Products
Sort by:
694 products
694 products
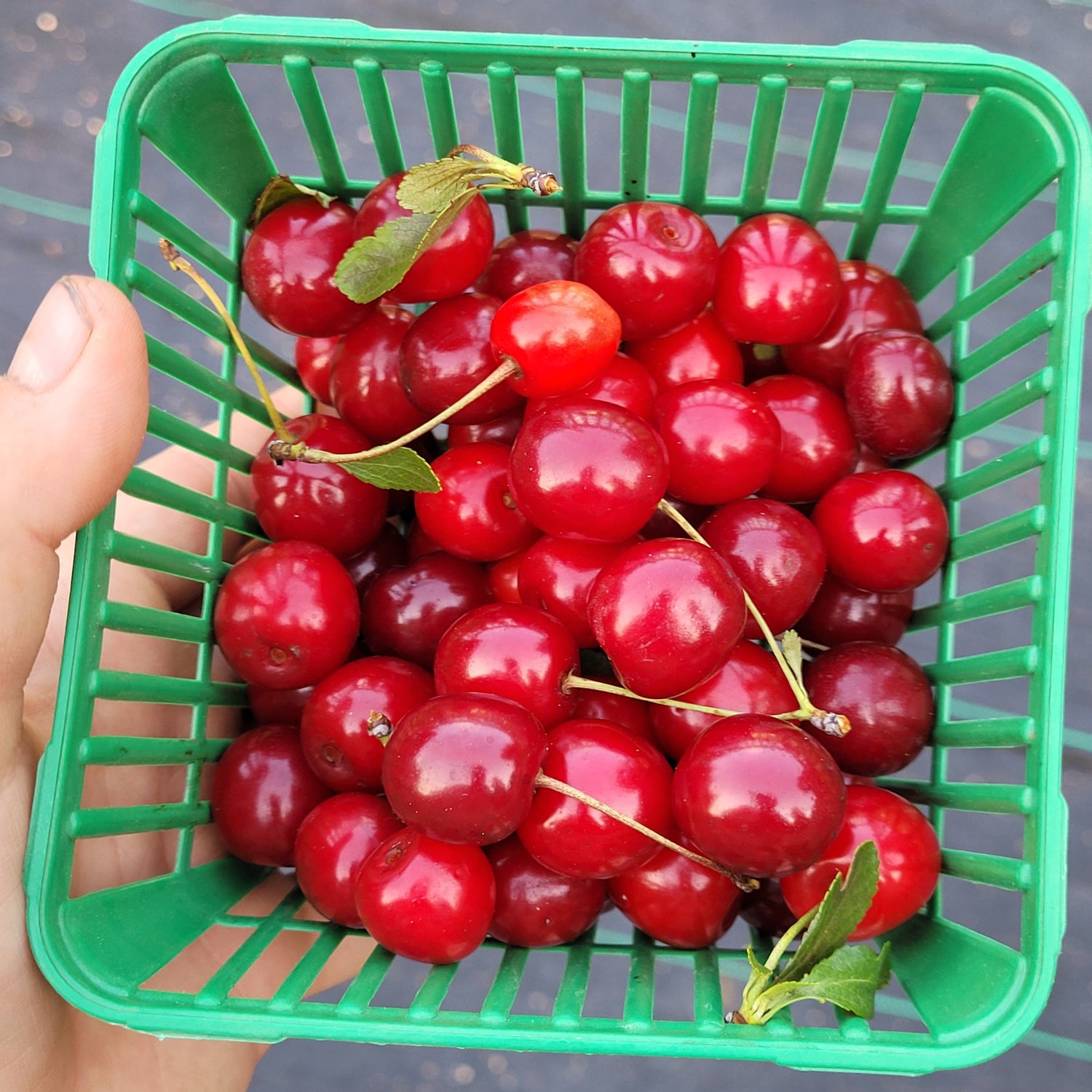
History: Compact Stella was developed at the Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York where dormant Stella scions underwent X-ray irradiation in 1964. This caused a mutation to occur, creating a cherry tree that was smaller in stature when fully grown than regular Stella cherry trees. In 1973 this smaller version of Stella was given the name Compact Stella.
Why We Grow It: Compact Stella sweet cherry trees bear very dark red heart-shaped fruit that is of high quality for fresh eating, and equally well-suited for canning, drying, or freezing. This compact version of the popular Stella sweet cherry is great for anyone with limited space. The typical mature height is 8-10 feet (2.5-3.0m), though they can reach up to 12 feet in optimal growing conditions.
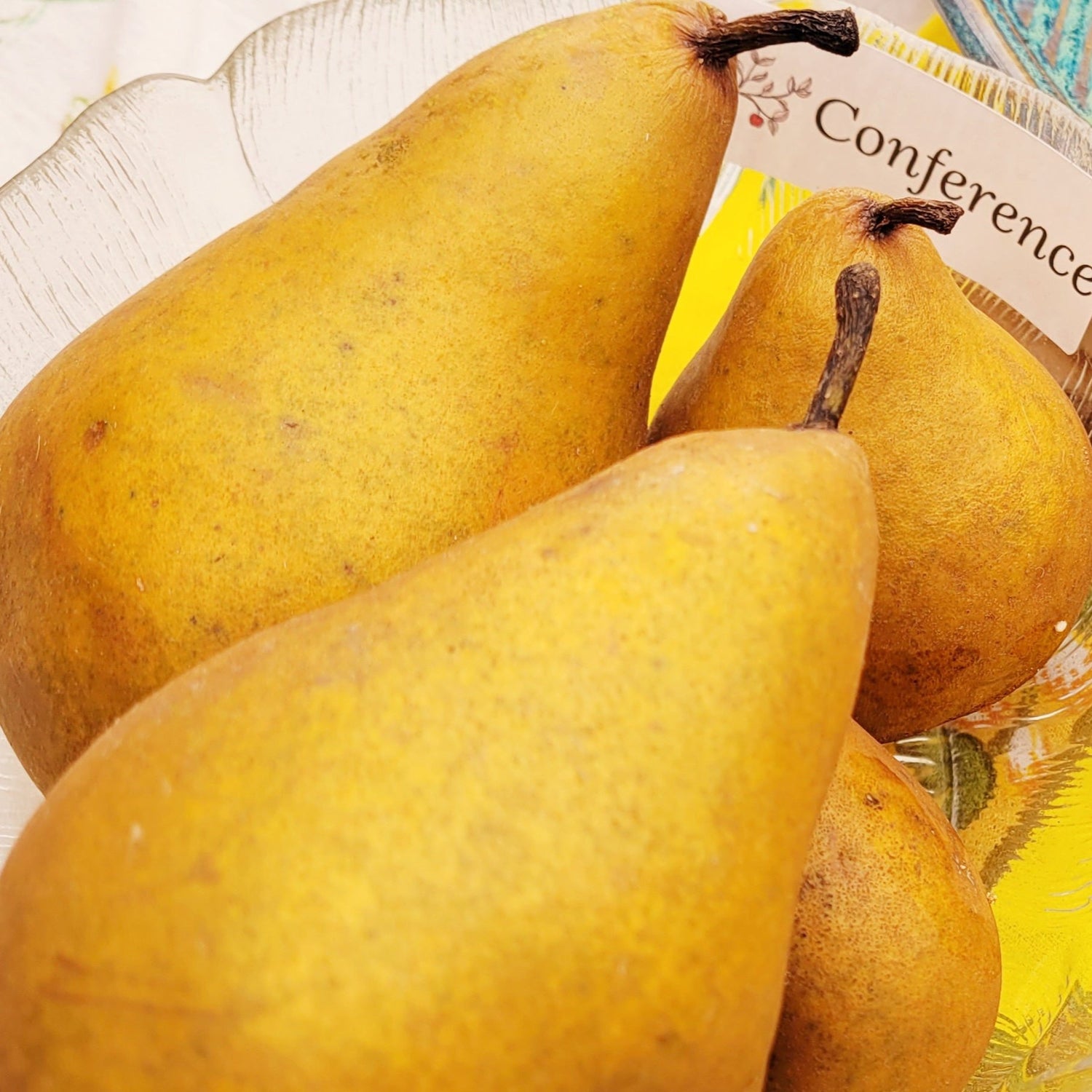
History: Conference pears were found growing in the nursery of Thomas Francis River in the UK in 1884. The following year, he introduced the variety at the National British Pear Conference in London where it won fist place, solidifying its reputation and earning its name. Conference pears continue to be grown in several European countries today where it remains very popular.
Why We Grow It: This old variety has remained popular due to its pleasant and sweet flavour. It can be eaten right off the tree and will keep for a couple months. The fruit itself has an elongated neck, giving it a rather odd appearance.
History: Conference pears were found growing in the nursery of Thomas Francis River in the UK in 1884. The following year, he introduced the variety at the National British Pear Conference in London where it won fist place, solidifying its reputation and earning its name. Conference pears continue to be grown in several European countries today where it remains very popular.
Why We Grow It: This old variety has remained popular due to its pleasant and sweet flavour. It can be eaten right off the tree and will keep for a couple months. The fruit itself has an elongated neck, giving it a rather odd appearance.
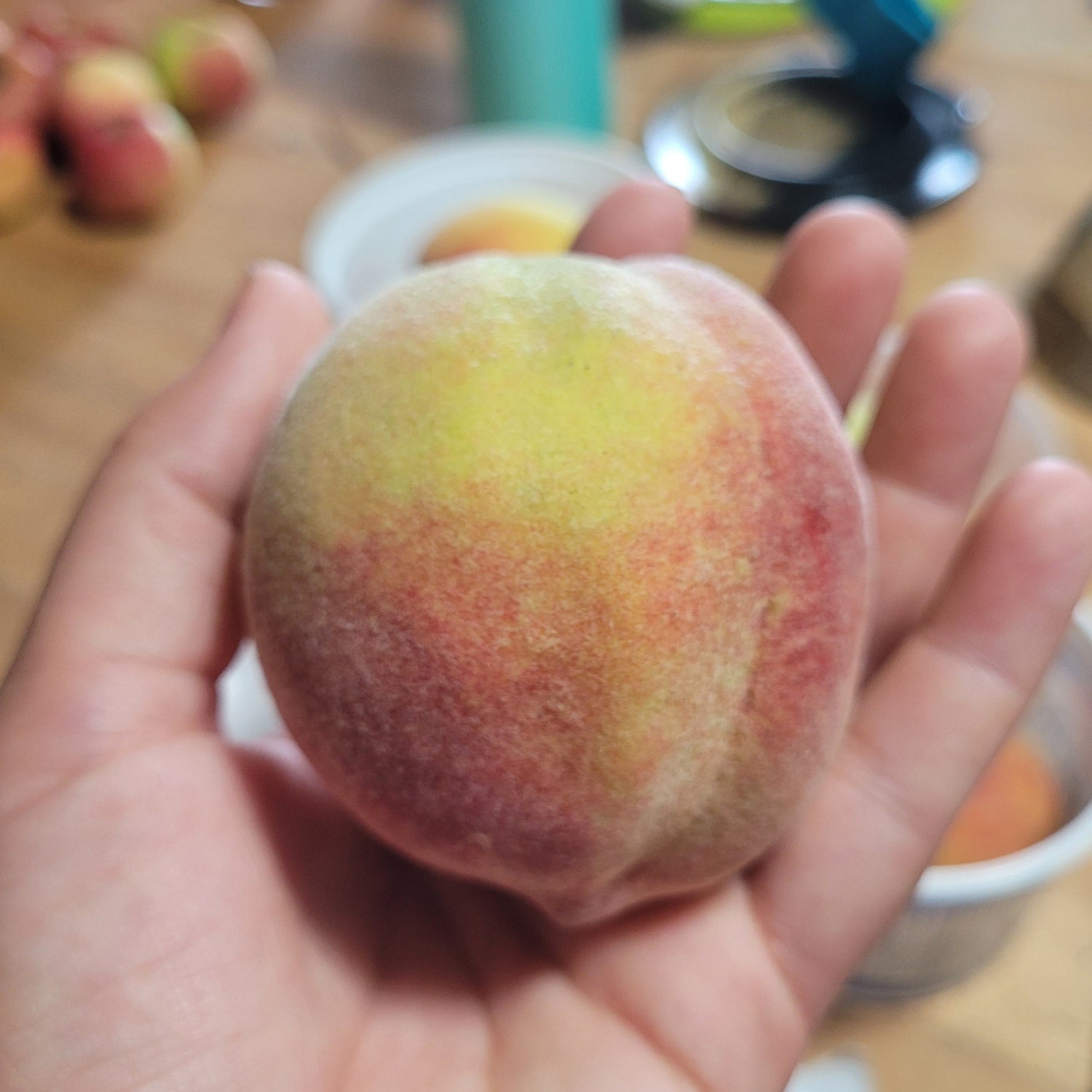
History: Contender was developed at the North Carolina Agricultural Experiment Station and released in 1988. It is one of several peaches developed by the station with the goal of creating late-blooming varieties that are better able to avoid spring frosts
Why We Grow It: Contender is a good-quality cold hardy peach. It produces large, freestone peaches with a sweet flavour that are great for eating fresh off the tree. The fruit is firm and slow to brown, also making it an excellent option for canning and freezing.
Species: Prunus pumila var. besseyi (Western sandcherry) x P. salicina (Japanese Plum)
History: Convoy was released by Boughen Nurseries in Manitoba in 1941. Like other chums, it was bred to produce a fruit with the hardiness of the western sandcherry but the fruit quality of a Japanese plum. Convoy was likely selected for being sweeter than most other chums.
Why We Grow It: Always on the lookout for unique trees, we are happy to offer chums! Convoy is a hardy shrub that produces a clingstone red fruit with yellow flesh. It has a mild sweet flavour that is good for fresh eating but it can also be used for baking, preserving, and canning. The shrub is generally resistant to plum diseases.
History: Cooke's Jumbo originated as a random mutation of an existing quince variety in an orchard in Dinuba, California. It was brought to the attention of the L.E. Cooke Company, for which it was later named, and introduced commercially in 1972.
Why We Grow It: The fruit produced by Cooke’s Jumbo are exceptionally large with greenish-yellow skin and firm white flesh. They are not generally eaten raw, but rather used for baking, jellies, or candied. This is one of the hardiest varieties of quince available.
History: Cooke's Jumbo originated as a random mutation of an existing quince variety in an orchard in Dinuba, California. It was brought to the attention of the L.E. Cooke Company, for which it was later named, and introduced commercially in 1972.
Why We Grow It: The fruit produced by Cooke’s Jumbo are exceptionally large with greenish-yellow skin and firm white flesh. They are not generally eaten raw, but rather used for baking, jellies, or candied. This is one of the hardiest varieties of quince available.
Coppice Agroforestry is a richly illustrated, comprehensive guide to resprout silviculture – managing trees and shrubs by coppicing, pollarding, shredding, and pleaching – for a continuous supply of small diameter polewood for products from firewood to fine furniture. Contextualizing resprout silviculture historically, ecologically, and economically, Coppice Agroforestry is a decade in the making, encyclopedic in scope, and written by the hand of a woodsman. Coppice Agroforestry is a deep dive into this ancient practice, blending it with modern science, systems thinking, and tools to land it firmly in the 21st century.
Species: Prunus persica
History: These seedlings are grown from Coralstar seeds collected from mother trees growing in Ontario. Coralstar was developed through the Fruit Acres Stellar Peach Breeding Program.
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! We expect that seedling peaches will be even hardier trees than their parents! The parent variety, Coralstar, is hardy and great for fresh eating and canning.
Please Note: Since peaches tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
Species: Salix babylonica 'Tortuosa' syn. S. matsudana
History: Corkscrew willows are a variant of the Chinese Willow which are native to parts of northern China. Willow trees have been cultivated for millennia in Asia and this variety was likely selected for its unique twisting branches.
Why We Grow It: Corkscrew willows are an attractive ornamental tree year-round, sporting delicate leaves most of the year and then fully displaying their twisted branches and trunks once they have dropped their leaves. The flowers they produce in the spring are attractive to a variety of pollinators. Just be mindful of where you plant the trees, the vigorous roots can be a problem near buildings and pipes!
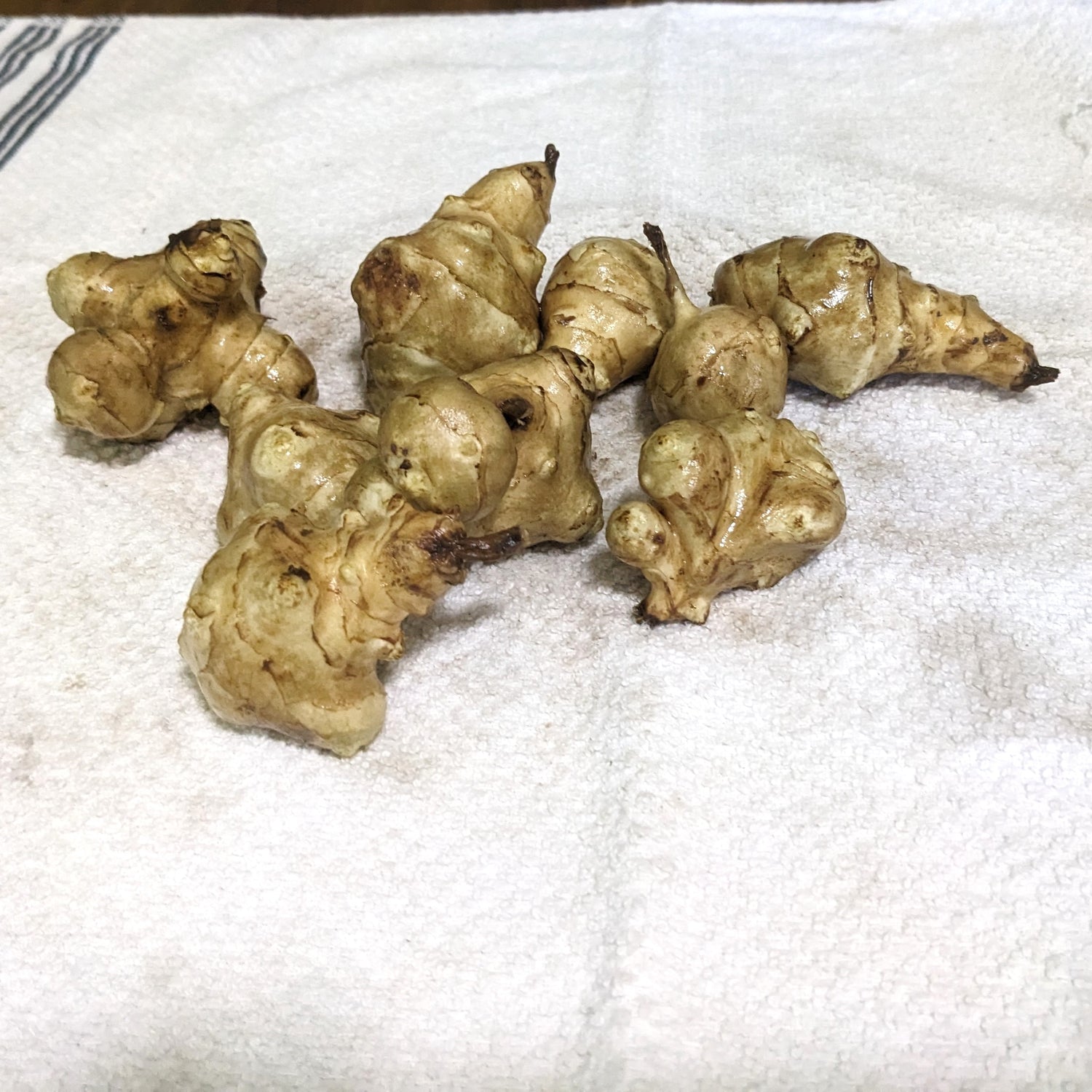
Species: Helianthus tuberosus, Sunchokes are also known as Jerusalem Artichokes or J Chokes
History: Corlis Bolton Haynes discovered a wild sunchoke growing on the farm her parents purchased in 1925 and then spent over sixty years selectively planting the biggest and smoothest tubers in order to improve on the plant. Corlis sadly passed away in 2003 but her family maintains the tradition of only replanting the biggest and best tubers.
Why We Grow It: This variety produces large, white, knobby tubers that like a potato can be prepared and eaten in a variety of ways! This variety is quite productive and the tall plants can be used as a temporary windbreak and/or privacy screen.
Species: Cornus mas
History: Cornelian Cherry (aka Cornel) is a dogwood species native to parts of Europe and Asia. The berries were traditionally used mainly in cooking and to make jams and alcohol and have also been used in traditional Chinese medicine along with the leaves. The wood is quite dense (it sinks in water!) and has been used to make tool handles, machine parts, weapons in Ancient Greece, and the sticks traditionally carried by the mounted herdsman in the Maremma region. In the UK there was some interest in its use as a garden plant starting in the mid 1500s but interest has mainly grown in the last century or so.
Why We Grow It: A novelty among the dogwoods, Cornelian Cherries produce small, red fruits that resemble cherries. The acidic fruit can be eaten fresh when they're quite ripe but are primarily used for cooking and preserves, similar to cranberries. They are also attractive ornamental plants, producing clusters of bright yellow flowers very early in the season.
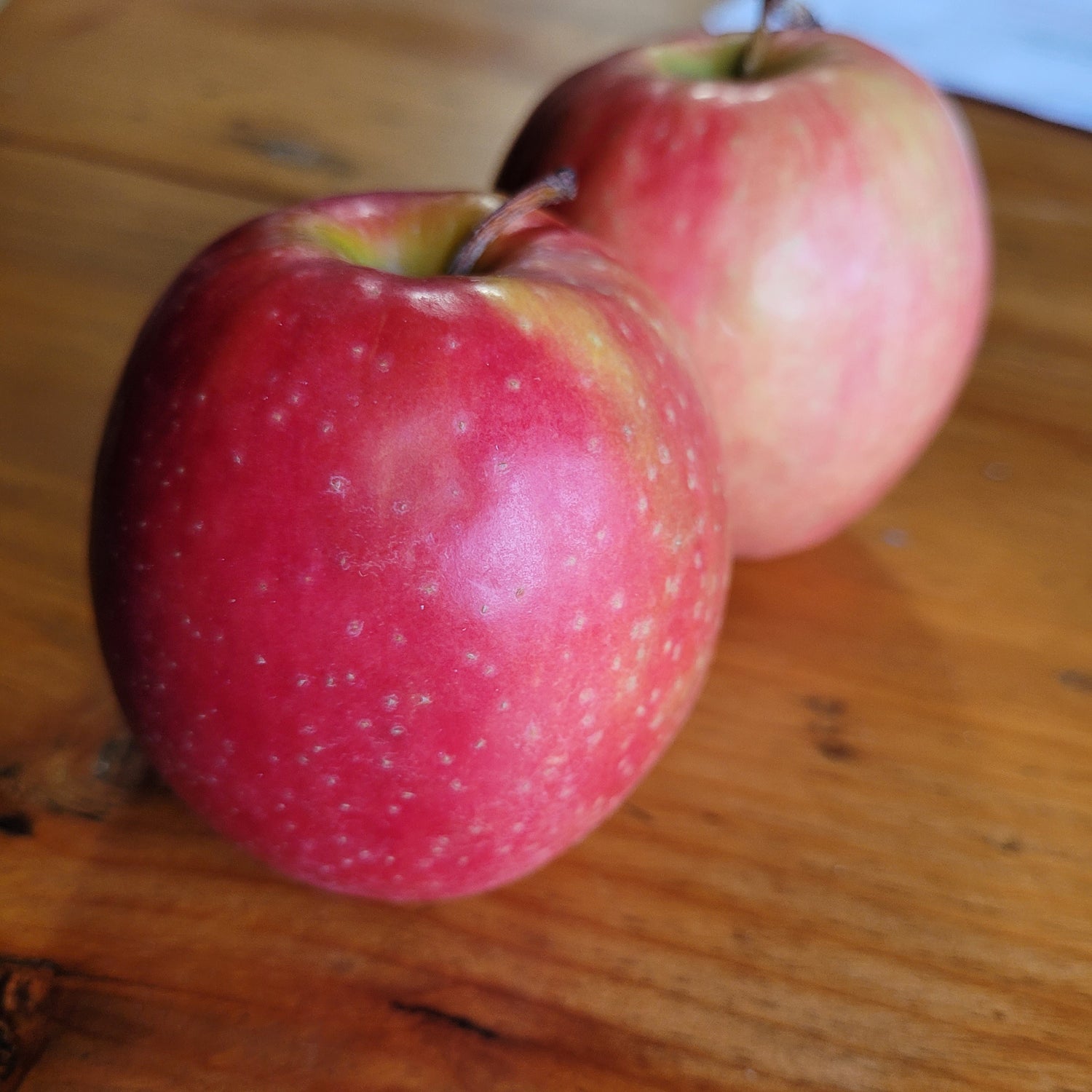
History: Cortland apples were first bred in 1898 by Cornell University in New York and introduced in 1915. Since then, they have become one of the top fifteen apples in the US and Canada, although the majority are still grown relatively close to the university where they originated. Cortland Nova Red is a redder sport of the original Cortland apple, making a more attractive fruit for those who value red apples.
Why We Grow It: Cortland is a sweet apple with crisp, juicy flesh. It is great for applesauce or drying as the flesh is slow to brown. The fruit keeps until Christmas under home storage conditions although the crispness and flavour does fade over time. This variety crops well annually and makes a good pollinator for others. The redder skin on this sport is quite attractive!
History: Cortland apples were first bred in 1898 by Cornell University in New York and introduced in 1915. Since then, they have become one of the top fifteen apples in the US and Canada, although the majority are still grown relatively close to the university where they originated. While there are different versions of Cortland available with features such as redder skin, we are happy to offer the original!
Why We Grow It: Especially with older, popular varieties, we are always happy to offer what is, to the best of our knowledge, the original strain. Cortland is a sweet apple with crisp, juicy flesh. It is great for applesauce or drying as the flesh is slow to brown. The fruit keeps until Christmas under home storage conditions although the crispness and flavour does fade over time. This variety crops well annually and makes a good pollinator for others.
This rustic fall quilt features country farm scenes in the centre of each patchwork block. Each scene has a different picture: an old hand pump, two barn scenes and an old farm wagon. All the elements of the quilt are coordinating, creating an eye-catching piece.
Lovely farmhouse decor for autumn! Use as a quilted table topper or wall quilt.
Size is about 18 inches square (45 cm).
Quilting is done using the freemotion technique (hand guided machine stitching, not computer) ensuring your quilt is one-of-a-kind.
Quilted table runners add an inviting touch to your decor. You can use these quilts in various other ways around your home too! Display on an old trunk or chest, on a dresser, over a chair back, in a basket, under a lamp. You can even hang them! Check out this blog post about how to hang small quilts.
At Momma Bears Quilts, care is taken to ensure you receive an outstanding product, by using quality workmanship and materials. In purchasing a luxury item, I understand you have chosen to outlay your precious dollars for something extra special. Your satisfaction is important to me!
History: Cox's Orange Pippin was first grown in England in 1830 and was named after the retired brewer and horticulturalist who first bred it, Richard Cox. Its excellent flavour has earned it a spot as one of the best fresh eating apples in England where it has remained popular ever since. In fact, it still accounts for over 50% of fresh eating apples grown in the UK today. Despite its reputation, it is seldom grown commercially in North America due to its precocious nature and susceptibility to many common apple diseases.
Why We Grow It: This apple's reputation is hard to ignore with its sweet, subtle, aromatic flavour and attractive orange-red skin. Not only is it good for fresh eating, it is also popular in cider blends.
History: Cox's Orange Pippin was first grown in England in 1830 and was named after the retired brewer and horticulturalist who first bred it, Richard Cox. Its excellent flavour has earned it a spot as one of the best fresh eating apples in England where it has remained popular ever since. In fact, it still accounts for over 50% of fresh eating apples grown in the UK today. Despite its reputation, it is seldom grown commercially in North America due to its precocious nature and susceptibility to many common apple diseases.
Why We Grow It: This apple's reputation is hard to ignore with its sweet, subtle, aromatic flavour and attractive orange-red skin. Not only is it good for fresh eating, it is also popular in cider blends.
History: Crimson Passion dwarf sour cherries are one of several dwarf sour cherries developed and released by the University of Saskatchewan with the goal of creating sour cherries that were cold hardy, shorter in stature, and produced good quality fruit. This initiative began in the 1940s and Crimson Passion was released as part of the Romance series in 2004. It is the sweetest of the Romance series cherries.
Why We Grow It: Crimson Passion produces large sweet fruit, excellent for fresh eating or processing. It contains the same sugar content (20-22 Brix) as sweet cherries, but also contains the tangy flavour of sour cherries, combining the best of both worlds into one cold-hardy shrub. This variety reaches up to 10' at maturity, great for anyone with limited space.
Check our our blog post with some tasty sour cherry recipes!
History: Crimson Rocket originated at the Appalachian Fruit Research Station in West Virginia as part of a breeding program to create columnar peach trees with good fruit quality. It was selected in 1996 for further testing and and patented in 2004.
Why We Grow It: Crimson Rocket is unique for its columnar growth, forming a narrow tree ideal for those with limited planting space! It produces freestone yellow peaches with a red blush with the perfect balance of sweet and tart, making it an excellent variety for fresh eating.
Bare Root Peach Trees:
We are very pleased to be able to offer peach trees to our customers. They are both challenging and rewarding plants to grow. However, due to the unique challenges of growing peach trees, and the increased care required for their success, we regrettably cannot offer our standard 90 day guarantee on peaches. Please inspect your peach trees to your satisfaction when you pick them up at the nursery, or immediately upon arrival if they are shipped. For shipped trees, make your claim within 7 days of receipt of the trees. After 7 days of receipt, you will have been deemed to have accepted the trees in as-is condition.
History: Crimson Rocket originated at the Appalachian Fruit Research Station in West Virginia as part of a breeding program to create columnar peach trees with good fruit quality. It was selected in 1996 for further testing and and patented in 2004.
Why We Grow It: Crimson Rocket is unique for its columnar growth, forming a narrow tree ideal for those with limited planting space! It produces freestone yellow peaches with a red blush with the perfect balance of sweet and tart, making it an excellent variety for fresh eating.
2025/2026 Staff Favourite
Cripps Pink Apples are Jodi's favourite this year! She has this to say about this variety: “I really like Cripps Pink for its crisp/crunchy bite texture along with its sweet-tart flavour. To top it off, they store well so I get to enjoy the crunch of them well into winter.”
All Staff Favourites are 20% off. The Staff Favourite Discount cannot be combined with other quantity discounts.
History: Cripps Pink was developed by John Cripps at the Western Australia Department of Agriculture in 1973 as a cross between Lady Williams (an Australian variety) and Golden Delicious. The successful result was introduced to the market in 1985. In just ten years, Cripps Pink became an extremely popular variety and over a million trees were planted in Australia alone. This variety remains popular in many countries around the world. This apple is also known as Pink Lady which is its brand name when the fruit meets very strict criteria for quality.
Why We Grow It: Cripps Pink has a refreshing honeyed sweet-tart flavour that makes it great for fresh eating, baking, and cider. The lovely fruit, yellow with a pinkish-red blush, is slow to brown and also stores exceptionally well.
History: Cupid is a part of the Romance series of dwarf sour cherry bushes developed and released by the University of Saskatchewan in 2004. Their goal was to create cold-hardy, dwarfing bushes with good quality fruit. Cupid was likely selected for its good flavour and unusually large cherries, the largest in the Romance series.
Why We Grow It: These dark red, cold-hardy cherries have a sweet-tart flavour that can be enjoyed fresh for fans of a more astringent flavour or used for cooking, baking, and preserving. Cupid has the largest cherries of all the dwarf sour cherries in the Romance series and also ripens the latest, helping to extend the season.
History: Dabinetts are an English cider apple named after William Dabinett who happened to find this variety growing in a hedge in the early 1900s. Since then the apple has become quite popular for use in making cider.
Why We Grow It: These smallish apples with speckled red skin produce a high-quality juice which can be used in single-variety ciders or blends. Dabinetts are classified as a bittersweet, are very resistant to scab, and are a reliable cropper.
History: This European plum has contentious origins, making it difficult to determine if it is very old or extremely old. The name 'damson' stems from the Latin 'damascenum' meaning 'plum of Damascus.' As the name implies, some believe this plum may have come from the ancient city of Damascus and was brought to England by the Romans, making this plum thousands of years old. While this theory has been highly contested, there is ample evidence to prove that Damson plums have been grown in England for hundreds of years. It was introduced to the US in 1800 and was a a favourite due to its adaptability to its new home.
Why We Grow It: Damson produces small round clingstone fruit with a deep blue/purple skin and spicy yellow flesh. They are sweet enough to eat but also have some astringency which makes them less palatable than other varieties. However, they are superb for cooking, preserving, and making jam. The tree blooms late which allows it to avoid early frosts and this variety is self-fertile.
History: This European plum has contentious origins, making it difficult to determine if it is very old or extremely old. The name 'damson' stems from the Latin 'damascenum' meaning 'plum of Damascus.' As the name implies, some believe this plum may have come from the ancient city of Damascus and was brought to England by the Romans, making this plum thousands of years old. While this theory has been highly contested, there is ample evidence to prove that Damson plums have been grown in England for hundreds of years. It was introduced to the US in 1800 and was a a favourite due to its adaptability to its new home.
Why We Grow It: Damson produces small round clingstone fruit with a deep blue/purple skin and spicy yellow flesh. They are sweet enough to eat but also have some astringency which makes them less palatable than other varieties. However, they are superb for cooking, preserving, and making jam. The tree blooms late which allows it to avoid early frosts and this variety is self-fertile.
Species: Prunus sp
History: These seedlings are grown from Damson plum seeds collected from our orchard. Damson is a plum that may stem from antiquity!
Why We Grow It: Seedling fruit trees are a great way to add some diversity and mystery to your garden or orchard! The parent variety, Damson, produces small blue fruit that are sweet and a little spiced. They are suitable for fresh eating and great for jams, preserves, etc. For a more detailed description, see the Damson page on our website here.
Please Note: Since plums tend to stay true to type more than apples, these seedlings will likely bear a strong resemblance to their parent variety. However, any specific information listed on this page should be taken with a grain of salt as there may be some variation from the parent tree.
History: Debbie's Gold was introduced by Aubins Nursery in Manitoba in 1980.
Why We Grow It: Debbie's Gold is a relatively new but promising apricot variety for us. It is very cold hardy and late blooming, which improves the chance of a crop in our climate. It produces small fruit with a rich apricot flavour with spicy notes.
History: Debbie's Gold was introduced by Aubins Nursery in Manitoba in 1980.
Why We Grow It: Debbie's Gold is a relatively new but promising apricot variety for us. It is very cold hardy and late blooming, which improves the chance of a crop in our climate. It produces small fruit with a rich apricot flavour with spicy notes.
History: Delbarestivale was developed by Delbard, a nursery in France, in the 1950s. Likely named as a portmanteau of 'Delbard' and 'estivale' (translated from French as 'summer') due to its early ripening time, this variety goes by many other names including Delcorf, Monidel, Dalili, and Ambassy. It was bred in an attempt to create an improved version of Golden Delicious. Although not quite as popular as Golden Delicious, it is still grown commercially in parts of France and England and the Royal Horticultural Society awarded it the Award of Garden Merit in 1998.
Why We Grow It: This French apple is very sweet but balanced nicely with a sharp flavour. The flesh is aromatic and crisp and the skin is a lovely, stripey bi-colour with reddish streaks overlaying green. The apples store quite well for an early-ripening variety, although they do tend to bruise easily.
Why We Grow It: Discovery is a slightly sweet apple with noticeable acidity, and under optimal conditions it can have a strawberry flavour. Like many early apples, it is great for sauce. The fruit is on the smaller side and has a flatter shape with greenish-yellow skin overlaid with a bright red blush. The red can sometimes stain the cream-coloured flesh inside, providing some visual appeal. The tree boasts some resistance to scab and although it can take a while to start bearing fruit, once it does it bears quite reliably.