Louis Bosc. Bosc's alternate names 'Beurre Bosc' refer to its buttery texture and 'Calebasse Bosc' refers to its gourd-like shape. Regardless of its origins, Bosc has remained popular and is grown in numerous countries around the world.
Why We Grow It: Bosc pears are long and slender with golden brown russetted skin. The flesh is of high quality, very sweet, and the pears store much better than most varieties. They can also be used to make a lovely tart, with a sprinkle of thyme for a savory delight!
History: Butirra Precoce Morettini was bred as a cross between Coscia and Bartlett in 1956 by A. Morettini as part of an Italian breeding program. It is mainly grown in Italy, Spain, and Portugal.
Why We Grow It: This is an excellent early ripening pear that is sweet and juicy, with crunchy medium-fine grained flesh which mellows in storage to a delectable buttery texture. It has mild floral notes, with just the right amount of sweetness. The tree produces reliable and heavy crops of yellow fruit with a vibrant red flush that store decently well.
History: Chojuro (translated from Japanese as 'plentiful') was found as a chance seedling in the orchard of Toma Tatsujiro in Japan around 1895. From there it became the most popular pear in Japan until modern varieties began to supplant it in the 1950s. In Kawasaki, the city where Toma's orchard was located, a monument still stands to commemorate his work as a pear breeder. Chojuro is the most popular Asian pear in North America.
Why We Grow It: This popular Japanese heritage variety is hard to turn down. The flattish round fruit has russeted brown skin and can be quite large, and is excellent quality when the fruit is left to ripen into October: the sweet, crisp flesh takes on notes of butterscotch and/or white freezie! We recommend picking it when the colours turns yellow-brown so it will store through winter, otherwise it does not keep if allowed to over-ripen on the tree.
History: Clapp's Favourite Pear originates from Massachusetts where Thaddeus Clapp discovered it as a chance seedling on his property in the 1850s. It was introduced commercially in the 1860s and continues to be grown in the UK and US today.
Why We Grow It: This old variety is hardy and regularly bears excellent medium-large fruit that are yellow with pink blush. They have good flavour but need to be enjoyed rather quickly since the fruit doesn't store long. The fruit needs to be picked about 10 days before completely ripe and allowed to ripen off the tree.
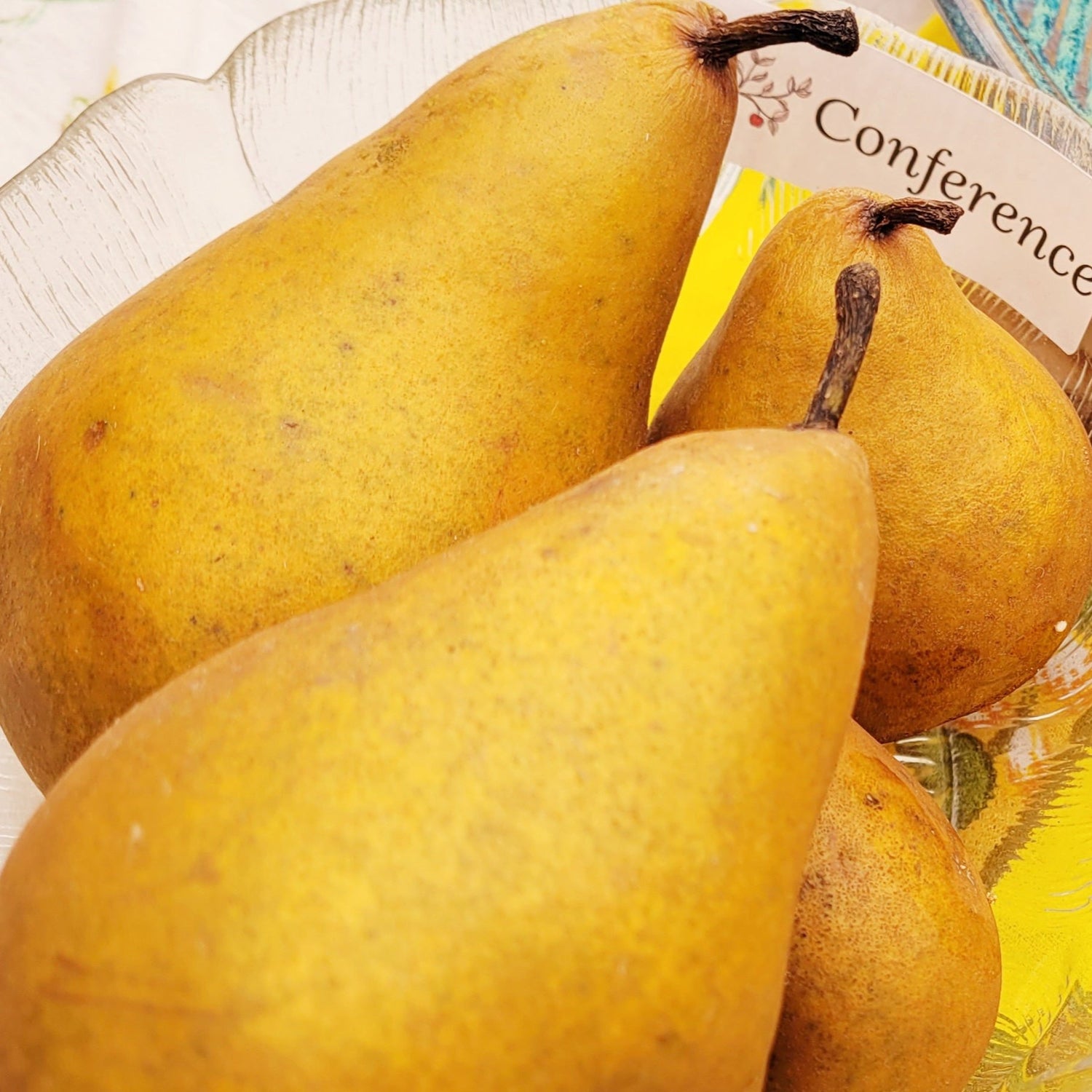
History: Conference pears were found growing in the nursery of Thomas Francis River in the UK in 1884. The following year, he introduced the variety at the National British Pear Conference in London where it won fist place, solidifying its reputation and earning its name. Conference pears continue to be grown in several European countries today where it remains very popular.
Why We Grow It: This old variety has remained popular due to its pleasant and sweet flavour. It can be eaten right off the tree and will keep for a couple months. The fruit itself has an elongated neck, giving it a rather odd appearance.
History: Doyenné du Comice was obtained from a garden in Angers in the 1840s as a sapling. In 1848 it bore its first pears which were quickly noted for their excellent flavour. Throughout the 1850s this variety reached other countries such as the UK and US, and in 1894 it was deemed "the best pear in the world" by the London Horticultural Journal. Whether or not it lives up to that much praise, it is still commonly grown, particularly in France.
Why We Grow It: It is certainly enticing to grow and eat what is considered one of the finest dessert pears. The fruit is medium in size with pale yellow skin and juicy, pale yellow flesh. It needs to ripen off the tree for about one month.
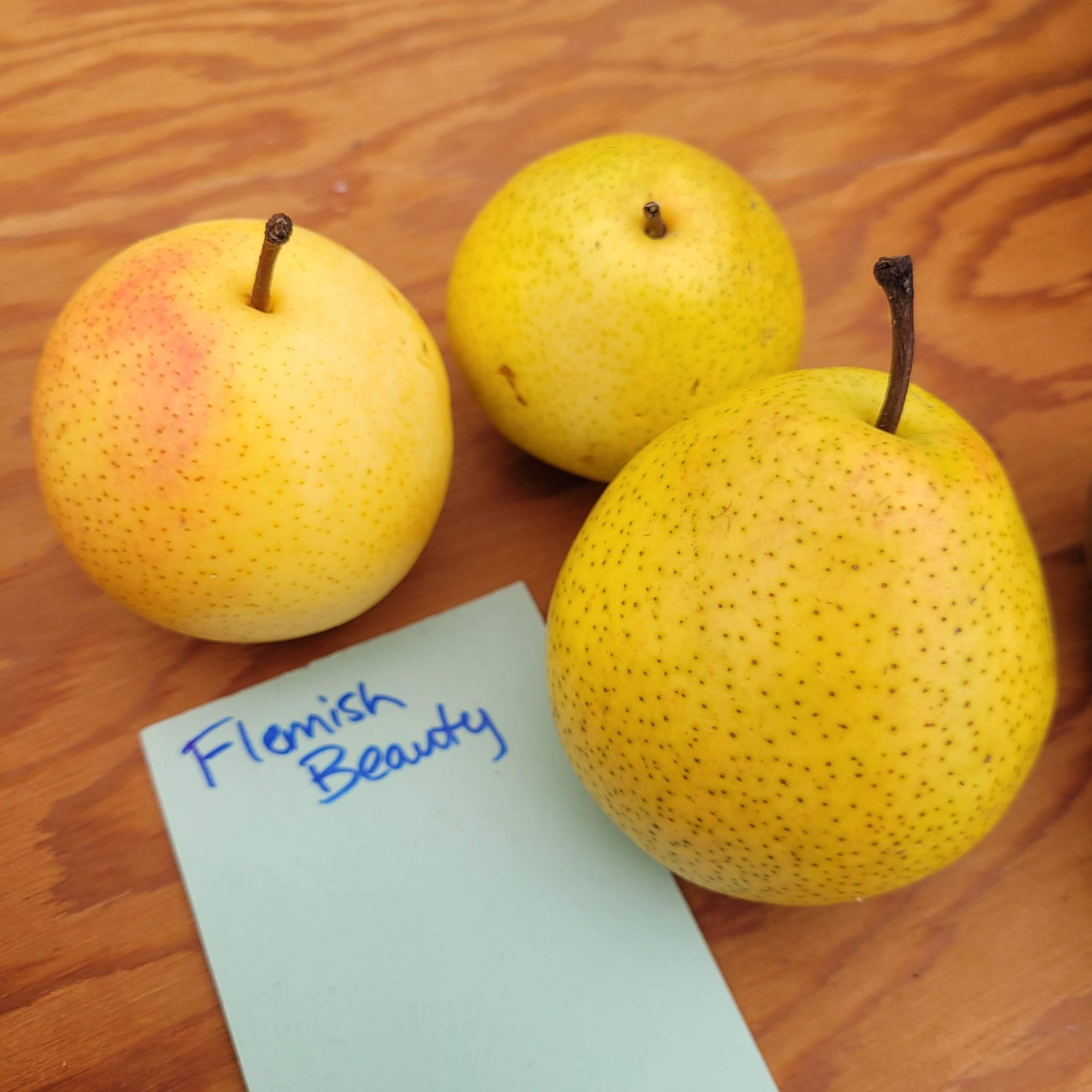
History: Flemish Beauty originated in Belgium in the early 1800s. At one point Flemish Beauty was one of the most common commercial varieties in the US.
Why We Grow It: Flemish Beauty's cold hardiness and good flavour makes this a popular variety. The fruit is large and greenish-yellow without much neck. It is known for being sweet and very juicy, great for fresh eating.
History: Hendre Huffcap was first recorded in England either in 1923 or 1963. The confusion stems from whether it and another variety called Lumberskull, which was recorded first in 1923, are actually the same variety. Hendre Huffcap remains a popular perry pear in England.
Why We Grow It: This popular English perry pear has endured due to the high quality juice it produces which is great on its own and in blends. The tree bears heavily and reliably, although some thinning is recommended since the branches can break under the weight of its own crops.
History: Jules d'Airoles was first discovered by Leon Leclerc in Laval, France, in 1836. It was named after Jules de Liron d'Airoles, a notable French horticulturalist and pomologist. Confusingly, this pear shares its name with a Belgian variety grown about twenty years later by François-Xavier Grégoire-Nélis.
Why We Grow It: This pear develops in storage to a wonderful treat: very sweet and a touch tangy, semi-fine juicy flesh, with pleasant tannic notes depending on the terroir. Smooth, thick green skin with a lovely rose blush where the sun touches the fruit.
History: Packham's Triumph were created by Charles Packham in 1896 in the town of Molong, located in Australia. His goal was to create a late-ripening pear and this popular pear proves he was indeed triumphant. This pear is most commonly grown in the southern hemisphere and the town of Molong is quite proud that such a beloved variety is part of their history.
Why We Grow It: Packham's Triumph is bright-yellow with russet mottling and smooth, white, juicy flesh that has an excellent flavour and smooth texture. The tree produces heavy and reliable crops.
History: Ping Guo Li (translated from Mandarin as 'apple pear') was developed by Jilin Sheng in China and likely named for its round, apple-like shape. While its exact age is unknown, this pear is considered to be an old variety.
Why We Grow It: This Asian pear is nothing but sweet and juicy melting goodness! Its flavour is quite sweet and is comparable to that of a European pear. So far it has performed very well in our test orchard and displays good cold-hardiness.
History: Thorne was discovered in Gloucestershire, England, in 1670. It was originally grown for cooking and fresh eating but is now primarily used to make perry. It is still commonly grown for perry production in England today.
Why We Grow It: This is the most reliable of the English perry pears for Canadian growing. Although this pear can be eaten fresh, it packs an astringent punch and is best made into a good perry instead.
History: Although its exact origins are unclear, it is believed that Barland comes from Bosbury in England. It was already well known by the late 1600s and its perry was believed to have medicinal properties. This perry pear has stood the test of time and is still widely grown in the UK.
Why We Grow It: Barland remains one of the most popular perry varieties. This bittersharp perry pear can be made into a good single-variety perry or added into blends.
History: Blakeney Red (aka Circus pear, Red pear, and Painted Lady) is believed to have originated in the English village of Blakeney, its birthplace and the prominent red blush on the fruit earning it its name. It may have been originally planted sometime in the 1700s but became better known starting around 1830 and was the most widely planted perry pear. It is still popular in the UK today and is gaining attention in North America as well. A yellow dye can also be made from this variety and it was used to dye khakis for British soldiers during WW1.
Why We Grow It: This perry pear produces small to medium yellow fruit with red blush and some russet. For those interested in perry, it's hard to ignore this variety's long history, although its quality can vary based on growing conditions.
History: Gin pears were first recorded in England in 1886. It was said the perry made from this pear had a juniper flavour, hence the name 'Gin.' It it still quite popular in parts of England.
Why We Grow It: The small fruit of this pear are used chiefly for perry, producing a good quality juice of medium tannins and acidity. The harvested fruit can be kept up to a month until pressing.
History: Winnal's Longdon was raised by a Mr. Winnall in the parish of Weston-under-Penyard, a village in England, around 1790. Despite being named after Winnall, Winnal's Longdon is now commonly spelled with only one 'L' after it was recorded incorrectly in the 1920s. This pear is still grown in small quantities in England.
Why We Grow It: This old English variety is a high quality perry pear. It was blended with Hendre Huffcap to form a perry which won the Long Ashton Perry competition many years in a row. The tree is known for its vigorous growth, heavy crops, and high resistance to scab which make it quite suitable for organic production.
Collections
Pyrus pyrifolia
Asian pears are wonderful low maintenance trees! They are regular, prolific producers in our test orchards. Asian pears, sometimes called Apple Pears, are crunchy and sweet, with a mild flavour. While some pears are partially self fertile, we recommend planting at least two different cultivars for reliable pollination; European and Asian pears do cross pollinate.